If librarians and steelworkers wanted state bail-outs, they should have done something
useful - like bankers
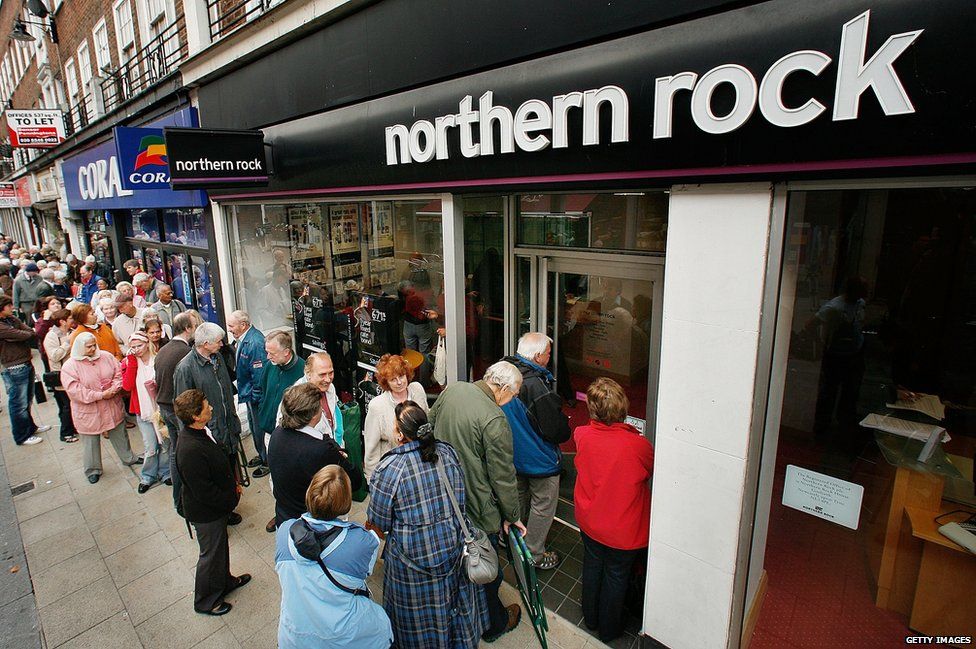
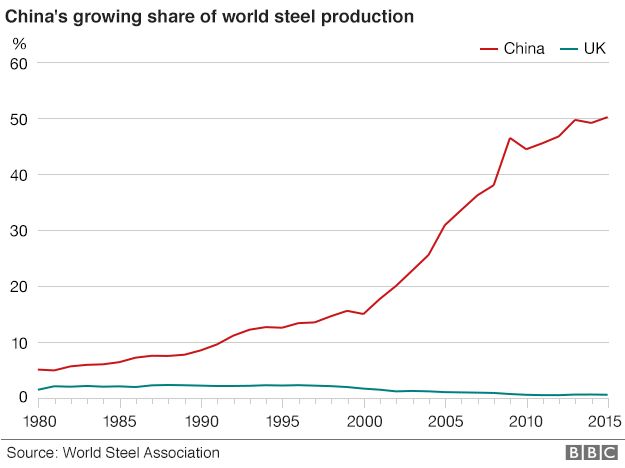
In any case the bankers deserved to be bailed out, as they couldn’t possibly anticipate that if they kept taking money it might eventually run out, whereas steelworkers have caused their own downfall by not being Chinese.
Mark Steel in The Independent
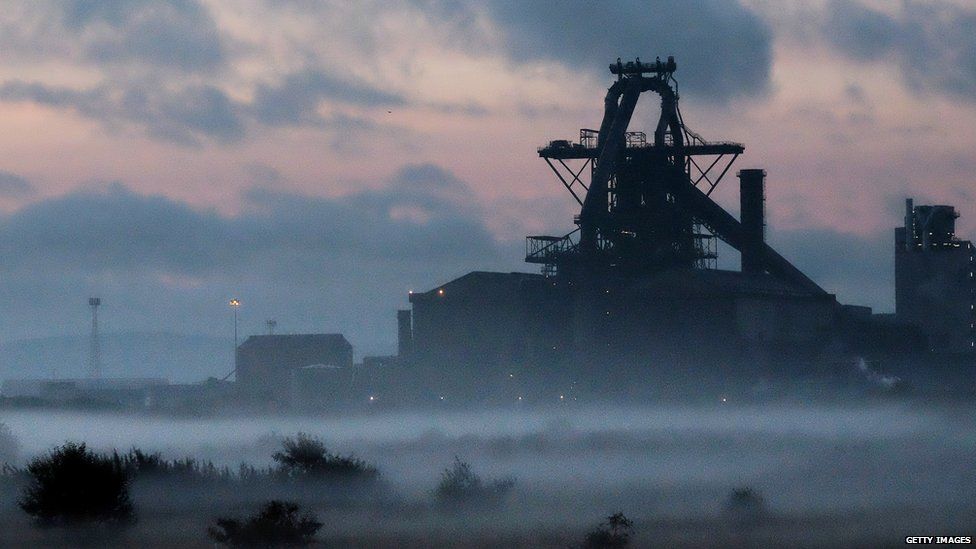
The main thing to realise with the current steel industry crisis is that the government has been clear and decisive. They’ve stated firmly, “We’re not ruling out anything at all, though we are ruling out nationalising anything as that doesn’t count as anything, but we will do anything we possibly can that won’t make a difference such as drawing a pretty picture of a caterpillar, and we’re doing all we can because as we keep saying there’s nothing we can do, but we do feel desperately sorry for anyone who loses their job which is why any steelworkers who become redundant will immediately be called in to the job centre for an interview and told they won’t get any benefits if their answer to ‘Why have you let yourself be put of work?’ is ‘There was nothing I could do’.”
---Also read
------
Some people have pointed out that other industries were bailed out by governments in the past - but this has only been if they’ve produced essential goods, such as hedge funds and executive bonuses, not frivolities like the stuff that makes ships and teaspoons.
In any case the bankers deserved to be bailed out, as they couldn’t possibly anticipate that if they kept taking money it might eventually run out, whereas steelworkers have caused their own downfall by not being Chinese.
Luckily this sound economics is understood across the country, including by the sensible wing of the Labour Party such as those in charge of Lambeth Council, who are closing half the borough’s libraries and turning them into gyms.
This is the sort of can-do attitude people want from Labour. Hopefully it will spark off other schemes, such as turning social services departments into sushi bars, or converting disabled people’s wheelchairs into drones so they can be rented out to the RAF.
There’s no point in complaining about this; it’s the way the free market works. And if the Chinese are flooding South London with cheap Agatha Christies, we just have to accept it, and ask the elderly people who rely on going to libraries as their only point of contact with the community to spend all morning performing 200 reps of 40 kilograms per calf on a multi-gym body-solid squat machine instead.
One of these libraries, the Tate, has been assessed as receiving an average of 600 visits per day. This may seem successful, but where the library has let itself down is forgetting to charge any of them money for borrowing books and bringing kids into reading classes.
Maybe the library service should learn from gyms, and only let them in if they pay £40 a month on a minimum two-year contract. They could even offer them special courses in which an instructor screams, “Right, everyone, let’s all read this week’s Economist - you CAN do it - let’s drive ourselves to the limit - GO – ‘the Yen faces unexpected slow down’ - come on Eileen pick it up, PUSH everyone!”
The council insists they will preserve the essence of the libraries, because each of the gyms will include a “lounge with a limited supply of books”. Obviously they won’t have all those unnecessary books you see in old-fashioned libraries, but surely no one’s so fussy they insist on any specific book, as most books are pretty much the same.
The council also agreed that “under-18s may not be allowed in these lounges”, which will surely improve the service as rooms with books aren’t a suitable environment for the young.
Surprisingly, the local population appears shamefully ignorant about economics - so there have been daily protests against the closures, in which thousands have taken part. It seems these people don’t understand that it may have been all right to build and maintain free libraries back in the 1930s, but you can’t expect us to keep funding the luxuries we could afford back then.
So the council demanded a banner was taken down at one library, which was changed each day to tell people how many days were left until it was closed. Maybe the council hoped that if people weren’t reminded of the closure, they just wouldn’t notice. Then eventually they’d all tell stories of success and improvement to each other, such as: “I asked for a reference book on growing cucumbers and was sent into the corner. After three weeks I didn’t feel I was making any progress with my gardening, but then someone told me I’d spent the whole time benching 140 kilograms and now I’m the all-Hertfordshire Over-60s Bodybuilding champion.”
Nevertheless, the protests continue. But the libraries have probably been lending the wrong assets if they want state intervention. Instead of irresponsibly lending books to people who live round the corner so they can read and study and educate and entertain themselves and their kids, they should have lent billions of dollars to anyone who asked for it, without even suggesting a 40p fine if they kept it a week too long.
Then, once they’d succeeded in ruining the world economy, they’d have had a very reasonable case for being bailed out - unlike these people who want to fund steelworks and libraries because they don’t understand the world economy.
------- The China Tariff matter
The main thing to realise with the current steel industry crisis is that the government has been clear and decisive. They’ve stated firmly, “We’re not ruling out anything at all, though we are ruling out nationalising anything as that doesn’t count as anything, but we will do anything we possibly can that won’t make a difference such as drawing a pretty picture of a caterpillar, and we’re doing all we can because as we keep saying there’s nothing we can do, but we do feel desperately sorry for anyone who loses their job which is why any steelworkers who become redundant will immediately be called in to the job centre for an interview and told they won’t get any benefits if their answer to ‘Why have you let yourself be put of work?’ is ‘There was nothing I could do’.”
---Also read
Steel v banks: Why they're different when it comes to a government bail-out
------
Some people have pointed out that other industries were bailed out by governments in the past - but this has only been if they’ve produced essential goods, such as hedge funds and executive bonuses, not frivolities like the stuff that makes ships and teaspoons.
In any case the bankers deserved to be bailed out, as they couldn’t possibly anticipate that if they kept taking money it might eventually run out, whereas steelworkers have caused their own downfall by not being Chinese.
Luckily this sound economics is understood across the country, including by the sensible wing of the Labour Party such as those in charge of Lambeth Council, who are closing half the borough’s libraries and turning them into gyms.
This is the sort of can-do attitude people want from Labour. Hopefully it will spark off other schemes, such as turning social services departments into sushi bars, or converting disabled people’s wheelchairs into drones so they can be rented out to the RAF.
There’s no point in complaining about this; it’s the way the free market works. And if the Chinese are flooding South London with cheap Agatha Christies, we just have to accept it, and ask the elderly people who rely on going to libraries as their only point of contact with the community to spend all morning performing 200 reps of 40 kilograms per calf on a multi-gym body-solid squat machine instead.
One of these libraries, the Tate, has been assessed as receiving an average of 600 visits per day. This may seem successful, but where the library has let itself down is forgetting to charge any of them money for borrowing books and bringing kids into reading classes.
Maybe the library service should learn from gyms, and only let them in if they pay £40 a month on a minimum two-year contract. They could even offer them special courses in which an instructor screams, “Right, everyone, let’s all read this week’s Economist - you CAN do it - let’s drive ourselves to the limit - GO – ‘the Yen faces unexpected slow down’ - come on Eileen pick it up, PUSH everyone!”
The council insists they will preserve the essence of the libraries, because each of the gyms will include a “lounge with a limited supply of books”. Obviously they won’t have all those unnecessary books you see in old-fashioned libraries, but surely no one’s so fussy they insist on any specific book, as most books are pretty much the same.
The council also agreed that “under-18s may not be allowed in these lounges”, which will surely improve the service as rooms with books aren’t a suitable environment for the young.
Surprisingly, the local population appears shamefully ignorant about economics - so there have been daily protests against the closures, in which thousands have taken part. It seems these people don’t understand that it may have been all right to build and maintain free libraries back in the 1930s, but you can’t expect us to keep funding the luxuries we could afford back then.
So the council demanded a banner was taken down at one library, which was changed each day to tell people how many days were left until it was closed. Maybe the council hoped that if people weren’t reminded of the closure, they just wouldn’t notice. Then eventually they’d all tell stories of success and improvement to each other, such as: “I asked for a reference book on growing cucumbers and was sent into the corner. After three weeks I didn’t feel I was making any progress with my gardening, but then someone told me I’d spent the whole time benching 140 kilograms and now I’m the all-Hertfordshire Over-60s Bodybuilding champion.”
Nevertheless, the protests continue. But the libraries have probably been lending the wrong assets if they want state intervention. Instead of irresponsibly lending books to people who live round the corner so they can read and study and educate and entertain themselves and their kids, they should have lent billions of dollars to anyone who asked for it, without even suggesting a 40p fine if they kept it a week too long.
Then, once they’d succeeded in ruining the world economy, they’d have had a very reasonable case for being bailed out - unlike these people who want to fund steelworks and libraries because they don’t understand the world economy.
@@@@@@
------- The China Tariff matter