'People will forgive you for being wrong, but they will never forgive you for being right - especially if events prove you right while proving them wrong.' Thomas Sowell
Search This Blog
Friday, 29 August 2025
Saturday, 22 June 2024
'Who says a dog cannot receive better treatment than a servant?': Hinduja family members sentenced to jail for exploiting domestic staff
Sam Jones in The FT
Four members of the multi-billionaire Hinduja clan, the UK’s wealthiest family, have been convicted of exploiting their domestic staff and sentenced to lengthy jail terms by a court in Geneva.
In a ruling on Friday, a panel of three judges found Prakash Hinduja, his wife Kamal, as well as their son Ajay and his wife, Namrata, guilty of serious employment offences related to Indian staff.
“They spent more on [their] dog than one of their servants,” Genevan public prosecutor Yves Bertossa told the court this week in a case that shed a harsh light on the punishing conditions to which one of the world’s wealthiest families subjected their workers.
The court cleared the four Hindujas of the more serious charge of human trafficking that had been brought by the authorities.
The domestic staff at the centre of the case, who were mostly illiterate, had been flown in directly from India to work at the family’s palatial home in Switzerland.
In a damning verdict, presiding judge Sabina Mascotto said the Hindujas had no excuses for their behaviour.
“[The workers] were exploited given their situation in India was so precarious and they were exploited as they didn’t know the language, had their passports confiscated and were only ever paid every 3-6 months,” said Mascotto.
“The four Hindujas knew the vulnerabilities of the staff and knew what the rules were in Switzerland, as they all were Swiss citizens and Ajay was educated in Switzerland,” she added.
The court nevertheless ruled that the employees had known the terms they were signing up for when they entered the family’s service in India and therefore could not have been said to be trafficked.
Reflecting the seriousness of the offences the four were convicted of, Prakash and Kamal were sentenced to four-and-a-half years in prison. Ajay and Namrata received a four-year sentence.
An appeal process could take years in Switzerland’s often slow-moving justice system, under which a judgment is not considered final until all avenues of appeal have been exhausted. The four Hinduja family members were not present at the court for the verdict.
Romain Jordan, a lawyer for the family, said his clients were “appalled and disappointed” by the court’s decision.
“Importantly, the family has been acquitted of human trafficking charges,” he said.
An appeal has already been filed. “Under Swiss law, the presumption of innocence is paramount until an adverse final judgment by the highest adjudicating authority is enforced,” Jordan emphasised.
Prakash is the second of three brothers behind the Hinduja Group, a sprawling multinational conglomerate with interests in everything from cars and petrochemicals to banking and armaments.
His older brothers Gopichand and Srichand settled in London in the 1980s and made it the centre of the group’s affairs. Gopichand, worth an estimated £35bn, is the UK’s richest man. Srichand died last May.
Prakash settled in Switzerland, from where he runs the family business. He was made a Swiss citizen in 2000. His younger brother, Ashok, runs the Hinduja Group’s Indian interests.
In a week of explosive revelations, Geneva’s public prosecutor accused Prakash, Kamal, Ajay and Namrata of treating their employees as indentured servants.
They were accused of keeping the staff trapped at a villa in the ultra-exclusive Geneva lakeside suburb of Cologny, where they slept in substandard conditions in basement rooms.
The workers were paid less than one-tenth of the salary they were entitled to under Swiss law, according to the prosecutor Bertossa.
One servant was paid just 7 Swiss francs a day, and worked as many as 18 hours, 7 days a week, Bertossa alleged. The family dog had more than three times as much spent on it, according to documents seized by police and presented to the court.
As well as attending to the family at Cologny, the retinue of staff travelled with the Hindujas to their ski chalet in the Swiss alps and villa on the Cote d’Azur, but otherwise had almost no personal freedom, Bertossa said.
Their passports were taken from them. They were paid in rupees into Indian bank accounts, which they did not have access to while in Switzerland, he said.
Giving testimony, members of the family denied the allegations against them, and said their staff had been like “members of the family.”
Ajay’s lawyer, Yael Hayat, told the court that the prosecutor’s claims about employees were exaggerated. “When they sit down to watch a movie with the kids, can that be considered work?” she asked the court to consider.
A civil case brought against the family on behalf of their staff was settled for an undisclosed sum last week.
Sunday, 17 September 2023
It’s a tragedy of modern plutocratic Britain: if you want to rise, follow the Piers Morgan playbook
It was one of the abiding mysteries of public life. How did Piers Morgan rise so far? I see him as a buffoon, a bully, a windbag. Yet, despite scandals that would have killed most people’s careers, he rose like a methane bubble in a slurry lagoon, occupying some of the most prestigious and lucrative positions in the media. This week, reflecting on the life and abuses of the plutocrat Mohamed Al Fayed, Private Eye magazine produced an explanation. It came from Morgan himself, writing about Fayed in 1999. “I’ve always made it a strict rule in life to ingratiate myself with three categories of people: newspaper owners, potential newspaper owners and billionaires. And since Mohamed Al Fayed is a billionaire and would love to own a newspaper, sucking up to him seems an extremely sensible move.”
The strategy is not unusual. But voicing it is. Morgan expressed the unspoken rule of public life out loud. If you want to get ahead, grovel to billionaires, especially those who own the media. The obvious coda to the rule is: “because they are the people with real power”.
Plenty of rules are broken without consequence. You can appear on the BBC while hiding your financial interests, breaking its editorial guidelines, as long as you are channelling the demands of the very rich. You can breach parliamentary rules without punishment – by lying, or by failing to update your register of interests, or by taking a second job without clearance when your ministerial career ends – as long as you remain a loyal servant of big money. But Morgan’s Rule is the one that must not be broken. If you are a political party and you want a sniff at power, if you are a commentator who wants to appear on the BBC, you must observe it. Otherwise you will be vilified or excluded.

Morgan and journalists like him are members of the concierge class, which provides a wide range of services to economic power. Some of them, such as editors of the billionaire media and the junktanks of Tufton Street, specialise in translating the outrageous demands of oligarchs and corporations into what looks like political common sense, or in attacking plutocrats’ critics or transferring blame for their impacts on to immigrants, the Labour party and other customary scapegoats.
Some of them, such as lobbyists, specialise in reputation-laundering: brokering deals between grim plutocrats and cultural institutions – universities, museums, opera houses, charities – which, in return for lavish donations, will name faculties, professorships, galleries, funds and prizes after their sponsors, transforming violent kleptocrats into pillars of society.
Others, including lawyers, accountants, bankers and wealth managers, specialise in hiding and washing their money, buying them special visas, or suing and hounding their critics. This is why organised crime loves London. It takes advantage of both England’s ultra-permissive financial laws and its ultra-repressive libel laws.
The government is always ready to help. In 2021, while Rishi Sunak was chancellor of the exchequer, lawyers acting for Yevgeny Prigozhin, the late brutal chief of Russia’s Wagner mercenary group, applied to the Treasury for permission to override the sanctions against him, so that he could sue the investigative journalist Eliot Higgins. Sunak’s Treasury granted the special licences they requested and even approved sanctions-busting flights to St Petersburg so they could plan their legal attack.
In this way a few dozen people, assisted by thousands of concierges, can dominate our lives. The system we call democracy is a mere patina, sticky and dimpled, on the surface of oligarchic power.
There are many ways in which economic power translates into political power, and none of them are good for us. The most obvious is campaign finance: the sponsorship not only of political parties but of entire systems of political thought and action. These transactions muscle the interests of society out of politicians’ minds. Some of them are enormous. Last year, the US website the Lever exposed a $1.3bn (£1bn) transfer of money from a little-known billionaire, Barre Seid, to a new political advocacy group run by an ultraconservative. How can mere citizens compete?

Financial power also ensures that the rules supposed to stop economic crime and the laundering of its proceeds contain loopholes wide enough for a superyacht to sail through. For the past few months, members of the House of Lords have been battling to remove the obvious get-out clauses from the economic crime bill passing through parliament. The government has thwarted it at every turn. In the debate on Monday, the Conservative peer Lord Agnew – the very opposite of a radical firebrand – complained that “the government continue to say one thing and then do something different”. Sunak’s administration, run by an oligarch for oligarchs, produces heart-thumping assurances that it will close the loopholes, then subtly tweaks the legislation to keep them open.
Money’s might ensures that its environmental impacts are unrestrained. Recently, I was told about a multimillionaire who had intended to fly in his private jet to a luxury resort, only to change his mind at the last minute and decide to go to a different place, with a shorter landing strip. The plane was too heavy to land there, so it sat on the tarmac and burnt off $15,000 of fuel before setting out. Sunak treats the UK as a flyover state, travelling by helicopter and private jet to places he could easily reach by train. Kylie Jenner and Floyd Mayweather zip about on private flights of less than 20 minutes. Each of them negates the efforts of thousands of ordinary mortals to live within the limits of a habitable planet.
But these specific impacts fail to capture the aggregate effect: the remarkable way in which society comes to reflect the demands of the ultra-rich. Almost everyone in public life accepts the same set of preposterous beliefs. That economic growth can continue indefinitely on a finite planet; that the unhindered acquisition of enormous fortunes by a few is acceptable, even commendable; that they should be allowed to own as much natural wealth as their money permits; that there’s nothing objectionable about a few offshore billionaires owning the media and setting the political agenda; that anyone who disputes such notions has no place in civil society. We are free to speak, up to but not beyond this point: the point on which everything hangs.
Morgan’s maxim is not just the unspoken rule. It is also the unspeakable truth. Everyone knows it, hardly any will mention it. It underpins our august institutions, our legal codes, our manners and mores. It is the great silence we need to break.
Saturday, 5 November 2022
Monday, 6 June 2022
Thursday, 3 March 2022
Thursday, 5 August 2021
Sunday, 26 April 2020
'Heads we win, tails you lose': how America's rich have turned pandemic into profit
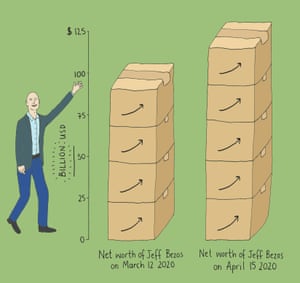
Never let a good crisis go to waste: as the coronavirus pandemic sweeps the world, America’s 1% have taken profitable advantage of the old saying.
Some of the richest people in the US have been at the front of the queue as the government has handed out trillions of dollars to prop up an economy it shuttered amid the coronavirus pandemic. At the same time, the billionaire class has added $308bn to its wealth in four weeks - even as a record 26 million people lost their jobs.
According to a new report from the Institute for Policy Studies, a progressive thinktank, between 18 March and 22 April the wealth of America’s plutocrats grew 10.5%. After the last recession, it took over two years for total billionaire wealth to get back to the levels they enjoyed in 2007.
Eight of those billionaires have seen their net worth surge by over $1bn each, including the Amazon boss, Jeff Bezos, and his ex-wife MacKenzie Bezos; Eric Yuan, founder of Zoom; the former Microsoft chief Steve Ballmer; and Elon Musk, the Tesla and SpaceX technocrat.
The billionaire bonanza comes as a flotilla of big businesses, millionaires and billionaires sail through loopholes in a $349bn bailout meant to save hard-hit small businesses. About 150 public companies managed to bag more than $600m in forgivable loans before the funds ran out. Among them was Shake Shack, a company with 6,000 employees valued at $2bn. It has since given the cash back but others have not.
Fisher Island, a members-only location off the coast of Miami where the average income of residents is $2.2m and the beaches are made from imported Bahamian sand, has received $2m in aid.
Its residents seemed to be doing fine even before the bailout. This month, the island purchased thousands of rapid Covid-19 blood test kits for all residents and workers. The rest of Florida is struggling. About 1% of Florida’s population has been tested for the coronavirus, behind the national figure of 4%. The state is also in the midst of an unemployment claims crisis, with its underfunded benefits system unable to cope with the volume of people filing.
The banks that were the largest recipients of bailout cash in the last recession have also done well, raking in $10bn in fees from the government loans, according to an analysis by National Public Radio.
“Heads we win, tails you lose,” said Chuck Collins, director of the program on inequality and the common good at the Institute for Policy Studies and co-author of the new report.
Collins said the pandemic had further exposed fault lines in the US body politic that have been widening the gap between the really rich and the rest over decades.
“The rules of the economy have been tipped in favor of asset owners against everyone else,” said Collins.
By 2016 – seven years after the end of the last recession – the bottom 90% of households in the US had still not recovered from the last downturn while the top 10% had more wealth than they had in 2007.
Throughout the recovery, stock market gains disproportionately favored the wealthy. The top 1% of households own nearly 38% of all stock, according to research by the New York University economist Edward Wolff. Even before the coronavirus hit, homeownership in the US – a traditional source of wealth growth – was well below its 2004 peak.
Nor did Americans earn more. Wage growth remained sluggish during the decade-long record-breaking growth in the jobs market that came after the last recession.
For black and Latin Americans, the situation is worse. The black-white wage gaps are larger today than they were in 1979.
Meanwhile, billionaires have been unable to put a well-heeled foot wrong. Billionaire wealth soared 1,130% in 2020 dollars between 1990 and 2020, according to the Institute for Policy Studies. That increase is more than 200 times greater than the 5.37% growth of median wealth in the US over this same period. And the tax obligations of America’s billionaires, measured as a percentage of their wealth, decreased 79% between 1980 and 2018.
So when the pandemic struck, those at the apex of the wealth pyramid were better positioned than ever to take advantage of the chaos. The rest, not so much.
Collins has been studying income inequality for 25 years and has seen the really rich win victory after victory. But even he was surprised by how quickly America’s billionaires have turned pandemic into profit. “I still get shocked,” he said.
Wednesday, 3 July 2019
After urging land reform I now know the brute power of our billionaire press
All billionaires want the same thing – a world that works for them. For many, this means a world in which they are scarcely taxed and scarcely regulated; where labour is cheap and the planet can be used as a dustbin; where they can flit between tax havens and secrecy regimes, using the Earth’s surface as a speculative gaming board, extracting profits and dumping costs. The world that works for them works against us.
So how, in nominal democracies, do they get what they want? They fund political parties and lobby groups, set up fake grassroots (Astroturf) campaigns and finance social media ads. But above all, they buy newspapers and television stations. The widespread hope and expectation a few years ago was that, in the internet age, news controlled by billionaires would be replaced by news controlled by the people: social media would break their grip. But social media is instead dominated by stories the billionaire press generates. As their crucial role in promoting Nigel Farage, Brexit and Boris Johnson suggests, the newspapers are as powerful as ever.
They use this power not only to promote the billionaires’ favoured people and ideas, but also to shut down change before it happens. They deploy their attack dogs to take down anyone who challenges the programme. It is one thing to know this. It is another to experience it. A month ago I and six others published a report commissioned by the Labour party called Land for the Many. It proposed a set of policies that would be of immense benefit to the great majority of Britain’s people: ensuring that everyone has a good, affordable home; improving public amenities; shifting tax from ordinary people towards the immensely rich; protecting the living world; and enhancing public control over the decisions that affect our lives. We showed how the billionaires and other oligarchs could be put back in their boxes.
The result has been four extraordinary weeks of attacks in the Mail, Express, Sun, Times and Telegraph. Our contention that oligarchic power is rooted in the ownership and control of land has been amply vindicated by the response of oligarchic power.
Some of these reports peddle flat-out falsehoods. A week ago the Mail on Sunday claimed that our report recommends a capital gains tax on people’s main homes. This “spiteful raid that will horrify millions” ensures “we will soon be joining the likes of China, Cuba, Laos and Vietnam in becoming one of the world’s few Marxist-Leninist states”. This claim was picked up, and often embellished, by all the other rightwing papers. The policy proved, the Telegraph said, that “keeping a hard-left Labour party out of office is not an academic ideological ambition but a deadly serious matter for millions of voters”. Boris Johnson, Philip Hammond and several other senior Tories weighed in, attacking our “mad” proposal.
But we made no such recommendation. We considered the idea, listed its possible advantages and drawbacks, then specifically rejected it. As they say in these papers, you couldn’t make it up. But they have.
There were dozens of other falsehoods: apparently we have proposed a “garden tax”; we intend to add “an extra £374 a year on top of what the typical household pays in council tax” (no such figure is mentioned in our report); and inspectors will be sent to people’s homes to investigate their bedrooms.
Dozens of reports claim that our proposals are “plans” hatched by Jeremy Corbyn: “Jeremy Corbyn’s garden tax bombshell”; “Jeremy Corbyn is planning a huge tax raid”; “Corbyn’s war on homeowners”. Though Corbyn is aware of our report, he has played no role in it. What it contains are not his plans but our independent policy suggestions, none of which has yet been adopted by Labour. The press response gives me an inkling of what it must be like to walk in his shoes, as I see my name (and his) attached to lurid schemes I’ve never heard of, and associated with Robert Mugabe, Nicolás Maduro and the Soviet Union. Not one of the many journalists who wrote these articles has contacted any of the authors of the report. Yet they harvested lengthy quotes denouncing us from senior Conservatives.
The common factor in all these articles is their conflation of the interests of the ultra-rich with the interests of the middle classes. While our proposals take aim at the oligarchs, and would improve the prospects of the great majority, they are presented as an attack on ordinary people. Progressive taxation, the protection of public space and good homes for all should strike terror into your heart.
We’ve lodged a complaint to the press regulator, Ipso, about one of the worst examples, and we might make others. But to pursue them all would be a full-time job (we wrote the report unpaid, in our own time). The simple truth is that we are being outgunned by the brute power of billionaires. And the same can be said for democracy.
It is easy to see why political parties have become so cautious and why, as a result, the UK is stuck with outmoded institutions and policies, and succumbs to ever more extreme and regressive forms of taxation and control. Labour has so far held its nerve – and this makes its current leadership remarkable. It has not allowed itself to be bullied by the billionaire press.
The old threat has not abated – it has intensified. If a newspaper is owned by a billionaire, be suspicious of every word you read in it. Check its sources, question its claims. And withhold your support from any party that allows itself to be bullied or – worse – guided by their agenda. Stand in solidarity with those who resist it.
Thursday, 18 April 2019
The billionaires’ donations will turn Notre Dame into a monument to hypocrisy

In 2017, a welter of stories appeared in the international press pointing out the brokenness of Paris’s Notre Dame. Cathedral officials showed journalists how patches of limestone would crumble at a finger’s touch. Gargoyles that had lost their heads were patched up with plastic pipes, while fallen balustrades were replaced with wooden planks. All this decay was caused by pollution, acid rain and eight centuries of use – but also official neglect was to blame. Keepers of the building had begged for more money, but neither the belt-tightening French government nor the wealthy grumbling about higher taxes gave enough.
Then came Holy Week 2019 and the inferno by the Seine and all of a sudden, nobody can give too much. After years of preaching the shrinking of the public sector, the French president, Emmanuel Macron, now wants to mobilise the full resources of the state to get the roofless cathedral rebuilt within just five years. And money from France’s billionaire class keeps raining down. In three days, the cathedral has been pledged €100m (£86m) from Francois-Henri Pinault, the ultimate owner of Gucci and Yves Saint Laurent; €200m (£172m) from the Arnault family of Louis Vuitton fame; another €200m from L’Oreal owners the Bettencourt Meyers family, and €100 from French oil giant Total.
From these two episodes just two years apart, we can draw two conclusions. The first is that what is happening this week is a remarkable display of public-sector coordination and private generosity, in the service of a great thing: the restoration of one of the world’s treasures. And the second is that the rebuilt cathedral will be a monument to the gigantic hypocrisy of austerity politics.

Francois-Henri Pinault, pictured with his wife, Salma Hayek, has pledged €100m to Notre Dame. Photograph: Nina Prommer/EPA
A heritage site that roused barely a shrug two years ago means the world this week. A billionaire class that shrieked at the wealth taxes of the former president François Hollande is happy to stump up whatever it takes now. A politician, Emmanuel Macron, who has repeatedly told the poor they must live on less and the workers that they must give more to bosses, now plays at being a national leader – like Charles de Gaulle with more hair wax. And a capital city that over the past few months has been under siege from the working poor of the gilets jaunes is reminded once again of the enormous wealth held by a very few of its citizens. Everything that was impossible as late as 2017 is now deemed essential in 2019.
Of course, we would prefer private millions to be pulled out from under goose-feather pillows and spent on public works. But we should also be asking why it takes an almighty conflagration to force this to happen; and why those generous donors are so averse to giving their money to democratically chosen priorities, which is what taxes represent. If the ultra-rich can chuck in so many millions of euros for a building, then what stops them ending hunger and poverty?
Few want to ask that question, nor the obvious follow-up about how much the mullti-billion-owning Catholic church will stump up. The press prefer instead to boggle at the nine-figure sums that have been magicked up, while Macron and others congratulate the donors without asking where that money came from. Some go further still. The editor of Moneyweek went so far as to remark on social media: “Billionaires can sometimes come in really handy.” Well, yes. And democracy can be such a downer and greater equality a massive drag.
But for those who care to look, there is plenty here that is ugly. No sooner had Pinault pledged his €100 million, then his consigliere, Jean-Jacques Aillagon, sprang forth to suggest that all such donations should receive a 90% tax deduction. In other words, the French public should pay for most of its beloved billionaires’ generosity. The suggestion was swiftly withdrawn, but its proposer is no naïf. A former culture minister, Aillagon knows that charitable giving in France attracts a 60% tax rebate: so for every €100m some industrialist papa gâteau wants to chip in, the public will pay €60m. At least Reuters reports that the Pinault family is sitting out this particular round and not claiming tax relief.
Then there’s the source of that €200m pledge from France’s richest man, Bernaud Arnault, who just a few years ago was reported to be applying for Belgian nationality. This was not to enjoy any tax advantages, said his spokesman, but purely to better order his affairs. Nothing to do with the fact that inheritance tax in Belgium is only 3%, while France charges 11%, non monsieur.

Such ghastliness is not France’s alone. It is international and it is orthodoxy. Just look at Thursday’s Guardian lead story on how 1% of people in England own 50% of its land. Or remind yourself of the Oxfam finding that last year, the world’s 2,200 billionaires got 12% wealthier, while the bottom 3.5 billion people grew 11% poorer. Those at the top extract their wealth from those below – and then are applauded when they chuck us their spare change. From here it is just a short selfie-stick shuffle to a rebuilt Notre Dame boasting an Arnault gallery and a L’Oreal visitor centre. I’m joking, you snort. In which case, let me take you to the Sackler gallery at London’s Serpentine, generously donated by the family that extracted millions from opioid addiction.
Not least among this litany of ironies is that it takes a Catholic cathedral to remind us that we have barely advanced an inch from the medieval buying of indulgences, when the rich could amass their fortunes in as filthy a fashion as they liked – and then donate to the Church to launder their reputations and ensure their salvation. What was it that old Friar Tetzel used to say? “As soon as gold in the coffer rings, the rescued soul to heaven springs.”
Wednesday, 11 July 2018
The staggering rise of India’s super-rich
On 3 May, at around 4.45pm, a short, trim Indian man walked quickly down London’s Old Compton Street, his head bowed as if trying not to be seen. From his seat by the window of a nearby noodle bar, Anuvab Pal recognised him instantly. “He is tiny, and his face had been all over every newspaper in India,” Pal recalled. “I knew it was him.”
Few in Britain would have given the passing figure a second look. And that, in a way, was the point. The man pacing through Soho on that Wednesday night was Nirav Modi: Indian jeweller, billionaire and international fugitive.
In February, Modi had fled his home country after an alleged $1.8bn fraud case in which the tycoon was accused of abusing a system that allowed his business to obtain cash advances illegally from one of India’s largest banks. Since then, his whereabouts had been a mystery. Indian newspapers speculated that he might be holed up in Hong Kong or New York. Indian courts issued warrants for his arrest, and the police tried, ineffectually, to track him down.
It was only by chance that Pal spotted him. A standup comic normally based in Mumbai, he happened to be in London for a run of gigs. “My ritual was to go to the same noodle bar, have a meal, and then head to the theatre,” Pal said. “I always sat by the window. And then suddenly Modi walks past. He was unshaven, and had those Apple earphones, the wireless ones. He looked like he was in a hurry.”
It was another month before the press finally caught up with Modi, as reports of his whereabouts emerged in June, along with the suggestion that he was planning to claim political asylum in the UK. (Modi denies wrongdoing, and did not respond to requests for comment.) In the process, Modi also gained entry into one of London’s more notorious fraternities: the small club of Indian billionaires who seem to end up in the British capital following scandals back at home.
The most prominent among these émigré moguls is India’s “King of Good Times”, Vijay Mallya, the one-time aviation magnate and brewer, who transformed Kingfisher beer into a global brand. A few years ago, Mallya was one of India’s most celebrated industrialists, famous for his mullet haircut and flamboyant lifestyle. But in early 2016, Indian authorities filed charges relating to the collapse of his Kingfisher airline, which went bust in spectacular fashion in 2012, leaving behind mountainous debts and irate, unpaid staff. And so, facing allegations of financial irregularities and of refusing to repay outstanding loans, Mallya quietly boarded a plane for Britain, too.
Like Modi, Mallya denies wrongdoing. Last month he released a long statement accusing India’s government of conducting a witch-hunt against him. And to the extent that this claim has some merit, it is because Indian prime minister Narendra Modi (no relation to Nirav Modi) has of late been under great pressure to bring supposedly errant tycoons such as Mallya to book.
Men like Mallya and Modi were members of India’s expanding billionaire class, of whom there are now 119 members, according to Forbes magazine.Last year their collective worth amounted to $440bn – more than in any other country, bar the US and China. By contrast, the average person in India earns barely $1,700 a year. Given its early stage of economic development, India’s new hyper-wealthy elite have accumulated more money, more quickly, than their plutocratic peers in almost any country in history.
Narendra Modi won an overwhelming election victory in 2014, having promised to put a stop to the spate of corruption scandals that had dogged India for much of the previous decade. Many involved prominent industrialists – some directly accused of corruption, while others had simply mismanaged their finances and miraculously managed to escape the consequences. Voters turned to Narendra Modi, the self-described son of a poor tea-seller, hoping he would deliver a new era of clean governance and rapid growth, ridding India of a growing reputation for crony capitalism.
Narendra Modi pledged to end a situation in which the country’s ultra-wealthy – sometimes called “Bollygarchs” – appeared to live by one set of rules, while India’s 1.3 billion people operated by another. Yet as they continue to hide out in cities like London, men like Mallya and Nirav Modi have come to be seen as representing the failure of that pledge; the Indian authorities “have a long road ahead”, as one headline put it in the Hindustan Times last year, referring to a “long and arduous” future extradition process in Mallya’s case.
And as Narendra Modi gears up for a tough re-election battle next year, he is fighting the perception that India is unable to bring such men to heel, and that it has been powerless to respond to the rise of this new moneyed elite and the scandals that have come with them. “This ongoing battle to get India’s big tycoons to play by the rules is one of the biggest challenges we face,” says Reuben Abraham, chief executive of the IDFC Institute, a Mumbai-based thinktank. “Getting it right is central to India’s economic and political future.”
India has long been a stratified society, marked by divisions of caste, race and religion. Prior to the country winning independence in 1947, its people were subjugated by imperial British administrators and myriad maharajas, and the feudal regional monarchies over which they presided. Even afterwards, India remained a grimly poor country, as its socialist leadership fashioned a notably inefficient state-planned economic model, closed off almost entirely from global trade. Over time, India grew more equal, if only in the limited sense that its elite remained poor by the standards of the industrialised west.
But no longer: the last three decades have seen an extraordinary explosion of wealth at the top of Indian society. In the mid-1990s, just two Indians featured in the annual Forbes billionaire list, racking up around $3bn between them. But against a backdrop of the gradual economic re-opening that began in 1991, this has quickly changed. By 2016, India had 84 entries on the Forbes billionaire list. Its economy was then worth around $2.3tn, according to the World Bank. China reached that level of GDP in 2006, but with just 10 billionaires to show for it. At the same stage of development, India had created eight times as many.
In part, this wealth is to be welcomed. This year India will be the world’s fastest-growing major economy. During the last two decades, it has grown more quickly than at any point its history, a record of economic expansion that helped to lift hundreds of millions out of poverty.
Nonetheless, India remains a poor country: in 2016, to be counted among its richest 1% required assets of just $32,892, according to research from Credit Suisse. Meanwhile, the top 10% of earners now take around 55% of all national income – the highest rate for any large country in the world.
Put another way, India has created a model of development in which the proceeds of growth flow unusually quickly to the very top. Yet perhaps because Indian society has long been deeply stratified, this dramatic increase in inequality has not received as much global attention as it deserves. For nearly a century prior to independence, India was governed by the British Raj – a term taken from the Sanskrit rājya, meaning “rule”. For half a century after 1947, a system dominated by pernickety industrial rules emerged, often known as the Licence-Permit-Quota Raj, or Licence Raj for short. Now a system has grown in their place once again: the billionaire Raj.
The rise of India’s super-rich – the first and most obvious manifestation of the billionaire Raj – was propelled by domestic economic reforms. Starting slowly in the 1980s, and then more dramatically against the backdrop of a wrenching financial crisis in 1991, India dismantled the dusty stockade of rules and tariffs that made up the Licence Raj. Companies that had been cosseted under the old regime were cleared out via a mix of deregulation, foreign investment and heightened competition. In sector after sector, from airlines and banks to steel and telecoms, the ranks of India’s tycoons began to swell.
Nothing symbolises the power of this billionaire class more starkly than Antilia, the residential skyscraper built in Mumbai by Mukesh Ambani, India’s richest man. Rising 173 metres above India’s financial capital, the steel-and-glass tower is rumoured to have cost more than $1bn to build, looming over a city in which half the population still live in slums.
Advertisement
Ambani owns Reliance Industries, an empire with interests stretching from petrochemicals to telecoms. (His father, Dhirubhai, from whom he inherited his company, was one of the main beneficiaries of the economic reforms of the 1980s.) At Antilia, Ambani entertains guests in a grand, chandeliered ballroom that takes up most of building’s ground floor. There are six storeys of parking for the family’s car collection, while the tower’s higher levels feature opulent apartments and hanging gardens. Further down, in sub-basement 2, the Ambanis keep a recreational floor, which includes an indoor football pitch. Antilia became an instant landmark upon its completion in 2010. The city had long been a place of stark divisions, yet the Ambani’s home almost seemed to magnify this segregation. (A spokesman for Reliance did not respond to a request for comment.)
The emergence of the Indian super-rich was bound up in larger global story. The early 2000s were the heyday of the so-called “great moderation”, when world interest rates stayed low and industrialised nations grew handsomely. This was also when the fortunes of India’s new tycoons began to change. Pumped up by foreign money, domestic bank loans and a surging sense of self-belief, industrialists went on a spending spree. Ambani dumped billions into oil refineries and petrochemical plants. Vijay Mallya spent heavily on new fleets of Airbus jets. Nirav Modi began building a global chain of jewellery stores. Stock markets boomed. From 2004 to 2014, India enjoyed the fastest expansion in its history, averaging growth of more than 8% a year.
The boom years brought benefits, most obviously by reintegrating India into the world economy. Yet this whirlwind growth also proved economically disruptive, socially bruising and environmentally destructive, leaving behind what the writer Rana Dasgupta describes as a sense of national trauma. India’s new wealth has been shared remarkably unevenly, too. Its richest 1% earned about 7% of national income in 1980; that figure rocketed to 22% by 2014, according to the World Inequality Report. Over the same period, the share held by the bottom 50% plunged from 23% to just 15%.
Unsurprisingly, some feel resentful. “You walk around the streets of this city, and the rage at Antilia has to be heard to be believed,” Meera Sanyal, a former international banker turned local anti-corruption campaigner, told me in 2014. Six years before that, in 2008, as the scale of India’s billionaire fortunes were becoming clear, Raghuram Rajan – an economist who would later become the head of India’s central bank – asked an even more pointed question about his country’s tycoon class: “If Russia is an oligarchy, how long can we resist calling India one?”
Back in London, Vijay Mallya feels unjustly targeted by India’s recent attempts to shed its reputation for crony capitalism, the second defining characteristic of the billionaire Raj. “I have been accused by politicians and the media alike of having stolen and run away with Rs 9,000 crores [90bn rupees, or $1.3bn] that was loaned to Kingfisher Airlines,” he wrote in his open letter last month. His case had become, he suggested, a “lightning rod for public anger” over the alleged misbehaviour of his fellow tycoons.
In spring 2017, I met Mallya at his London home, a Grade I-listed town house a short walk from Baker Street tube station. A variety of Rolls-Royces and Bentleys were parked along the mews at the rear, alongside a fat silver Maybach with the number plate VJM 1, which idled outside Mallya’s back door. Inside, he sheltered behind a grand wooden table, a gold lighter and two mobile phones lined up in front of him. At one point I asked to be excused to visit the toilet. A flunky ushered me into a golden bathroom, with a shiny gold seat to match its golden taps and loo-roll holder. The fluffy hand towels were white, but each one came embossed with the letters “VJM” in gold thread.
On the surface, Mallya still seemed every bit the ebullient tycoon of old: a bulky man in a red polo shirt, with gold bracelets on each wrist and a chunky diamond ear stud. But by then he had been stuck in Britain for more than a year, and grew downbeat as the afternoon wound on and our conversation turned to his business troubles and the state of his homeland. “India has corruption running in its veins,” he said with a sigh. “And that’s not something one is going to change overnight.”
With his shoulder-length hair and taste for bling, Mallya had long honed an image as the most piratical of India’s generation of entrepreneurs. A specially kitted-out Boeing 727, its bar well-stocked with his own Kingfisher beer, whisked him between parties and business meetings – a distinction that was, in any case, often hazy. “It was all a bit ridiculous,” one ex-board member at a Mallya company told me.
Now marooned in London, Mallya had plenty of time to ponder his missteps. Once a member of the Rajya Sabha, the Indian upper house of parliament, his diplomatic passport has been cancelled. As a long-time UK resident, he was permitted to stay in the country, but without travel documents he was unable to travel, curtailing his notorious jetsetting lifestyle almost entirely. Earlier this month, a UK court issued an order allowing authorities trying to recover debts to enter his various British properties.
In his pomp, Mallya seemed to represent a new India. In a country whose old commercial elite had been dominated by cautious, discreet industrialists, Mallya was different: rich, powerful and not inclined to hide it. Not all of India’s pioneers behaved in this way – its software and IT billionaires, for instance, were typically less flamboyant figures. But while Mallya continues to deny that he did anything wrong, he admits that he has become what he calls the “poster boy” for a moment of public anger against India’s rich, as many newly wealthy business figures found themselves mired in allegations of wrongdoing.
India’s old system created fertile ground for corruption, forcing citizens and businesses alike to pay myriad bribes for basic state services. But these humdrum problems were trivial compared with the grand scandals that emerged during the 2000s. Assets worth billions were gifted under the table to big tycoons by senior politicians and bureaucrats in what became known as the “season of scams”. Giant kickbacks helped businesses acquire land, bypass environmental rules and win infrastructure contracts. Headlines filled up with fresh outrages, from fraudulent public housing schemes to dodgy road-building projects.
Many of those who backed India’s economic reforms hoped that a more free-market economy would lead to more honest government. Instead, crony capitalism infiltrated almost every area of national life. Hundreds of billions of dollars were siphoned away, according to some estimates, by a shadowy alliance of colluding politicians and business tycoons. India’s old system of retail corruption went wholesale.
Many politicians also became astoundingly rich, and would have made the Forbes list had their holdings not been hidden carefully in shell companies and foreign banks. Rapid economic growth increased the value of political power, and what could be extracted from it. Political parties had to raise more money, to fight elections and fund the patronage that kept them in office. One estimate suggested that India’s 2014 election cost close to $5bn, a huge increase over the cheap and cheerful polls of the pre-liberalisation era. Election experts believe most of this money is brought in illegally from favoured tycoons, in exchange for unknown future favours.
Politicians spend the money to fund campaigns, but also on handing out favours, jobs and cash to constituents. “It’s sort of an unholy nexus,” as Raghuram Rajan put it to me during his tenure as head of India’s central bank. “Poor public services? Politician fills the gap; politician gets the resources from the businessman; politician gets re-elected by the electorate for whom he’s filling the gap.”
This nexus between business and politics lies at the heart of the third problem of India’s billionaire Raj, namely the boom-and-bust cycle of its industrial economy. In recent decades, China went on the largest infrastructure building spree in history, but almost all of it was delivered by state-backed companies. By contrast, India’s mid-2000s boom was dominated almost exclusively by its private-sector tycoons, giving the industrialists and the conglomerates they run a position of outsized importance in India’s economic development.
Bollygarchs borrowed huge sums from state-backed banks and invested with gleeful abandon, in one of the largest deployments of private capital since America built its railroad network 150 years earlier. But when India’s good times came to an end after the global financial crisis, the tycoons’ hubris was exposed, leaving their businesses over-stretched and struggling to repay their debts. In 2017, 10 years on from the crisis, India’s banks were still left holding at least $150bn of bad assets.
Since taking office, Narendra Modi has tried, often ineffectually, to fix this corporate- and bank-debt crisis, alongside the related problems of cronyism and the super-rich that contributed to it. Watching developments such as these, some argue that the power of India’s tycoon class is fading. Yet India’s ultra-wealthy are still thriving, while its ranks of billionaires keep swelling, and will continue to do so.
There is every reason to believe that on its current course, the country’s the gap between rich and poor will widen, too. Perversely, the closer India comes to its achieving its ambitions of Chinese-style double-digit levels of economic growth, the faster this will happen. On most measures, it should already be ranked alongside South Africa and Brazil as one of the world’s least-equal countries. Even more importantly, poor countries that start off with high levels of inequality often struggle to reverse that trend as they grow richer.
Many experts believe India needs to act. “The main danger with extreme inequality is that if you don’t solve this through peaceful and democratic institutions then it will be solved in other ways … and that’s extremely frightening,” as French economist Thomas Piketty has said of India’s future, pointing to likely rising future tensions between the wealthy and the rest.
India is now entering a new phase of development, as it tries to follow Asian economies such as South Korea and Malaysia out of poverty and towards full “middle-income” status. There is no reason this cannot happen. But as we’ve seen in Latin America, the economies with the widest social divides have tended to be the ones that are most likely to get stuck in the “middle-income trap”, achieving moderate prosperity but failing to become rich. The more successful countries of east Asia, by contrast, grew prosperous while managing to stay egalitarian, partly by building basic social safety nets and ensuring that their wealthiest citizens paid their taxes. Of the two models, it seems clear which India should want to follow.
Much the same is true of corruption. India’s old system of cronyism, with its political favours and risk-free bank loans, has came under intense scrutiny, but the battle against corruption is at best half-won. Kickbacks still dominate swathes of public life, from land purchase to municipal contracts. State and city governments are just as venal as ever. Surveys report that India remains Asia’s most bribe-ridden nation. “For any society to lift itself out of absolute poverty, it needs to build three critical state institutions: taxation, law and security,” according to the economist Paul Collier. All three in India – the revenue service, the lower levels of the judiciary and the police – still suffer endemic corruption. Perhaps most importantly, the country’s under-the-table political funding system remains largely untouched.
Progress in fixing India’s problems of corporate and bank debt has also been frustratingly slow. Modi has introduced some important measures, including a new bankruptcy law and a series of bank recapitalisations. But more radical options have been ignored, notably the privatisation of struggling public-sector lenders.
If these struggles sound familiar, that is because they are. India is far from the first country to enjoy a period of rampant cronyism and wild growth, and then grapple with how to respond. In Britain, the onset of the industrial revolution in the mid-19th century kicked off such a moment, as captured in the novels of Charles Dickens and Anthony Trollope. But the more obvious parallel is with America, and the era between the end of the civil war in 1865 and the turn of the 20th century: the Gilded Age, or the era of “the great corporation, the crass plutocrat [and] the calculating political boss”, as one historian put it.
India’s own Gilded Age is different in many ways, but it shares at least one characteristic – namely, that such a period of early industrialisation is also a time of rapid political and economic change, in which it should be possible to invoke what the philosopher Richard Rorty once called the “romance of a national future”, the sense of hope that infuses powers on the rise.
India is set to grow in economic might throughout this century, as America did during the 19th. By some accounts, it has already overtaken China as the world’s most populous nation; in others, the baton will pass during the next decade or two. Whatever the case, the fate of a large slice of humanity depends on India getting its economic model right. Meanwhile, as democracy falters in the west, so its future in India has never been more critical. To make this transition, India’s billionaire Raj must become a passing phase, not a permanent condition. India’s ambition to lead the second half of the “Asian century” – and the world’s hopes for a fairer and more democratic future – depend on getting this transition right.
Sunday, 8 July 2018
The Billionaire Raj: A chronicle of economic India
India is now one of the world’s economic hotspots. Stock images of starving children, miserable peasants and cheating shop owners have been augmented with those of high-tech development and booming cities. India is now the world’s fastest-growing economy. It is about to become the third-largest economy — at least in terms of purchasing power dollars if not yet real ones. Foreign investors are rushing in. In The Billionaire Raj, James Crabtree has written a compelling guide to what awaits them.
To make India more accessible to the western investor, Crabtree draws an analogy between America’s Gilded Age at the end of the 19th century — that plutocratic moment of the Vanderbilts, Goulds, Rockefellers — and the newest of India’s billionaires. Did you know that India now has more billionaires than Russia?
This sudden enrichment was the result of the long boom of globalisation from 1991-2008. India had initiated reforms to escape from four decades of conservative socialism, initiated by Jawaharlal Nehru, which did not trust private business and put the state in command. The Indian state is inefficient as it is, but disastrous in running business. Its airline Air India has racked up billions in losses; its banks are mired in non-performing loans.
In 1991, Manmohan Singh, then finance minister, bit the bullet and began to liberalise the economy. Tariffs were cut, import licensing was removed, and the rupee was devalued twice within a week. He had little choice because India had run out of foreign exchange reserves and had to pawn its gold to secure a loan from the International Monetary Fund.
The reforms took time to work but, from 1998 onwards, the economy secured high single-digit growth rates, triple the so-called “Hindu growth rate” of 3 per cent per year that prevailed during the first 30 years of independence. With a decade-long growth spurt from 1998 to 2008 came the vast fortunes generated in a crony-capitalist relationship between the ruling Congress party and its private sector clients and financiers. Crabtree, a former FT Mumbai correspondent, gives us a detailed treatment of the links between the politicians needing money to finance elections that were both costly and cheap. (The 2014 elections cost $5bn — or $6 per voter.)
Crabtree gives entertaining portraits of some billionaires. The opening chapters cover Mukesh Ambani and his towering residential extravaganza Antilla, the most expensive house ever built in India, which now dominates the Mumbai skyline; the fugitive Vijay Mallya, a drinks tycoon who was once known as the King of Good Times; the reticent Gautam Adani, an infrastructure entrepreneur who owns ports, mines and refineries. Dhirubhai Ambani, the patriarch of the Reliance group, figured out how to negotiate government regulations and expand his business while keeping the ruling party on his side. Mallya went so far as to be voted into a seat in the Rajya Sabha, the upper house of parliament, after a reported donation of 550m rupees ($10m in those days). Adani prospered in Gujarat with the reported blessings of Narendra Modi while he was chief minister of the state in India’s north-west, where the politician enjoyed both a clean reputation and business-friendly credentials.
Crabtree shows both how deep corruption reaches into electoral politics — but also how functional it is
Beyond the personalities lies another part of the puzzle. Corruption has gone deep in the system. Elections cannot be financed with just legally declared donations. The donors want to escape attention of the tax man, as do the party leaders. It is a symbiotic relationship. Not even Prime Minister Modi, as he has been since 2014, is about to change it, though he has moved against crony capitalism. Armed with an electoral majority, he has set about breaking the political mould, ending the near 70-year hegemony of Congress. He has sundered the crony ties that the top echelon of government enjoyed with the “promoters” of infrastructure projects during the Congress years. Back then the nationalised banks had to lend money to a favoured few and it was understood that the money would not be repaid. No more. Insolvency procedures have been toughened. Debtors can no longer shield their assets from creditors. It was this that sent Mallya abroad.
This book was written before these drastic changes. But whether he wins or loses the next elections, Modi has made revival of crony capitalism difficult.
There are also other concerns. Crabtree worries over Modi’s dual persona as a development enthusiast as well as a Hindu nationalist. The fear is that this may increase intolerance towards minorities — Muslims and Christians — and disrupt peaceful economic progress.
Crabtree’s vivid portrayal of the corruption of politics is very informative, and thought-provoking. He travels the country to show both how deep corruption reaches into electoral politics — but also how functional it is. When an economy is regulated, riddled with permits needed to do business, a few palms may need to be greased. A payment — or rent, as economists call it — may be required. But the rewards are considerable. The corruption market works. It may be immoral but it is not inefficient.
It would be better if India became less corrupt. Crabtree thinks so. That would require a lot of courage and an ability to pursue radical reform. The leader who embarks upon it risks unpopularity — as Modi is now finding out.
These are matters that cannot be settled in a single book. Crabtree has given us the most comprehensive and eminently readable tour of economic India, which, as he shows, cannot be understood without a knowledge of how political India works.
Friday, 6 July 2018
The George Soros philosophy – and its fatal flaw
In late May, the same day she got fired by the US TV network ABC for her racist tweet about Obama adviser Valerie Jarrett, Roseanne Barr accused Chelsea Clinton of being married to George Soros’s nephew. “Chelsea Soros Clinton,” Barr tweeted, knowing that the combination of names was enough to provoke a reaction. In the desultory exchange that followed, the youngest Clinton responded to Roseanne by praising Soros’s philanthropic work with his Open Society Foundations. To which Barr responded in the most depressing way possible, repeating false claims earlier proferred by rightwing media personalities: “Sorry to have tweeted incorrect info about you! Please forgive me! By the way, George Soros is a nazi who turned in his fellow Jews 2 be murdered in German concentration camps & stole their wealth – were you aware of that? But, we all make mistakes, right Chelsea?”
Barr’s tweet was quickly retweeted by conservatives, including Donald Trump Jr. This shouldn’t have surprised anyone. On the radical right, Soros is as hated as the Clintons. He is a verbal tic, a key that fits every hole. Soros’s name evokes “an emotional outcry from the red-meat crowds”, one former Republican congressman recently told the Washington Post. They view him as a “sort of sinister [person who] plays in the shadows”. This antisemitic caricature of Soros has dogged the philanthropist for decades. But in recent years the caricature has evolved into something that more closely resembles a James Bond villain. Even to conservatives who reject the darkest fringes of the far right, Breitbart’s description of Soros as a “globalist billionaire” dedicated to making America a liberal wasteland is uncontroversial common sense.
The trouble with charitable billionaires
In spite of the obsession with Soros, there has been surprisingly little interest in what he actually thinks. Yet unlike most of the members of the billionaire class, who speak in platitudes and remain withdrawn from serious engagement with civic life, Soros is an intellectual. And the person who emerges from his books and many articles is not an out-of-touch plutocrat, but a provocative and consistent thinker committed to pushing the world in a cosmopolitan direction in which racism, income inequality, American empire, and the alienations of contemporary capitalism would be things of the past. He is extremely perceptive about the limits of markets and US power in both domestic and international contexts. He is, in short, among the best the meritocracy has produced.
It is for this reason that Soros’s failures are so telling; they are the failures not merely of one man, but of an entire class – and an entire way of understanding the world. From his earliest days as a banker in postwar London, Soros believed in a necessary connection between capitalism and cosmopolitanism. For him, as for most of the members of his cohort and the majority of the Democratic party’s leadership, a free society depends on free (albeit regulated) markets. But this assumed connection has proven to be a false one. The decades since the end of the cold war have demonstrated that, without a perceived existential enemy, capitalism tends to undermine the very culture of trust, compassion and empathy upon which Soros’s “open society” depends, by concentrating wealth in the hands of the very few.
Instead of the global capitalist utopia predicted in the halcyon 1990s by those who proclaimed an end to history, the US is presently ruled by an oafish heir who enriches his family as he dismantles the “liberal international order” that was supposed to govern a peaceful, prosperous and united world. While Soros recognised earlier than most the limits of hypercapitalism, his class position made him unable to advocate the root-and-branch reforms necessary to bring about the world he desires. The system that allows George Soros to accrue the wealth that he has done has proven to be one in which cosmopolitanism will never find a stable home.
The highlights of Soros’s biography are well known. Born to middle-class Jewish parents in Budapest in 1930 as György Schwartz, Soros – his father changed the family name in 1936 to avoid antisemitic discrimination – had a tranquil childhood until the second world war, when after the Nazi invasion of Hungary he and his family were forced to assume Christian identities and live under false names. Miraculously, Soros and his family survived the war, escaping the fate suffered by more than two-thirds of Hungary’s Jews. Feeling stifled in newly communist Hungary, in 1947 Soros immigrated to the UK, where he studied at the London School of Economics and got to know the Austrian-born philosopher Karl Popper, who became his greatest interlocutor and central intellectual influence.
In 1956, Soros moved to New York to pursue a career in finance. After spending over a decade working in various Wall Street positions, in the late 1960s he founded the Quantum Fund, which became one of the most successful hedge funds of all time. As his fund amassed staggering profits, Soros personally emerged as a legendary trader; most famously, in November 1992 he earned more than $1bn and “broke the Bank of England” by betting that the pound was priced too highly against the Deutschmark.

Karl Popper, whose writings were a key influence on Soros’s thinking about the ‘open society’. Photograph: Popperfoto
Today, Soros is one of the richest men in the world and, along with Bill Gates and Mark Zuckerberg, one of the US’s most politically influential philanthropists. But unlike Gates and Zuckerberg, Soros has long pointed to academic philosophy as his source of inspiration. Soros’s thought and philanthropic career are organised around the idea of the “open society,” a term developed and popularised by Popper in his classic work The Open Society and Its Enemies. According to Popper, open societies guarantee and protect rational exchange, while closed societies force people to submit to authority, whether that authority is religious, political or economic.
Since 1987, Soros has published 14 books and a number of pieces in the New York Review of Books, New York Times and elsewhere. These texts make it clear that, like many on the centre-left who rose to prominence in the 1990s, Soros’s defining intellectual principle is his internationalism. For Soros, the goal of contemporary human existence is to establish a world defined not by sovereign states, but by a global community whose constituents understand that everyone shares an interest in freedom, equality and prosperity. In his opinion, the creation of such a global open society is the only way to ensure that humanity overcomes the existential challenges of climate change and nuclear proliferation.
Unlike Gates, whose philanthropy focuses mostly on ameliorative projects such as eradicating malaria, Soros truly wants to transform national and international politics and society. Whether or not his vision can survive the wave of antisemitic, Islamophobic and xenophobic rightwing nationalism ascendant in the US and Europe remains to be seen. What is certain is that Soros will spend the remainder of his life attempting to make sure it does.
Soros began his philanthropic activities in 1979, when he “determined after some reflection that I had enough money” and could therefore devote himself to making the world a better place. To do so, he established the Open Society Fund, which quickly became a transnational network of foundations. Though he made some effort at funding academic scholarships for black students in apartheid South Africa, Soros’s primary concern was the communist bloc in eastern Europe; by the end of the 80s, he had opened foundation offices in Hungary, Poland, Czechoslovakia, Bulgaria and the Soviet Union itself. Like Popper before him, Soros considered the countries of communist eastern Europe to be the ultimate models of closed societies. If he were able to open these regimes, he could demonstrate to the world that money could – in some instances, at least – peacefully overcome oppression without necessitating military intervention or political subversion, the favoured tools of cold war leaders.
Soros set up his first foreign foundation in Hungary in 1984, and his efforts there serve as a model of his activities during this period. Over the course of the decade, he awarded scholarships to Hungarian intellectuals to bring them to the US; provided Xerox machines to libraries and universities; and offered grants to theatres, libraries, intellectuals, artists and experimental schools. In his 1990 book Opening the Soviet System, Soros wrote that he believed his foundation had helped “demolish the monopoly of dogma [in Hungary] by making an alternate source of financing available for cultural and social activities”, which, in his estimation, played a crucial role in producing the internal collapse of communism.
Soros’s use of the word dogma points to two critical elements of his thought: his fierce belief that ideas, more than economics, shape life, and his confidence in humanity’s capacity for progress. According to Soros, the dogmatic mode of thinking that characterised closed societies made it impossible for them to accommodate to the changing vicissitudes of history. Instead, “as actual conditions change”, people in closed societies were forced to abide by an atavistic ideology that was increasingly unpersuasive. When this dogma finally became too obviously disconnected from reality, Soros claimed, a revolution that overturned the closed society usually occurred. By contrast, open societies were dynamic and able to correct course whenever their dogmas strayed too far from reality.
As he witnessed the Soviet empire’s downfall between 1989 and 1991, Soros needed to answer a crucial strategic question: now that the closed societies of eastern Europe were opening, what was his foundation to do? On the eve of the Soviet Union’s dissolution, Soros published an updated version of Opening the Soviet System, titled Underwriting Democracy, which revealed his new strategy: he would dedicate himself to building permanent institutions that would sustain the ideas that motivated anticommunist revolutions, while modelling the practices of open society for the liberated peoples of eastern Europe. The most important of these was Central European University (CEU), which opened in Budapest in 1991. Funded by Soros, CEU was intended to serve as the wellspring for a new, transnational, European world – and the training ground for a new, transnational, European elite.
How could Soros ensure that newly opened societies would remain free? Soros had come of age in the era of the Marshall Plan, and experienced American largesse firsthand in postwar London. To him, this experience showed that weakened and exhausted societies could not be rehabilitated without a substantial investment of foreign aid, which would alleviate extreme conditions and provide the minimum material base that would enable the right ideas about democracy and capitalism to flourish.
For this reason, in the late 80s and early 90s Soros repeatedly argued that “only the deus ex machina of western assistance” could make the eastern bloc permanently democratic. “People who have been living in a totalitarian system all their lives,” he claimed, “need outside assistance to turn their aspirations into reality.” Soros insisted that the US and western Europe give the countries of eastern Europe a substantial amount of pecuniary aid, provide them with access to the European Common Market, and promote cultural and educational ties between the west and the east “that befit a pluralistic society”. Once accomplished, Soros avowed, western Europe must welcome eastern Europe into the European community, which would prevent the continent’s future repartitioning.
Soros’s prescient pleas went unheeded. From the 1990s on, he has attributed the emergence of kleptocracy and hypernationalism in the former eastern bloc to the west’s lack of vision and political will during this crucial moment. “Democracies,” he lamented in 1995, seem to “suffer from a deficiency of values … [and] are notoriously unwilling to take any pain when their vital self-interests are not directly threatened.” For Soros, the west had failed in an epochal task, and in so doing had revealed its shortsightedness and fecklessness.
But it was more than a lack of political will that constrained the west during this moment. In the era of “shock therapy”, western capital did flock to eastern Europe – but this capital was invested mostly in private industry, as opposed to democratic institutions or grassroots community-building, which helped the kleptocrats and anti-democrats seize and maintain power. Soros had identified a key problem but was unable to appreciate how the very logic of capitalism, which stressed profit above all, would necessarily undermine his democratic project. He remained too wedded to the system he had conquered.
In the wake of the cold war, Soros dedicated himself to exploring the international problems that prevented the realisation of a global open society. After the 1997 Asian financial crisis, in which a currency collapse in south-east Asia engendered a world economic downturn, Soros wrote books addressing the two major threats he believed beset open society: hyperglobalisation and market fundamentalism, both of which had become hegemonic after communism’s collapse.
Soros argued that the history of the post-cold war world, as well as his personal experiences as one of international finance’s most successful traders, demonstrated that unregulated global capitalism undermined open society in three distinct ways. First, because capital could move anywhere to avoid taxation, western nations were deprived of the finances they needed to provide citizens with public goods. Second, because international lenders were not subject to much regulation, they often engaged in “unsound lending practices” that threatened financial stability. Finally, because these realities increased domestic and international inequality, Soros feared they would encourage people to commit unspecified “acts of desperation” that could damage the global system’s viability.
Soros saw, far earlier than most of his fellow centre-leftists, the problems at the heart of the financialised and deregulated “new economy” of the 1990s and 2000s. More than any of his liberal peers, he recognised that embracing the most extreme forms of its capitalist ideology might lead the US to promote policies and practices that undermined its democracy and threatened stability both at home and abroad.
In Soros’s opinion, the only way to save capitalism from itself was to establish a “global system of political decision-making” that heavily regulated international finance. Yet as early as 1998, Soros acknowledged that the US was the primary opponent of global institutions; by this point in time, Americans had refused to join the International Court of Justice; had declined to sign the Ottawa treaty on banning landmines; and had unilaterally imposed economic sanctions when and where they saw fit. Still, Soros hoped that, somehow, American policymakers would accept that, for their own best interests, they needed to lead a coalition of democracies dedicated to “promoting the development of open societies [and] strengthening international law and the institutions needed for a global open society”.
But Soros had no programme for how to modify American elites’ increasing hostility to forms of internationalism that did not serve their own military might or provide them with direct and visible economic benefits. This was a significant gap in Soros’s thought, especially given his insistence on the primacy of ideas in engendering historical change. Instead of thinking through this problem, however, he simply declared that “change would have to begin with a change of attitudes, which would be gradually translated into a change of policies”. Soros’s status as a member of the hyper-elite and his belief that, for all its hiccups, history was headed in the right direction made him unable to consider fully the ideological obstacles that stood in the way of his internationalism.
The George W Bush administration’s militarist response to the attacks of September 11 compelled Soros to shift his attention from economics to politics. Everything about the Bush administration’s ideology was anathema to Soros. As Soros declared in his 2004 The Bubble of American Supremacy, Bush and his coterie embraced “a crude form of social Darwinism” that assumed that “life is a struggle for survival, and we must rely mainly on the use of force to survive”. Whereas before September 11, “the excesses of [this] false ideology were kept within bounds by the normal functioning of our democracy”, after it Bush “deliberately fostered the fear that has gripped the country” to silence opposition and win support for a counterproductive policy of militaristic unilateralism. To Soros, assertions such as “either you are with us, or you are with the terrorists” eerily echoed the rhetoric of the Nazis and Soviets, which he hoped to have left behind in Europe. Soros worried, wisely, that Bush would lead the nation into “a permanent state of war” characterised by foreign intervention and domestic oppression. The president was thus not only a threat to world peace, but also to the very idea of open society.
Nevertheless, Soros was confident that Bush’s “extremist ideology” did not correspond “to the beliefs and values of the majority of Americans”, and he expected that John Kerry would win the 2004 presidential election. Kerry’s victory, Soros anticipated, would spur “a profound reconsideration of America’s role in the world” that would lead citizens to reject unilateralism and embrace international cooperation.
But Kerry did not win, which forced the philanthropist to question, for the first time, ordinary Americans’ political acumen. After the 2004 election, Soros underwent something like a crisis of faith. In his 2006 book The Age of Fallibility, Soros attributed Bush’s re-election to the fact that the US was “a ‘feel-good’ society unwilling to face unpleasant reality”. Americans, Soros avowed, would rather be “grievously misled by the Bush administration” than confront the failures of Afghanistan, Iraq and the war on terror head-on. Because they were influenced by market fundamentalism and its obsession with “success”, Soros continued, Americans were eager to accept politicians’ claims that the nation could win something as absurd as a war on terror.
Bush’s victory convinced Soros that the US would survive as an open society only if Americans began to acknowledge “that the truth matters”; otherwise, they would continue to support the war on terror and its concomitant horrors. How Soros could change American minds, though, remained unclear.
The financial crisis of 2007-2008 encouraged Soros to refocus on economics. The collapse did not surprise him; he considered it the predictable consequence of market fundamentalism. Rather, it convinced him that the world was about to witness, as he declared in his 2008 book The New Paradigm for Financial Markets, “the end of a long period of relative stability based on the US as the dominant power and the dollar as the main international reserve currency”.
Anticipating American decline, Soros started to place his hopes for a global open society on the European Union, despite his earlier anger at the union’s members for failing to fully welcome eastern Europe in the 90s. Though he admitted that the EU had serious problems, it was nevertheless an organisation in which nations voluntarily “agreed to a limited delegation of sovereignty” for the common European good. It thus provided a regional model for a world order based on the principles of open society.
Soros’s hopes in the EU, however, were quickly dashed by three crises that undercut the union’s stability: the ever-deepening international recession, the refugee crisis, and Vladimir Putin’s revanchist assault on norms and international law. While Soros believed western nations could theoretically mitigate these crises, he concluded that, in a repetition of the failures of the post-Soviet period, they were unlikely to band together to do so. In the last 10 years, Soros has been disappointed by the facts that the west refused to forgive Greece’s debt; failed to develop a common refugee policy; and would not consider augmenting sanctions on Russia with the material and financial support Ukraine required to defend itself after Putin’s 2014 annexation of Crimea. He was further disturbed that many nations in the EU, from the UK to Poland, witnessed the re-emergence of a rightwing ethnonationalism thought lost to history. Once Britain voted to leave the union in 2016, he became convinced that “the disintegration of the EU [was] practically irreversible”. The EU did not serve as the model Soros hoped it would.
Soros experienced firsthand the racialised authoritarianism that in the last decade has threatened not only the EU, but democracy in Europe generally. Since 2010, the philanthropist has repeatedly sparred with Viktor Orbán, the authoritarian, anti-immigrant prime minister of Hungary. Recently, Soros accused Orbán of “trying to re-establish the kind of sham democracy that prevailed [in Hungary] in the period between the first and second world wars”. In his successful re-election campaign earlier this year, Orbán spent much of his time on the campaign trail demonising Soros, playing on antisemitic tropes and claiming that Soros was secretly plotting to send millions of immigrants to Hungary. Orbán has also threatened the Central European University – which his government derisively refers to as “the Soros university” – with closure, and last month parliament passed new anti-immigration legislation known as the “Stop Soros” laws.
But while Orbán threatens Hungary’s open society, it is Donald Trump who threatens the open society writ large. Soros has attributed Trump’s victory to the deleterious effects market fundamentalism and the Great Recession had on American society. In a December 2016 op-ed, Soros argued that Americans voted for Trump, “a con artist and would-be dictator”, because “elected leaders failed to meet voters’ legitimate expectations and aspirations [and] this failure led electorates to become disenchanted with the prevailing versions of democracy and capitalism”.
Instead of fairly distributing the wealth created by globalisation, Soros argued, capitalism’s “winners” failed to “compensate the losers”, which led to a drastic increase in domestic inequality – and anger. Though Soros believed that the US’s “Constitution and institutions … are strong enough to resist the excesses of the executive branch”, he worried that Trump would form alliances with Putin, Orbán and other authoritarians, which would make it near-impossible to build a global open society. In Hungary, the US and many of the parts of the world that have attracted Soros’s attention and investment, it is clear that his project has stalled.
Soros’s path ahead is unclear. On one hand, some of Soros’s latest actions suggest he has moved in a left-wing direction, particularly in the areas of criminal justice reform and refugee aid. He recently created a fund to assist the campaign of Larry Krasner, the radical Philadelphia district attorney, and backed three California district-attorney candidates similarly devoted to prosecutorial reform. He has also invested $500m to alleviate the global refugee crisis.
On the other hand, some of his behaviour indicates that Soros remains committed to a traditional Democratic party ill-equipped to address the problems that define our moment of crisis. During the 2016 Democratic primary race, he was an avowed supporter of Hillary Clinton. And recently, he lambasted potential Democratic presidential candidate Kirsten Gillibrand for urging Al Franken to resign due to his sexual harassment of the radio host Leeann Tweeden. If Soros continues to fund truly progressive projects, he will make a substantial contribution to the open society; but if he decides to defend banal Democrats, he will contribute to the ongoing degradation of American public life.
Throughout his career, Soros has made a number of wise and exciting interventions. From a democratic perspective, though, this single wealthy person’s ability to shape public affairs is catastrophic. Soros himself has recognised that “the connection between capitalism and democracy is tenuous at best”. The problem for billionaires like him is what they do with this information. The open society envisions a world in which everyone recognises each other’s humanity and engages each other as equals. If most people are scraping for the last pieces of an ever-shrinking pie, however, it is difficult to imagine how we can build the world in which Soros – and, indeed, many of us – would wish to live. Presently, Soros’s cosmopolitan dreams remain exactly that. The question is why, and the answer might very well be that the open society is only possible in a world where no one – whether Soros, or Gates, or DeVos, or Zuckerberg, or Buffett, or Musk, or Bezos – is allowed to become as rich as he has.
.png)
.png)
.png)






