'People will forgive you for being wrong, but they will never forgive you for being right - especially if events prove you right while proving them wrong.' Thomas Sowell
Search This Blog
Monday, 27 May 2024
Saturday, 7 October 2023
Saturday, 6 November 2021
Never mind aid, never mind loans: what poor nations are owed is reparations
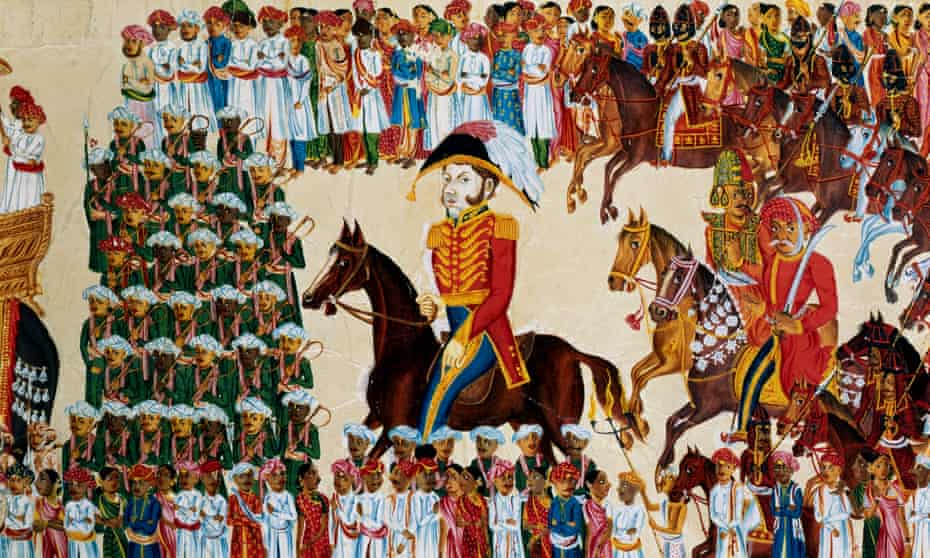 Excerpt from a painting depicting the British East India Company in India, 1825-1830. Photograph: Print Collector/Getty Images
Excerpt from a painting depicting the British East India Company in India, 1825-1830. Photograph: Print Collector/Getty Images The story of the past 500 years can be crudely summarised as follows. A handful of European nations, which had mastered both the art of violence and advanced seafaring technology, used these faculties to invade other territories and seize their land, labour and resources.
Competition for control of other people’s lands led to repeated wars between the colonising nations. New doctrines – racial categorisation, ethnic superiority and a moral duty to “rescue” other people from their “barbarism” and “depravity” – were developed to justify the violence. These doctrines led, in turn, to genocide.
The stolen labour, land and goods were used by some European nations to stoke their industrial revolutions. To handle the greatly increased scope and scale of transactions, new financial systems were established that eventually came to dominate their own economies. European elites permitted just enough of the looted wealth to trickle down to their labour forces to seek to stave off revolution – successfully in Britain, unsuccessfully elsewhere.
At length, the impact of repeated wars, coupled with insurrections by colonised peoples, forced the rich nations to leave most of the lands they had seized, formally at least. These territories sought to establish themselves as independent nations. But their independence was never more than partial. Using international debt, structural adjustment, coups, corruption (assisted by offshore tax havens and secrecy regimes), transfer pricing and other clever instruments, the rich nations continued to loot the poor, often through the proxy governments they installed and armed.
Unwittingly at first, then with the full knowledge of the perpetrators, the industrial revolutions released waste products into the Earth’s systems. At first, the most extreme impacts were felt in the rich nations, whose urban air and rivers were poisoned, shortening the lives of the poor. The wealthy removed themselves to places they had not trashed. Later, the rich countries discovered they no longer needed smokestack industries: through finance and subsidiaries, they could harvest the wealth manufactured by dirty business overseas.
Some of the pollutants were both invisible and global. Among them was carbon dioxide, which did not disperse but accumulated in the atmosphere. Partly because most rich nations are temperate, and partly because of extreme poverty in the former colonies caused by centuries of looting, the effects of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases are felt most by those who have benefited least from their production. If the talks in Glasgow are not to be experienced as yet another variety of oppression, climate justice should be at their heart.
The wealthy nations, always keen to position themselves as saviours, have promised to help their former colonies adjust to the chaos they have caused. Since 2009, these rich countries have pledged $100bn (£75bn) a year to poorer ones in the form of climate finance. Even if this money had materialised, it would have been a miserly token. By comparison, since 2015, the G20 nations have spent $3.3tn on subsidising their fossil fuel industries. Needless to say, they have failed to keep their wretched promise.
In the latest year for which we have figures, 2019, they provided $80bn. Of this, just $20bn was earmarked for “adaptation”: helping people adjust to the chaos we have imposed on them. And only about 7% of these stingy alms went to the poorest countries that need the money most.
Instead, the richest nations have poured money into keeping out the people fleeing from climate breakdown and other disasters. Between 2013 and 2018, the UK spent almost twice as much on sealing its borders as it did on climate finance. The US spent 11 times, Australia 13 times, and Canada 15 times more. Collectively, the rich nations are surrounding themselves with a climate wall, to exclude the victims of their own waste products.
But the farce of climate finance doesn’t end there. Most of the money the rich nations claim to be providing takes the form of loans. Oxfam estimates that, as most of it will have to be repaid with interest, the true value of the money provided is around one third of the nominal sum. Highly indebted nations are being encouraged to accumulate more debt to finance their adaptation to the disasters we have caused. It is staggeringly, outrageously unfair.
Never mind aid, never mind loans; what the rich nations owe the poor is reparations. Much of the harm inflicted by climate breakdown makes a mockery of the idea of adaptation: how can people adapt to temperatures higher than the human body can withstand; to repeated, devastating cyclones that trash homes as soon as they are rebuilt; to the drowning of entire archipelagos; to the desiccation of vast tracts of land, making farming impossible? But while the concept of irreparable “loss and damage” was recognised in the Paris agreement, the rich nations insisted that this “does not involve or provide a basis for any liability or compensation”.
By framing the pittance they offer as a gift, rather than as compensation, the states that have done most to cause this catastrophe can position themselves, in true colonial style, as the heroes who will swoop down and rescue the world: this was the thrust of Boris Johnson’s opening speech, invoking James Bond, at Glasgow: “We have the ideas. We have the technology. We have the bankers.”
But the victims of the rich world’s exploitation don’t need James Bond, nor other white saviours. They don’t need Johnson’s posturing. They don’t need his skinflint charity, or the deadly embrace of the bankers who fund his party. They need to be heard. And they need justice.
Monday, 4 October 2021
Wednesday, 25 August 2021
Who’s to blame for the Afghanistan chaos? Remember the war’s cheerleaders
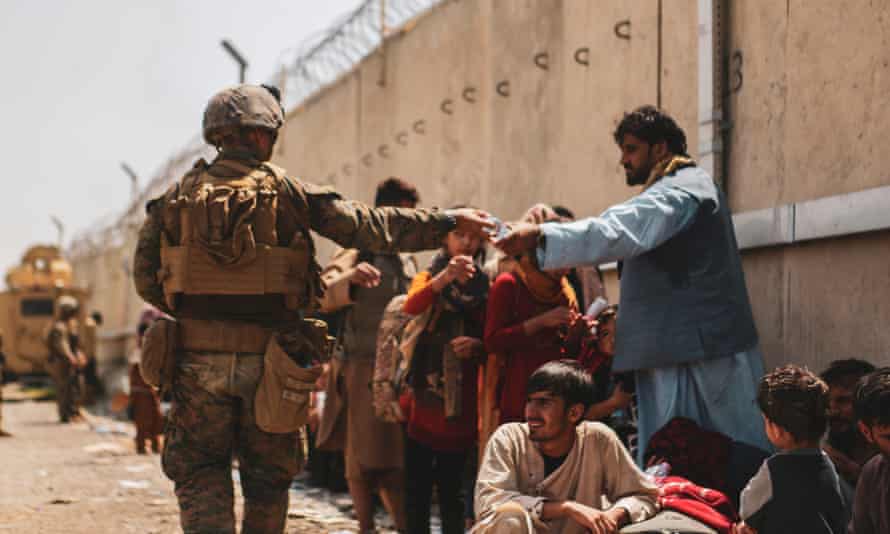 ‘Cheerleading for the war in Afghanistan was almost universal, and dissent was treated as intolerable.’ A US marine with evacuees at Kabul airport. Photograph: U.S. Central Command Public Affairs vis Getty Images
‘Cheerleading for the war in Afghanistan was almost universal, and dissent was treated as intolerable.’ A US marine with evacuees at Kabul airport. Photograph: U.S. Central Command Public Affairs vis Getty ImagesEveryone is to blame for the catastrophe in Afghanistan, except the people who started it. Yes, Joe Biden screwed up by rushing out so chaotically. Yes, Boris Johnson and Dominic Raab failed to make adequate and timely provisions for the evacuation of vulnerable people. But there is a frantic determination in the media to ensure that none of the blame is attached to those who began this open-ended war without realistic aims or an exit plan, then waged it with little concern for the lives and rights of the Afghan people: the then US president, George W Bush, the British prime minister Tony Blair and their entourages.
Indeed, Blair’s self-exoneration and transfer of blame to Biden last weekend was front-page news, while those who opposed his disastrous war 20 years ago remain cancelled across most of the media. Why? Because to acknowledge the mistakes of the men who prosecuted this war would be to expose the media’s role in facilitating it.
Any fair reckoning of what went wrong in Afghanistan, Iraq and the other nations swept up in the “war on terror” should include the disastrous performance of the media. Cheerleading for the war in Afghanistan was almost universal, and dissent was treated as intolerable. After the Northern Alliance stormed into Kabul, torturing and castrating its prisoners, raping women and children, the Telegraph urged us to “just rejoice, rejoice”, while the Sun ran a two-page editorial entitled “Shame of the traitors: wrong, wrong, wrong … the fools who said Allies faced disaster”. In the Guardian, Christopher Hitchens, a convert to US hegemony and war, marked the solemnity of the occasion with the words: “Well, ha ha ha, and yah, boo. It was … obvious that defeat was impossible. The Taliban will soon be history.”
The few journalists and public figures who dissented were added to the Telegraph’s daily list of “Osama bin Laden’s useful idiots”, accused of being “anti-American” and “pro-terrorism”, mocked, vilified and de-platformed almost everywhere. In the Independent, David Aaronovitch claimed that if you opposed the ongoing war, you were “indulging yourself in a cosmic whinge”.
Everyone I know in the US and the UK who was attacked in the media for opposing the war received death threats. Barbara Lee, the only member of Congress who voted against granting the Bush government an open licence to use military force, needed round-the-clock bodyguards. Amid this McCarthyite fervour, peace campaigners such as Women in Black were listed as “potential terrorists” by the FBI. The then US secretary of state, Colin Powell, sought to persuade the emir of Qatar to censor Al Jazeera, one of the few outlets that consistently challenged the rush to war. After he failed, the US bombed Al Jazeera’s office in Kabul.
The broadcast media were almost exclusively reserved for those who supported the adventure. The same thing happened before and during the invasion of Iraq, when the war’s opponents received only 2% of BBC airtime on the subject. Attempts to challenge the lies that justified the invasion – such as Saddam Hussein’s alleged possession of weapons of mass destruction and his supposed refusal to negotiate – were drowned in a surge of patriotic excitement.
So why is so much of the media so bloodthirsty? Why do they love bombs and bullets so much, and diplomacy so little? Why do they take such evident delight in striking a pose atop a heap of bodies, before quietly shuffling away when things go wrong?
An obvious answer is the old adage that “if it bleeds it leads”, so there’s an inbuilt demand for blood. I remember as if it were yesterday the moment I began to hate the industry I work for. In 1987, I was producing a current affairs programme for the BBC World Service. It was a slow news day, and none of the stories gave us a strong lead for the programme. Ten minutes before transmission, the studio door flew open and the editor strode in. He clapped his hands and shouted: “Great! 110 dead in Sri Lanka!” News is spectacle, and nothing delivers spectacle like war.
Another factor in the UK is a continued failure to come to terms with our colonial history. For centuries the interests of the nation have been conflated with the interests of the rich, while the interests of the rich depended to a remarkable degree on colonial loot and the military adventures that supplied it. Supporting overseas wars, however disastrous, became a patriotic duty.
For all the current breastbeating about the catastrophic defeat in Afghanistan, nothing has been learned. The media still regale us with comforting lies about the war and occupation. They airbrush the drone strikes in which civilians were massacred and the corruption permitted and encouraged by the occupying forces. They seek to retrofit justifications to the decision to go to war, chief among them securing the rights of women.
But this issue, crucial as it was and remains, didn’t feature among the original war aims. Nor, for that matter, did overthrowing the Taliban. Bush’s presidency was secured, and his wars promoted, by American ultra-conservative religious fundamentalists who had more in common with the Taliban than with the brave women seeking liberation. In 2001, the newspapers now backcasting themselves as champions of human rights mocked and impeded women at every opportunity. The Sun was running photos of topless teenagers on Page 3; the Daily Mail ruined women’s lives with its Sidebar of Shame; extreme sexism, body shaming and attacks on feminism were endemic.
Those of us who argued against the war possessed no prophetic powers. I asked the following questions in the Guardian not because I had any special information or insight, but because they were bleeding obvious. “At what point do we stop fighting? At what point does withdrawal become either honourable or responsible? Having once engaged its forces, are we then obliged to reduce Afghanistan to a permanent protectorate? Or will we jettison responsibility as soon as military power becomes impossible to sustain?” But even asking such things puts you beyond the pale of acceptable opinion.
You can get away with a lot in the media, but not, in most outlets, with opposing a war waged by your own nation – unless your reasons are solely practical. If your motives are humanitarian, you are marked from that point on as a fanatic. Those who make their arguments with bombs and missiles are “moderates” and “centrists”; those who oppose them with words are “extremists”. The inconvenient fact that the “extremists” were right and the “centrists” were wrong is today being strenuously forgotten.
Tuesday, 1 June 2021
Why every single statue should come down
Having been a black leftwing Guardian columnist for more than two decades, I understood that I would be regarded as fair game for the kind of moral panics that might make headlines in rightwing tabloids. It’s not like I hadn’t given them the raw material. In the course of my career I’d written pieces with headlines such as “Riots are a class act”, “Let’s have an open and honest conversation about white people” and “End all immigration controls”. I might as well have drawn a target on my back. But the only time I was ever caught in the tabloids’ crosshairs was not because of my denunciations of capitalism or racism, but because of a statue – or to be more precise, the absence of one.
The story starts in the mid-19th century, when the designers of Trafalgar Square decided that there would be one huge column for Horatio Nelson and four smaller plinths for statues surrounding it. They managed to put statues on three of the plinths before running out of money, leaving the fourth one bare. A government advisory group, convened in 1999, decided that this fourth plinth should be a site for a rotating exhibition of contemporary sculpture. Responsibility for the site went to the new mayor of London, Ken Livingstone.
Livingstone, whom I did not know, asked me if I would be on the committee, which I joined in 2002. The committee met every six weeks, working out the most engaged, popular way to include the public in the process. I was asked if I would chair the meetings because they wanted someone outside the arts and I agreed. What could possibly go wrong?
Well, the Queen Mother died. That had nothing to do with me. Given that she was 101 her passing was a much anticipated, if very sad, event. Less anticipated was the suggestion by Simon Hughes, a Liberal Democrat MP and potential candidate for the London mayoralty, that the Queen Mother’s likeness be placed on the vacant fourth plinth. Worlds collided.
The next day, the Daily Mail ran a front page headline: “Carve her name in pride - Join our campaign for a statue of the Queen Mother to be erected in Trafalgar Square (whatever the panjandrums of political correctness say!)” Inside, an editorial asked whether our committee “would really respond to the national mood and agree a memorial in Trafalgar Square”.
Never mind that a committee, convened by parliament, had already decided how the plinth should be filled. Never mind that it was supposed to be an equestrian statue and that the Queen Mother will not be remembered for riding horses. Never mind that no one from the royal family or any elected official had approached us.
The day after that came a double-page spread headlined “Are they taking the plinth?”, alongside excerpts of articles I had written several years ago, taken out of context, under the headline “The thoughts of Chairman Gary”. Once again the editorial writers were upon us: “The saga of the empty plinth is another example of the yawning gap between the metropolitan elite hijacking this country and the majority of ordinary people who simply want to reclaim Britain as their own.”
The Mail’s quotes were truer than it dared imagine. It called on people to write in, but precious few did. No one was interested in having the Queen Mother in Trafalgar Square. The campaign died a sad and pathetic death. Luckily for me, it turned out that, if there was a gap between anyone and the ordinary people of the country on this issue, then the Daily Mail was on the wrong side of it.
This, however, was simply the most insistent attempt to find a human occupant for the plinth. Over the years there have been requests to put David Beckham, Bill Morris, Mary Seacole, Benny Hill and Paul Gascoigne up there. None of these figures were particularly known for riding horses either. But with each request I got, I would make the petitioner an offer: if you can name those who occupy the other three plinths, then the fourth is yours. Of course, the plinth was not actually in my gift. But that didn’t matter because I knew I would never have to deliver. I knew the answer because I had made it my business to. The other three were Maj Gen Sir Henry Havelock, who distinguished himself during what is now known as the Indian Rebellion of 1857, when an uprising of thousands of Indians ended in slaughter; Gen Sir Charles Napier, who crushed a rebellion in Ireland and conquered the Sindh province in what is now Pakistan; and King George IV, an alcoholic, debtor and womaniser.
The petitioners generally had no idea who any of them were. And when they finally conceded that point, I would ask them: “So why would you want to put someone else up there so we could forget them? I understand that you want to preserve their memory. But you’ve just shown that this is not a particularly effective way to remember people.”
In Britain, we seem to have a peculiar fixation with statues, as we seek to petrify historical discourse, lather it in cement, hoist it high and insist on it as a permanent statement of fact, culture, truth and tradition that can never be questioned, touched, removed or recast. This statue obsession mistakes adulation for history, history for heritage and heritage for memory. It attempts to detach the past from the present, the present from morality, and morality from responsibility. In short, it attempts to set our understanding of what has happened in stone, beyond interpretation, investigation or critique.
But history is not set in stone. It is a living discipline, subject to excavation, evolution and maturation. Our understanding of the past shifts. Our views on women’s suffrage, sexuality, medicine, education, child-rearing and masculinity are not the same as they were 50 years ago, and will be different again in another 50 years. But while our sense of who we are, what is acceptable and what is possible changes with time, statues don’t. They stand, indifferent to the play of events, impervious to the tides of thought that might wash over them and the winds of change that that swirl around them – or at least they do until we decide to take them down.
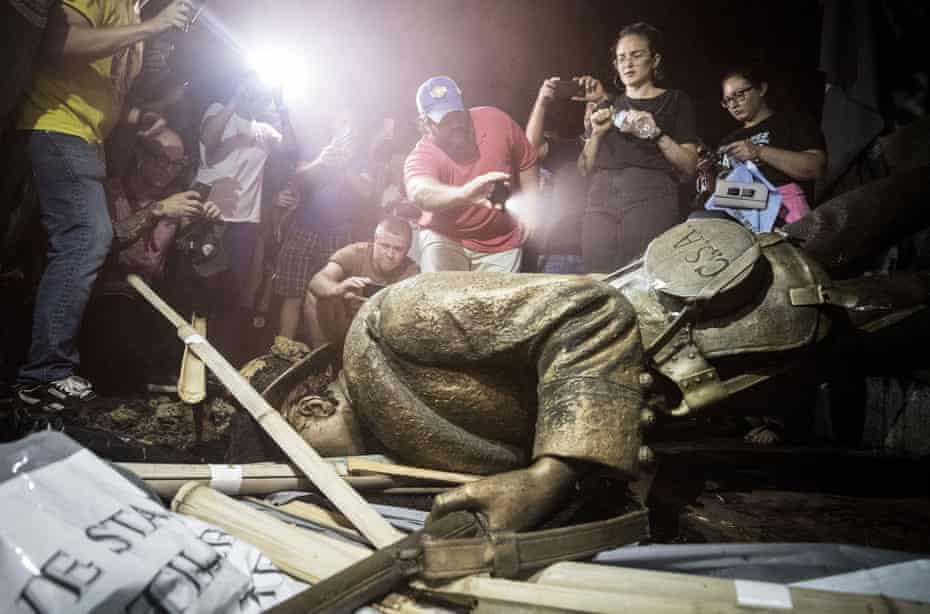
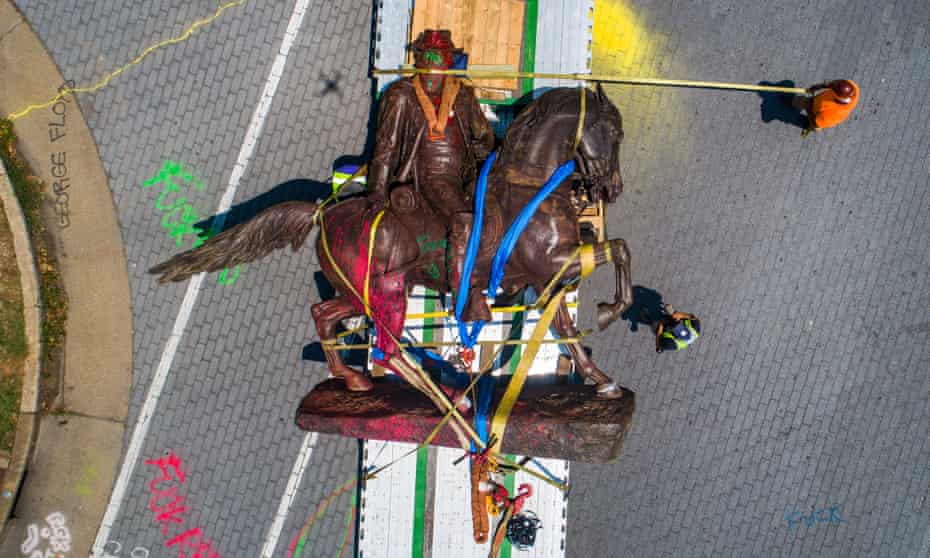 Workers removing a statue of Confederate general JEB Stuart in Richmond, Virginia, July 2020. Photograph: Jim Lo Scalzo/EPA
Workers removing a statue of Confederate general JEB Stuart in Richmond, Virginia, July 2020. Photograph: Jim Lo Scalzo/EPAIn recent months, I have been part of a team at the University of Manchester’s Centre on the Dynamics of Ethnicity (Code) studying the impact of the Black Lives Matter movement on statues and memorials in Britain, the US, South Africa, Martinique and Belgium. Last summer’s uprisings, sparked by the police murder of George Floyd in Minneapolis, spread across the globe. One of the focal points, in many countries, was statues. Belgium, Brazil, Ireland, Portugal, the Netherlands and Greenland were just a few of the places that saw statues challenged. On the French island of Martinique, the statue of Joséphine de Beauharnais, who was born to a wealthy colonial family on the island and later became Napoleon’s first wife and empress, was torn down by a crowd using clubs and ropes. It had already been decapitated 30 years ago.
Across the US, Confederate generals fell, were toppled or voted down. In the small town of Lake Charles, Louisiana, nature presented the local parish police jury with a challenge. In mid-August last year, the jury voted 10-4 to keep a memorial monument to the soldiers who died defending the Confederacy in the civil war. Two weeks later, Hurricane Laura blew it down. Now the jury has to decide not whether to take it down, but whether to put it back up again.
And then, of course, in Britain there was the statue of Edward Colston, a Bristol slave trader, which ended up in the drink. Britain’s major cities, including Manchester, Glasgow, Birmingham and Leeds, are undertaking reviews of their statues.
Many spurious arguments have been made about these actions, and I will come to them in a minute. But the debate around public art and memorialisation, as it pertains to statues, should be engaged not ducked. One response I have heard is that we should even out the score by erecting statues of prominent black, abolitionist, female and other figures that are underrepresented. I understand the motivation. To give a fuller account of the range of experiences, voices, hues and ideologies that have made us what we are. To make sure that public art is rooted in the lives of the whole public, not just a part of it, and that we all might see ourselves in the figures that are represented.
But while I can understand it, I do not agree with it. The problem isn’t that we have too few statues, but too many. I think it is a good thing that so many of these statues of pillagers, plunderers, bigots and thieves have been taken down. I think they are offensive. But I don’t think they should be taken down because they are offensive. I think they should be taken down because I think all statues should be taken down.
Here, to be clear, I am talking about statues of people, not other works of public memorials such as the Vietnam Veterans Memorial in Washington DC, the Holocaust memorial in Berlin or the Famine memorial in Dublin. I think works like these serve the important function of public memorialisation, and many have the added benefit of being beautiful.
The same cannot be said of statues of people. I think they are poor as works of public art and poor as efforts at memorialisation. Put more succinctly, they are lazy and ugly. So yes, take down the slave traders, imperial conquerors, colonial murderers, warmongers and genocidal exploiters. But while you’re at it, take down the freedom fighters, trade unionists, human rights champions and revolutionaries. Yes, remove Columbus, Leopold II, Colston and Rhodes. But take down Mandela, Gandhi, Seacole and Tubman, too.
I don’t think those two groups are moral equals. I place great value on those who fought for equality and inclusion and against bigotry and privilege. But their value to me need not be set in stone and raised on a pedestal. My sense of self-worth is not contingent on seeing those who represent my viewpoints, history and moral compass forced on the broader public. In the words of Nye Bevan, “That is my truth, you tell me yours.” Just be aware that if you tell me your truth is more important than mine, and therefore deserves to be foisted on me in the high street or public park, then I may not be listening for very long.
For me the issue starts with the very purpose of a statue. They are among the most fundamentally conservative – with a small c – expressions of public art possible. They are erected with eternity in mind – a fixed point on the landscape. Never to be moved, removed, adapted or engaged with beyond popular reverence. Whatever values they represent are the preserve of the establishment. To put up a statue you must own the land on which it stands and have the authority and means to do so. As such they represent the value system of the establishment at any given time that is then projected into the forever.
That is unsustainable. It is also arrogant. Societies evolve; norms change; attitudes progress. Take the mining magnate, imperialist and unabashed white supremacist Cecil Rhodes. He donated significant amounts of money with the express desire that he be remembered for 4,000 years. We’re only 120 years in, but his wish may well be granted. The trouble is that his intention was that he would be remembered fondly. And you can’t buy that kind of love, no matter how much bronze you lather it in. So in both South Africa and Britain we have been saddled with these monuments to Rhodes.
The trouble is that they are not his only legacy. The systems of racial subjugation in southern Africa, of which he was a principal architect, are still with us. The income and wealth disparities in that part of the world did not come about by bad luck or hard work. They were created by design. Rhodes’ design. This is the man who said: “The native is to be treated as a child and denied franchise. We must adopt a system of despotism, such as works in India, in our relations with the barbarism of South Africa.” So we should not be surprised if the descendants of those so-called natives, the majority in their own land, do not remember him fondly.
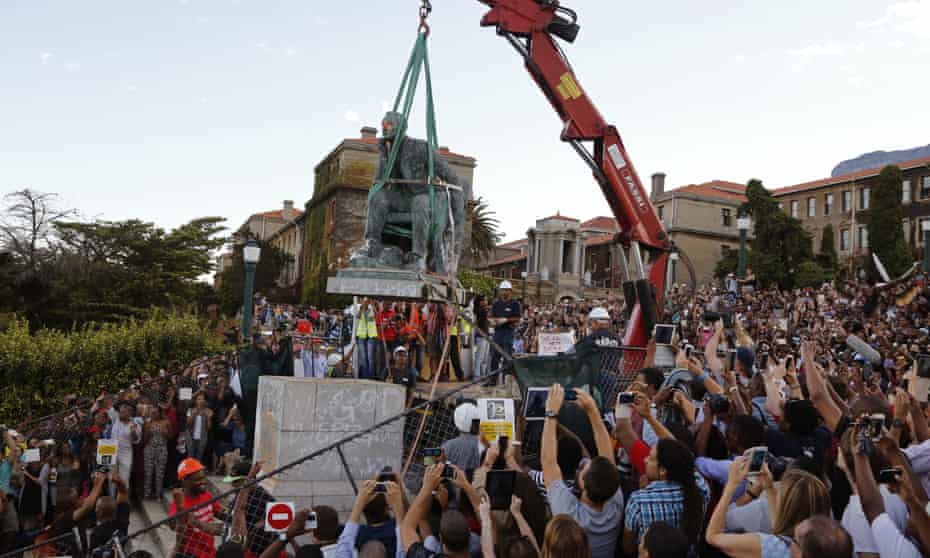
A similar story can be told in the southern states of the US. In his book Standing Soldiers, Kneeling Slaves, the American historian Kirk Savage writes of the 30-year period after the civil war: “Public monuments were meant to yield resolution and consensus, not to prolong conflict … Even now to commemorate is to seek historical closure, to draw together the various strands of meaning in an historical event or personage and condense its significance.”
Clearly these statues – of Confederate soldiers in the South, or of Rhodes in South Africa and Oxford – do not represent a consensus now. If they did, they would not be challenged as they are. Nobody is seriously challenging the statue of the suffragist Millicent Fawcett in Parliament Square, because nobody seriously challenges the notion of women’s suffrage. Nor is anyone seeking historical closure via the removal of a statue. The questions that some of these monuments raise – of racial inequality, white supremacy, imperialism, colonialism and slavery – are still very much with us. There is a reason why these particular statues, and not, say, that of Robert Raikes, who founded Sunday schools, which stands in Victoria Embankment Gardens in London, were targeted during the Black Lives Matter protests.
But these statues never represented a consensus, even when they were erected. Take the statues of Confederate figures in Richmond, Virginia that were the focus of protests last summer. Given that the statues represented men on the losing side of the civil war, they certainly didn’t represent a consensus in the country as a whole. The northern states wouldn’t have appreciated them. But closer to home, they didn’t even represent the general will of Richmond at the time. The substantial African American population of the city would hardly have been pleased to see them up there. And nor were many whites, either. When a labour party took control of Richmond city council in the late 1880s, a coalition of blacks and working-class whites refused to vote for an unveiling parade for the monument because it would “benefit only a certain class of people”.
Calls for the removal of statues have also raised the charge that longstanding works of public art are at the mercy of political whim. “Is nothing sacred?” they cry. “Who next?” they ask, clutching their pearls and pointing to Churchill. But our research showed these statues were not removed as a fad or in a feverish moment of insubordination. People had been calling for them to be removed for half a century. And the issue was never confined to the statue itself. It was always about what the statue represented: the prevailing and persistent issues that remained, and the legacy of whatever the statue was erected to symbolise.
One of the greatest distractions when it comes to removing statues is the argument that to remove a statue is to erase history; that to change something about a statue is to tamper with history. This is such errantarrant nonsense it is difficult to know where to begin, so I guess it would make sense to begin at the beginning.
Statues are not history; they represent historical figures. They may have been set up to mark a person’s historical contribution, but they are not themselves history. If you take down Nelson Mandela’s bust on London’s South Bank, you do not erase the history of the anti-apartheid struggle. Statues are symbols of reverence; they are not symbols of history. They elevate an individual from a historical moment and celebrate them.
Nobody thinks that when Iraqis removed statues of Saddam Hussein from around the country they wanted him to be forgotten. Quite the opposite. They wanted him, and his crimes, to be remembered. They just didn’t want him to be revered. Indeed, if the people removing a statue are trying to erase history, then they are very bad at it. For if the erection of a statue is a fact of history, then removing it is no less so. It can also do far more to raise awareness of history. More people know about Colston and what he did as a result of his statue being taken down than ever did as a result of it being put up. Indeed, the very people campaigning to take down the symbols of colonialism and slavery are the same ones who want more to be taught about colonialism and slavery in schools. The ones who want to keep them up are generally the ones who would prefer we didn’t study what these people actually did.
But to claim that statues represent history does not merely misrepresent the role of statues, it misunderstands history and their place in it. Let’s go back to the Confederate statues for a moment. The American civil war ended in 1865. The South lost. Much of its economy and infrastructure were laid to waste. Almost one in six white Southern men aged 13 to 43 died; even more were wounded; more again were captured.
Southerners had to forget the reality of the civil war before they could celebrate it. They did not want to remember the civil war as an episode that brought devastation and humiliation. Very few statues went up in the decades immediately after the war. According to the Southern Poverty Law Centre, nearly 500 monuments to Confederate white supremacy were erected across the country – many in the North – between 1885 and 1915. More than half were built within one seven-year period, between 1905 and 1912.

The timing was no coincidence. It was long enough since the horrors of the civil war that it could be misremembered as a noble defence of racialised regional culture rather than just slavery. As such, it represented a sanitised, partial and selective version of history, based less in fact than toxic nostalgia and melancholia. It’s not history that these statues’ protectors are defending: it’s mythology.
Colston, an official in the Royal African Company, which reportedly sold as many as 100,000 west Africans into slavery, died in 1721. His statue didn’t go up until 1895, more than 150 years later. This was no coincidence, either. Half of the monuments taken down or seriously challenged recently were put up in the three decades between 1889 and 1919. This was partly an aesthetic trend of the late Victorian era. But it should probably come as little surprise that the statues that anti-racist protesters wanted to be taken down were those erected when Jim Crow segregation was firmly installed in the US, and at the apogee of colonial expansion.
Statues always tell us more about the values of the period when they were put up than about the story of the person depicted. Two years before Martin Luther King’s death, a poll showed that the majority of Americans viewed him unfavourably. Four decades later, when Barack Obama unveiled a memorial to King in Washington DC, 91% of Americans approved. Rather than teaching us about the past, his statue distorts history. As I wrote in my book The Speech: The Story Behind Dr Martin Luther King Jr’s Dream, “White America came to embrace King in the same way that white South Africans came to embrace Nelson Mandela: grudgingly and gratefully, retrospectively, selectively, without grace or guile. Because by the time they realised their hatred of him was spent and futile, he had created a world in which loving him was in their own self-interest. Because, in short, they had no choice.”
One claim for not bringing down certain statues of people who committed egregious acts is that we should not judge people of another time by today’s standards. I call this the “But that was before racism was bad” argument or, as others have termed it, the Jimmy Savile defence.
Firstly, this strikes me as a very good argument for not erecting statues at all, since there is no guarantee that any consensus will persist. Just because there may be a sense of closure now doesn’t mean those issues won’t one day be reopened. But beyond that, by the time many of these statues went up there was already considerable opposition to the deeds that had made these men (and they are nearly all men) rich and famous. In Britain, slavery had been abolished more than 60 years before Colston’s statue went up. The civil war had been over for 30 years before most statues of Confederate generals went up. Cecil Rhodes and King Leopold II of Belgium were both criticised for their vile racist acts and views by their contemporaries. In other words, not only was what they did wrong, but it was widely known to be wrong at the time they did it. By the time they were set in stone there were significant movements, if not legislation, condemning the very things that had made them rich and famous.

A more honest appraisal of why the removal of these particular statues rankles with so many is that they do not actually want to engage with the history they represent. Power, and the wealth that comes with it, has many parents. But the brutality it takes to acquire it is all too often an orphan. According to a YouGov poll last year, only one in 20 Dutch, one in seven French, one in 5 Brits and one in four Belgians and Italians believe their former empire is something to be ashamed of. If these statues are supposed to tell our story, then why, after more than a century, do so few people actually know it?
This brings me to my final point. Statues do not just fail to teach us about the past, or give a misleading idea about particular people or particular historical events – they also skew how we understand history itself. For when you put up a statue to honour a historical moment, you reduce that moment to a single person. Individuals play an important role in history. But they don’t make history by themselves. There are always many other people involved. And so what is known as the Great Man theory of history distorts how, why and by whom history is forged.
Consider the statue of Rosa Parks that stands in the US Capitol. Parks was a great woman, whose refusal to give up her seat for a white woman on a bus in Montgomery, Alabama challenged local segregation laws and sparked the civil rights movement. When Parks died in 2005, her funeral was attended by thousands, and her contribution to the civil rights struggle was eulogised around the world.
But the reality is more complex. Parks was not the first to plead not guilty after resisting Montgomery’s segregation laws on its buses. Before Parks, there was a 15-year-old girl named Claudette Colvin. Colvin was all set to be the icon of the civil rights movement until she fell pregnant. Because she was an unmarried teenager, she was dropped by the conservative elders of the local church, who were key leaders of the movement. When I interviewed Colvin 20 years ago, she was just getting by as a nurses’ aide and living in the Bronx, all but forgotten.
And while what Parks did was a catalyst for resistance, the event that forced the segregationists to climb down wasn’t the work of one individual in a single moment, but the year-long collective efforts of African Americans in Montgomery who boycotted the buses – maids and gardeners who walked miles in sun and rain, despite intimidation, those who carpooled to get people where they needed to go, those who sacrificed their time and effort for the cause. The unknown soldiers of civil rights. These are the people who made it happen. Where is their statue? Where is their place in history? How easily and wilfully the main actors can be relegated to faceless extras.
I once interviewed the Uruguayan writer Eduardo Galeano, who confessed that his greatest fear was “that we are all suffering from amnesia”. Who, I asked, is responsible for this forgetfulness? “It’s not a person,” he explained. “It’s a system of power that is always deciding in the name of humanity who deserves to be remembered and who deserves to be forgotten … We are much more than we are told. We are much more beautiful.”
Statues cast a long shadow over that beauty and shroud the complexity even of the people they honour. Now, I love Rosa Parks. Not least because the story usually told about her is so far from who she was. She was not just a hapless woman who stumbled into history because she was tired and wanted to sit down. That was not the first time she had been thrown off a bus. “I had almost a life history of being rebellious against being mistreated against my colour,” she once said. She was also an activist, a feminist and a devotee of Malcolm X. “I don’t believe in gradualism or that whatever should be done for the better should take for ever to do,” she once said.
Of course I want Parks to be remembered. Of course I want her to take her rightful place in history. All the less reason to diminish that memory by casting her in bronze and erecting her beyond memory.
So let us not burden future generations with the weight of our faulty memory and the lies of our partial mythology. Let us not put up the people we ostensibly cherish so that they can be forgotten and ignored. Let us elevate them, and others – in the curriculum, through scholarships and museums. Let us subject them to the critiques they deserve, which may convert them from inert models of their former selves to the complex, and often flawed, people that they were. Let us fight to embed the values of those we admire in our politics and our culture. Let’s cover their anniversaries in the media and set them in tests. But the last thing we should do is cover their likeness in concrete and set them in stone.
Friday, 2 April 2021
Wednesday, 17 March 2021
Why can't Britain handle the truth about Winston Churchill?

A baleful silence attends one of the most talked-about figures in British history. You may enthuse endlessly about Winston Churchill “single-handedly” defeating Hitler. But mention his views on race or his colonial policies, and you’ll be instantly drowned in ferocious and orchestrated vitriol.
In a sea of fawningly reverential Churchill biographies, hardly any books seriously examine his documented racism. Nothing, it seems, can be allowed to complicate, let alone tarnish, the national myth of a flawless hero: an idol who “saved our civilisation”, as Boris Johnson claims, or “humanity as a whole”, as David Cameron did. Make an uncomfortable observation about his views on white supremacy and the likes of Piers Morgan will ask: “Why do you live in this country?”
Not everyone is content to be told to be quiet because they would be “speaking German” if not for Churchill. Many people want to know more about the historical figures they are required to admire uncritically. The Black Lives Matter protests last June – during which the word “racist” was sprayed in red letters on Churchill’s statue in Parliament Square, were accompanied by demands for more education on race, empire and the figures whose statues dot our landscapes.
Yet providing a fuller picture is made difficult. Scholars who explore less illustrious sides of Churchill are treated dismissively. Take the example of Churchill College, Cambridge, where I am a teaching fellow. In response to calls for fuller information about its founder, the college set up a series of events on Churchill, Empire and Race. I recently chaired the second of these, a panel discussion on “The Racial Consequences of Mr Churchill”.
Even before it took place, the discussion was repeatedly denounced in the tabloids and on social media as “idiotic”, a “character assassination” aimed at “trashing” the great man. Outraged letters to the college said this was academic freedom gone too far, and that the event should be cancelled. The speakers and I, all scholars and people of colour, were subjected to vicious hate mail, racist slurs and threats. We were accused of treason and slander. One correspondent warned that my name was being forwarded to the commanding officer of an RAF base near my home.
The college is now under heavy pressure to stop doing these events. After the recent panel, the rightwing thinktank Policy Exchange, which is influential in government circles – and claims to champion free speech and controversial views on campus – published a “review” of the event. The foreword, written by Churchill’s grandson Nicholas Soames, stated that he hoped the review would “prevent such an intellectually dishonest event from being organised at Churchill College in the future – and, one might hope, elsewhere”.
It’s ironic. We’re told by government and media that “cancel culture” is an imposition of the academic left. Yet here it is in reality, the actual “cancel culture” that prevents a truthful engagement with British history. Churchill was an admired wartime leader who recognised the threat of Hitler in time and played a pivotal role in the allied victory. It should be possible to recognise this without glossing over his less benign side. The scholars at the Cambridge event – Madhusree Mukerjee, Onyeka Nubia and Kehinde Andrews – drew attention to Churchill’s dogged advocacy of British colonial rule; his contributing role in the disastrous 1943 Bengal famine, in which millions of people died unnecessarily; his interest in eugenics; and his views, deeply retrograde even for his time, on race.
Churchill is on record as praising “Aryan stock” and insisting it was right for “a stronger race, a higher-grade race” to take the place of indigenous peoples. He reportedly did not think “black people were as capable or as efficient as white people”. In 1911, Churchill banned interracial boxing matches so white fighters would not be seen losing to black ones. He insisted that Britain and the US shared “Anglo-Saxon superiority”. He described anticolonial campaigners as “savages armed with ideas”.
Even his contemporaries found his views on race shocking. In the context of Churchill’s hard line against providing famine relief to Bengal, the colonial secretary, Leo Amery, remarked: “On the subject of India, Winston is not quite sane … I didn’t see much difference between his outlook and Hitler’s.”
Just because Hitler was a racist does not mean Churchill could not have been one. Britain entered the war, after all, because it faced an existential threat – and not primarily because it disagreed with Nazi ideology. Noting affinities between colonial and Nazi race-thinking, African and Asian leaders queried Churchill’s double standards in firmly rejecting self-determination for colonial subjects who were also fighting Hitler.
It is worth recalling that the uncritical Churchill-worship that is so dominant today was not shared by many British people in 1945, when they voted him out of office before the war was even completely over. Many working-class communities in Britain, from Dundee to south Wales, felt strong animosity towards Churchill for his willingness to mobilise military force during industrial disputes. As recently as 2010, Llanmaes community council opposed the renaming of a military base to Churchill Lines.
Critical assessment is not “character assassination”. Thanks to the groupthink of “the cult of Churchill”, the late prime minister has become a mythological figure rather than a historical one. To play down the implications of Churchill’s views on race – or suggest absurdly, as Policy Exchange does, that his racist words meant “something other than their conventional definition” – speaks to me of a profound lack of honesty and courage.
This failure of courage is tied to a wider aversion to examining the British empire truthfully, perhaps for fear of what it might say about Britain today. A necessary national conversation about Churchill and the empire he was so committed to is one necessary way to break this unacceptable silence.
Saturday, 2 January 2021
The backlash against colonialism holds lessons in guilt and gratitude
Descendants of conquerors and the conquered must move towards a universal account of history writes Mihir Bose in The FT
In the tsunami of words on the poisonous legacy of slavery and empire generated by the death of George Floyd, an African-American who was killed in Minneapolis in May by a white police officer, two stand out: “gratitude” and “guilt”.
Should descendants of those who built empires on the back of exploitation feel guilty for what their ancestors did? Or should the descendants of the colonised feel gratitude that their ancestors were conquered?
My wife is a descendant of the conquerors, having been born into the British Cecil family which has produced prime ministers and great political leaders. I am one of “midnight’s children”, born a few months before India won its freedom from British colonial rule in 1947. While I joke that she is a child of the conquerors and I of the conquered, I do not expect my wife to feel guilty for what her ancestors did. But I do reject the idea that I should be thankful that my ancestors were conquered.
That the conquered should feel gratitude was a view often expressed during the days of the British empire. It was not uncommon for the British to say that the Indians needed to be “civilised”. As Winston Churchill, who was then out of government and campaigning against self-rule for India, put it very bluntly in a speech in 1931, the vast majority of Indians “are primitive people”.
Today, some historians imply I should be grateful for colonial legacies. Niall Ferguson, in his book Empire: How Britain Made the Modern World makes the argument that the empire “enhanced global welfare — in other words was a good thing”. He adds that it brought free markets and the rule of law. Other individuals are still as blunt as Churchill.
While I do not think my ancestors needed to be civilised by Europeans, they had many faults. My family are high-caste Hindus and there is no denying the abominable way these upper echelons of society treated the so-called untouchable castes, now known as Dalits. My abiding childhood memory is of my mother giving the sweeper woman tea and sweets, thinking she was being generous, while telling us that nobody should ever use her cup and plate.
Years ago, I visited Bangladesh, where my family is from. While very hospitable, the Muslims there made it clear they had not forgotten the dreadful way my rich Hindu ancestors had treated theirs. I know I need to acknowledge such historical truths, but I do not see why I should feel personally guilty.
The same applies to my wife. For example, on a family trip (including nephews and nieces) to the National Portrait Gallery before the Covid-19 pandemic, we stopped before a portrait of Arthur Balfour, nephew of three-times prime minister Lord Salisbury and himself a prime minister. The potted history mentioned that, as foreign secretary, he was the author of the 1917 Balfour Declaration in support of “the establishment in Palestine of a national home for the Jewish people”.
I pointed out that, a few months before, he had warned the British cabinet in a memo, that Indians would not be able to manage parliamentary democracy because they were not of the same race as Europeans. Even education would not bridge the racial divide. Balfour and his fellow cabinet ministers, presided over by Lloyd George, did not dispute Lord Curzon’s estimate that it would take Indians 500 years to learn to rule themselves. I said this not to make my wife’s family feel guilty, but to highlight that the history we have been taught is far from the complete picture.
This is what we need to tackle: call it the “Machiavelli problem”. More than 1,500 years before the Renaissance diplomat and philosopher wrote his book on statecraft, The Prince, an Indian called Chanakya wrote a treatise on the same subject called Arthashastra, as a handbook for a great king.
Niccolò Machiavelli may or may not have known about its existence but it cannot be disputed that, while Machiavelli was merely a theoretician, Chanakya helped build one of India’s greatest empires. Indian schoolboys know of both men and the diplomatic enclave in New Delhi is called Chanakyapuri. Yet Chanakya is often described as the Indian Machiavelli and he is hardly known outside India.
The result of imbalances like these is that descendants of the conquered, like me, always carry two bags: one containing the conqueror’s history, the other that of the conquered. Descendants of the conquerors, like my wife, only have to worry about the first bag.
Unless we can equalise these historical weights and start to move towards a truly universal history, the past will continue to divide us and we shall always be wrestling with the problems of guilt and gratitude.
Sunday, 12 July 2020
Thursday, 11 June 2020
Clive of India was a vicious asset-stripper. His statue has no place on Whitehall
When Robert Clive, who established British rule in India, died by his own hand in 1774, he was widely reviled as one of the most hated men in England.
His body was buried in a secret night-time ceremony, in an unmarked grave, without a plaque. Clive left no suicide note, but Samuel Johnson reflected the widespread view as to his motives: Clive “had acquired his fortune by such crimes that his consciousness of them impelled him to cut his own throat”.
Clive’s death followed soon after two whistleblowers had revealed the scale of the devastation and asset-stripping of Bengal under his rule. “We have murdered, deposed, plundered and usurped,” wrote Horace Walpole. “Say what think you of the famine in Bengal, in which three millions perished, being caused by a monopoly of the provisions by the East India Company?” That summer, a satire was published in London lampooning Clive as Lord Vulture, an unstable imperial harpy, “utterly deaf to every sentiment of justice and humanity… whose avarice knows no bounds”.
Clive was hauled before parliament with calls to strip him of both his peerage and his wealth. The select committee found, in addition to lucrative insider dealing, that “presents” worth over £2m had been distributed in Bengal, and recommended that the “very great sums of money … appropriated” by Clive and his henchmen be reimbursed. Despite escaping formal censure, Clive came to be seen as the monstrous embodiment of the East India Company’s violence and corruption.
But just as statues of defeated Confederate generals rose in the southern United States, long after their deaths, as totems to a white supremacy that was felt to be under threat during the civil rights movement, so, in due course, Clive was subject to an equally remarkable metamorphosis: in the early 20th century, as resistance was beginning to threaten the foundations of the Raj, Lord Vulture was miraculously transformed into the heroic Clive of India. Like the erection of the Confederate statues, even at the time it was a deeply controversial matter.
In 1907 the former viceroy, Lord Curzon, recently returned from India, threw his weight behind a campaign to erect a memorial to “the Victor of [the battle of] Plassey”. His successor, Lord Minto, already dealing with the serious unrest caused by Curzon’s partition of Bengal, was horrified at the proposal, and called it “needlessly provocative”. The secretary of state for India, outside whose office the statue was to be raised, wearily agreed with Minto and wrote that he was beginning to wish that Clive had been defeated at Plassey.
Today Clive’s statue stands outside the Foreign Office at the very centre of British government, just behind Downing Street. Yet clearly this is not a man we should be honouring today. If at the time many thought the statue should never have been erected, now, as we stand at this crucial crossroads after the toppling of Edward Colston, the moment has definitely come for it to be sent to a museum. There it can be used to instruct future generations about the darkest chapters of the British past.
It is not just that this statue stands as a daily challenge to every British person whose grandparents came from the former colonies. Perhaps more damagingly still, its presence outside the Foreign Office encourages dangerous neo-imperial fantasies among the descendants of the colonisers.
In Britain, study of the empire is still largely absent from the history curriculum. This still tends to go from the Tudors to the Nazis, Henry to Hitler, with a brief visit to William Wilberforce and Florence Nightingale along the way. We are thus given the impression that the British were always on the side of the angels. We remain almost entirely ignorant about the long history of atrocities and exploitation that accompanied the building of our colonial system. Now, more than ever, we badly need to understand what is common knowledge elsewhere: that for much of history we were an aggressively racist and expansionist force responsible for violence, injustice and war crimes on every continent.
We also need to know how far the British, every bit as much as the Germans, helped codify a system of scientific racism, creating a hierarchy of race that put white Caucasians at the top and blacks, “wandering Jews” and Indian Muslims at the bottom. Yet while the Germans have faced up to the darkest periods of their past, and are taught about it unvarnished in their schools, we have not even made a start to this process. Instead, while we understand that the Belgian and German empires were deeply sinister, the Raj, we like to believe, was like some enormous rose-tinted Merchant Ivory film writ large over the plains of Hindustan, all parasols and Simla tea parties, friendly elephants and handsome, croquet-playing maharajahs.
This has become a real problem. Our vast ignorance of everything that is most uncomfortable about our imperial past is damaging, every day, our relations with the rest of the world. In particular our misplaced nostalgia for our imperial past is encouraging us to overplay our Brexit hand. Contrary to fantasies of Brexiters, our former colonies are not about to warmly embrace us. Nor can we kickstart the empire, as if it were some sort of old motorbike that has been left in a garage for 70 years. The strategy of trying to strike trade deals with Commonwealth countries - dubbed Empire 2.0 by some in the Civil Service – has been a total failure.
Indians, in particular, have bitter memories of British rule. In their eyes we came as looters, and subjected them to centuries of humiliation. The economic figures speak for themselves. In 1600, when the East India Company was founded, Britain was generating 1.8% of the world’s GDP, while India was producing 22.5%. By the peak of the Raj, those figures had more or less been reversed: India was reduced from the world’s leading manufacturing nation to a symbol of famine and deprivation.
Removing the statue of Clive from the back of Downing Street would give us an opportunity finally to begin the long overdue process of education and atonement. In 1947, at the end of the Raj, Indians removed all their imperial statues to suburban parks where explanatory texts gave them proper historical context. We could do the same. Alternately, by placing Clive and others of his ilk in a museum, perhaps one modelled on the brilliantly nuanced and hugely moving National Museum of African American History & Culture in Washington DC, we can finally begin to face up to what we have done and so begin the process of apologising for the many things we need to apologise for. Only then will we properly be able to move on, free from the heavy baggage of our imperial past.
Monday, 28 May 2018
In silencing Euroscepticism, Italy’s president has gifted its far right
Italy should be doing well. Unlike Britain, it exports considerably more to the rest of the world than it imports, while its government spends less (excluding interest payments) than the taxes it receives. And yet Italy is stagnating, its population in a state of revolt following two lost decades.

Italian president names interim prime minister until fresh elections
While it is true that Italy is in serious need of reforms, those who blame the stagnation on domestic inefficiencies and corruption must explain why Italy grew so fast throughout the postwar period until it entered the eurozone. Was its government and polity more efficient and virtuous in the 1970s and 1980s? Hardly.
The singular reason for Italy’s woes is its membership of a terribly designed monetary union, the eurozone, in which the Italian economy cannot breathe and which consecutive German governments refuse to reform.
In 2015 the Greek people elected a progressive, Europeanist government with a mandate to demand a new deal within the eurozone. In the space of six months, under the guidance of the German government, the European Union and its central bank crushed us. A few months later, I was asked by the Italian daily newspaper Corriere della Sera if I thought European democracy was at risk. I answered: “Greece surrendered but it was Europe’s democracy that was mortally wounded. Unless Europeans realise that their economy is run by unelected and unaccountable pseudo-technocrats, committing one gross error after another, our democracy will remain a figment of our collective imagination.”
Since then, the pro-establishment government of Italy’s Democratic party implemented, one after the other, the policies that the unelected bureaucrats of the EU demanded. The result was more stagnation. And so, in March, a national election delivered an absolute parliamentary majority to two anti-establishment parties which, despite their differences, shared doubts about Italy’s eurozone membership and a hostility to migrants. It was the bitter harvest of absent prospects and withering hope.
After a few weeks of the kind of post-election horse-trading common in countries like Italy and Germany, the Five Star Movement and League leaders Luigi Di Maio and Matteo Salvini struck a deal to form a government. Alas, President Sergio Mattarella used the powers bestowed upon him by the Italian constitution to prevent the formation of that government and, instead, handed the mandate to a technocrat, a former IMF employee who stands no chance of a vote of confidence in parliament.
No, Mattarella chose to clash with an absolute majority of lawmakers for another reason: his disapproval of the finance minister designate. Why? Because the said gentleman, while fully qualified for the job, and despite his declaration that he would abide by the EU’s rules, had in the past expressed doubts about the eurozone’s architecture and has favoured a plan of EU exit just in case it was needed. It was as if Mattarella declared that reasonableness from a prospective finance minister constitutes grounds for his or her exclusion from the post.
What is so striking is that there is no thinking economist anywhere in the world who does not share concern about the eurozone’s faulty architecture. No prudent finance minister would neglect to develop a plan for euro exit. Indeed, I have it on good authority that the German finance ministry, the European Central Bank and every major bank and corporation have plans in place for the possible exit from the eurozone of Italy, even of Germany. Is Mattarella telling us that the Italian finance minister is banned from thinking of such a plan?
Beyond his moral failure, the president has made a major tactical blunder
Beyond his moral failure to oppose the League’s industrial-scale misanthropy, the president has made a major tactical blunder: he fell right into Salvini’s trap. The formation of another “technical” government, under a former IMF apparatchik, is a fantastic gift to Salvini’s party.
Salvini is secretly salivating at the thought of another election – one that he will fight not as the misanthropic, divisive populist that he is, but as the defender of democracy against the Deep Establishment. He has already scaled the moral high ground with the stirring words: “Italy is not a colony, we are not slaves of the Germans, the French, the spread or finance.”
If Mattarella takes solace from the fact that previous Italian presidents managed to put in place technical governments that did the establishment’s job (so “successfully” that the country’s political centre imploded), he is very badly mistaken. This time around he, unlike his predecessors, has no parliamentary majority to pass a budget or indeed to lend his chosen government a vote of confidence. Thus, the president is forced to call fresh elections that, courtesy of his moral drift and tactical blunder, will return an even stronger majority for Italy’s xenophobic political forces, possibly in alliance with the enfeebled Forza Italia of Silvio Berlusconi.
Saturday, 11 November 2017
How colonial violence came home: the ugly truth of the first world war
Today on the Western Front,” the German sociologist Max Weber wrote in September 1917, there “stands a dross of African and Asiatic savages and all the world’s rabble of thieves and lumpens.” Weber was referring to the millions of Indian, African, Arab, Chinese and Vietnamese soldiers and labourers, who were then fighting with British and French forces in Europe, as well as in several ancillary theatres of the first world war.
Faced with manpower shortages, British imperialists had recruited up to 1.4 million Indian soldiers. France enlisted nearly 500,000 troops from its colonies in Africa and Indochina. Nearly 400,000 African Americans were also inducted into US forces. The first world war’s truly unknown soldiers are these non-white combatants.
Ho Chi Minh, who spent much of the war in Europe, denounced what he saw as the press-ganging of subordinate peoples. Before the start of the Great War, Ho wrote, they were seen as “nothing but dirty Negroes … good for no more than pulling rickshaws”. But when Europe’s slaughter machines needed “human fodder”, they were called into service. Other anti-imperialists, such as Mohandas Gandhi and WEB Du Bois, vigorously supported the war aims of their white overlords, hoping to secure dignity for their compatriots in the aftermath. But they did not realise what Weber’s remarks revealed: that Europeans had quickly come to fear and hate physical proximity to their non-white subjects – their “new-caught sullen peoples”, as Kipling called colonised Asians and Africans in his 1899 poem The White Man’s Burden.
These colonial subjects remain marginal in popular histories of the war. They also go largely uncommemorated by the hallowed rituals of Remembrance Day. The ceremonial walk to the Cenotaph at Whitehall by all major British dignitaries, the two minutes of silence broken by the Last Post, the laying of poppy wreaths and the singing of the national anthem – all of these uphold the first world war as Europe’s stupendous act of self-harm. For the past century, the war has been remembered as a great rupture in modern western civilisation, an inexplicable catastrophe that highly civilised European powers sleepwalked into after the “long peace” of the 19th century – a catastrophe whose unresolved issues provoked yet another calamitous conflict between liberal democracy and authoritarianism, in which the former finally triumphed, returning Europe to its proper equilibrium.
With more than eight million dead and more than 21 million wounded, the war was the bloodiest in European history until that second conflagration on the continent ended in 1945. War memorials in Europe’s remotest villages, as well as the cemeteries of Verdun, the Marne, Passchendaele, and the Somme enshrine a heartbreakingly extensive experience of bereavement. In many books and films, the prewar years appear as an age of prosperity and contentment in Europe, with the summer of 1913 featuring as the last golden summer.
But today, as racism and xenophobia return to the centre of western politics, it is time to remember that the background to the first world war was decades of racist imperialism whose consequences still endure. It is something that is not remembered much, if at all, on Remembrance Day.
At the time of the first world war, all western powers upheld a racial hierarchy built around a shared project of territorial expansion. In 1917, the US president, Woodrow Wilson, baldly stated his intention, “to keep the white race strong against the yellow” and to preserve “white civilisation and its domination of the planet”. Eugenicist ideas of racial selection were everywhere in the mainstream, and the anxiety expressed in papers like the Daily Mail, which worried about white women coming into contact with “natives who are worse than brutes when their passions are aroused”, was widely shared across the west. Anti-miscegenation laws existed in most US states. In the years leading up to 1914, prohibitions on sexual relations between European women and black men (though not between European men and African women) were enforced across European colonies in Africa. The presence of the “dirty Negroes” in Europe after 1914 seemed to be violating a firm taboo.
 Injured Indian soldiers being cared for by the Red Cross in England in March 1915. Photograph: De Agostini Picture Library/Biblioteca Ambrosiana
Injured Indian soldiers being cared for by the Red Cross in England in March 1915. Photograph: De Agostini Picture Library/Biblioteca Ambrosiana“These savages are a terrible danger,” a joint declaration of the German national assembly warned in 1920, to “German women”. Writing Mein Kampf in the 1920s, Adolf Hitler would describe African soldiers on German soil as a Jewish conspiracy aimed to topple white people “from their cultural and political heights”. The Nazis, who were inspired by American innovations in racial hygiene, would in 1937 forcibly sterilise hundreds of children fathered by African soldiers. Fear and hatred of armed “niggers” (as Weber called them) on German soil was not confined to Germany, or the political right. The pope protested against their presence, and an editorial in the Daily Herald, a British socialist newspaper, in 1920 was titled “Black Scourge in Europe”.
This was the prevailing global racial order, built around an exclusionary notion of whiteness and buttressed by imperialism, pseudo-science and the ideology of social Darwinism. In our own time, the steady erosion of the inherited privileges of race has destabilised western identities and institutions – and it has unveiled racism as an enduringly potent political force, empowering volatile demagogues in the heart of the modern west.
Today, as white supremacists feverishly build transnational alliances, it becomes imperative to ask, as Du Bois did in 1910: “What is whiteness that one should so desire it?” As we remember the first global war, it must be remembered against the background of a project of western global domination – one that was shared by all of the war’s major antagonists. The first world war, in fact, marked the moment when the violent legacies of imperialism in Asia and Africa returned home, exploding into self-destructive carnage in Europe. And it seems ominously significant on this particular Remembrance Day: the potential for large-scale mayhem in the west today is greater than at any other time in its long peace since 1945.
When historians discuss the origins of the Great War, they usually focus on rigid alliances, military timetables, imperialist rivalries, arms races and German militarism. The war, they repeatedly tell us, was the seminal calamity of the 20th century – Europe’s original sin, which enabled even bigger eruptions of savagery such as the second world war and the Holocaust. An extensive literature on the war, literally tens of thousands of books and scholarly articles, largely dwells on the western front and the impact of the mutual butchery on Britain, France, and Germany – and significantly, on the metropolitan cores of these imperial powers rather than their peripheries. In this orthodox narrative, which is punctuated by the Russian Revolution and the Balfour declaration in 1917, the war begins with the “guns of August” in 1914, and exultantly patriotic crowds across Europe send soldiers off to a bloody stalemate in the trenches. Peace arrives with the Armistice of 11 November 1918, only to be tragically compromised by the Treaty of Versailles in 1919, which sets the stage for another world war.
In one predominant but highly ideological version of European history – popularised since the cold war – the world wars, together with fascism and communism, are simply monstrous aberrations in the universal advance of liberal democracy and freedom. In many ways, however, it is the decades after 1945 – when Europe, deprived of its colonies, emerged from the ruins of two cataclysmic wars – that increasingly seem exceptional. Amid a general exhaustion with militant and collectivist ideologies in western Europe, the virtues of democracy – above all, the respect for individual liberties – seemed clear. The practical advantages of a reworked social contract, and a welfare state, were also obvious. But neither these decades of relative stability, nor the collapse of communist regimes in 1989, were a reason to assume that human rights and democracy were rooted in European soil.
Instead of remembering the first world war in a way that flatters our contemporary prejudices, we should recall what Hannah Arendt pointed out in The Origins of Totalitarianism – one of the west’s first major reckonings with Europe’s grievous 20th-century experience of wars, racism and genocide. Arendt observes that it was Europeans who initially reordered “humanity into master and slave races” during their conquest and exploitation of much of Asia, Africa and America. This debasing hierarchy of races was established because the promise of equality and liberty at home required imperial expansion abroad in order to be even partially fulfilled. We tend to forget that imperialism, with its promise of land, food and raw materials, was widely seen in the late 19th century as crucial to national progress and prosperity. Racism was – and is – more than an ugly prejudice, something to be eradicated through legal and social proscription. It involved real attempts to solve, through exclusion and degradation, the problems of establishing political order, and pacifying the disaffected, in societies roiled by rapid social and economic change.
 Senegalese soldiers serving in the French army on the western front in June 1917. Photograph: Galerie Bilderwelt/Getty Images
Senegalese soldiers serving in the French army on the western front in June 1917. Photograph: Galerie Bilderwelt/Getty ImagesIn the early 20th century, the popularity of social Darwinism had created a consensus that nations should be seen similarly to biological organisms, which risked extinction or decay if they failed to expel alien bodies and achieve “living space” for their own citizens. Pseudo-scientific theories of biological difference between races posited a world in which all races were engaged in an international struggle for wealth and power. Whiteness became “the new religion”, as Du Bois witnessed, offering security amid disorienting economic and technological shifts, and a promise of power and authority over a majority of the human population.
The resurgence of these supremacist views today in the west – alongside the far more widespread stigmatisation of entire populations as culturally incompatible with white western peoples – should suggest that the first world war was not, in fact, a profound rupture with Europe’s own history. Rather it was, as Liang Qichao, China’s foremost modern intellectual, was already insisting in 1918, a “mediating passage that connects the past and the future”.
The liturgies of Remembrance Day, and evocations of the beautiful long summer of 1913, deny both the grim reality that preceded the war and the way it has persisted into the 21st century. Our complex task during the war’s centenary is to identify the ways in which that past has infiltrated our present, and how it threatens to shape the future: how the terminal weakening of white civilisation’s domination, and the assertiveness of previously sullen peoples, has released some very old tendencies and traits in the west.
Nearly a century after first world war ended, the experiences and perspectives of its non-European actors and observers remain largely obscure. Most accounts of the war uphold it as an essentially European affair: one in which the continent’s long peace is shattered by four years of carnage, and a long tradition of western rationalism is perverted.
Relatively little is known about how the war accelerated political struggles across Asia and Africa; how Arab and Turkish nationalists, Indian and Vietnamese anti-colonial activists found new opportunities in it; or how, while destroying old empires in Europe, the war turned Japan into a menacing imperialist power in Asia.
A broad account of the war that is attentive to political conflicts outside Europe can clarify the hyper-nationalism today of many Asian and African ruling elites, most conspicuously the Chinese regime, which presents itself as avengers of China’s century-long humiliation by the west.
Recent commemorations have made greater space for the non-European soldiers and battlefields of the first world war: altogether more than four million non-white men were mobilised into European and American armies, and fighting happened in places very remote from Europe – from Siberia and east Asia to the Middle East, sub-Saharan Africa, and even the South Pacific islands. In Mesopotamia, Indian soldiers formed a majority of Allied manpower throughout the war. Neither Britain’s occupation of Mesopotamia nor its successful campaign in Palestine would have occurred without Indian assistance. Sikh soldiers even helped the Japanese to evict Germans from their Chinese colony of Qingdao.
Scholars have started to pay more attention to the nearly 140,000 Chinese and Vietnamese contract labourers hired by the British and French governments to maintain the war’s infrastructure, mostly digging trenches. We know more about how interwar Europe became host to a multitude of anticolonial movements; the east Asian expatriate community in Paris at one point included Zhou Enlai, later the premier of China, as well as Ho Chi Minh. Cruel mistreatment, in the form of segregation and slave labour, was the fate of many of these Asians and Africans in Europe. Deng Xiaoping, who arrived in France just after the war, later recalled “the humiliations” inflicted upon fellow Chinese by “the running dogs of capitalists”.
But in order to grasp the current homecoming of white supremacism in the west, we need an even deeper history – one that shows how whiteness became in the late 19th century the assurance of individual identity and dignity, as well as the basis of military and diplomatic alliances.
Such a history would show that the global racial order in the century preceding 1914 was one in which it was entirely natural for “uncivilised” peoples to be exterminated, terrorised, imprisoned, ostracised or radically re-engineered. Moreover, this entrenched system was not something incidental to the first world war, with no connections to the vicious way it was fought or to the brutalisation that made possible the horrors of the Holocaust. Rather, the extreme, lawless and often gratuitous violence of modern imperialism eventually boomeranged on its originators.
In this new history, Europe’s long peace is revealed as a time of unlimited wars in Asia, Africa and the Americas. These colonies emerge as the crucible where the sinister tactics of Europe’s brutal 20th-century wars – racial extermination, forced population transfers, contempt for civilian lives – were first forged. Contemporary historians of German colonialism (an expanding field of study) try to trace the Holocaust back to the mini-genocides Germans committed in their African colonies in the 1900s, where some key ideologies, such as Lebensraum, were also nurtured. But it is too easy to conclude, especially from an Anglo-American perspective, that Germany broke from the norms of civilisation to set a new standard of barbarity, strong-arming the rest of the world into an age of extremes. For there were deep continuities in the imperialist practices and racial assumptions of European and American powers.
Indeed, the mentalities of the western powers converged to a remarkable degree during the high noon of “whiteness” – what Du Bois, answering his own question about this highly desirable condition, memorably defined as “the ownership of the Earth for ever and ever”. For example, the German colonisation of south-west Africa, which was meant to solve the problem of overpopulation, was often assisted by the British, and all major western powers amicably sliced and shared the Chinese melon in the late 19th century. Any tensions that arose between those dividing the booty of Asia and Africa were defused largely peacefully, if at the expense of Asians and Africans.
 Campaigners calling for the removal of a statue of British imperialist Cecil Rhodes (upper right) at Oriel College in Oxford. Photograph: Martin Godwin for the Guardian
Campaigners calling for the removal of a statue of British imperialist Cecil Rhodes (upper right) at Oriel College in Oxford. Photograph: Martin Godwin for the GuardianThis is because colonies had, by the late 19th century, come to be widely seen as indispensable relief-valves for domestic socio-economic pressures. Cecil Rhodes put the case for them with exemplary clarity in 1895 after an encounter with angry unemployed men in London’s East End. Imperialism, he declared, was a “solution for the social problem, ie in order to save the 40 million inhabitants of the United Kingdom from a bloody civil war, we colonial statesmen must acquire new lands to settle the surplus population, to provide new markets for the goods produced in the factories and mines”. In Rhodes’ view, “if you want to avoid civil war, you must become imperialists”.
Rhodes’ scramble for Africa’s gold fields helped trigger the second Boer war, during which the British, interning Afrikaner women and children, brought the term “concentration camp” into ordinary parlance. By the end of the war in 1902, it had become a “commonplace of history”, JA Hobson wrote, that “governments use national animosities, foreign wars and the glamour of empire-making in order to bemuse the popular mind and divert rising resentment against domestic abuses”.
With imperialism opening up a “panorama of vulgar pride and crude sensationalism”, ruling classes everywhere tried harder to “imperialise the nation”, as Arendt wrote. This project to “organise the nation for the looting of foreign territories and the permanent degradation of alien peoples” was quickly advanced through the newly established tabloid press. The Daily Mail, right from its inception in 1896, stoked vulgar pride in being white, British and superior to the brutish natives – just as it does today.
At the end of the war, Germany was stripped of its colonies and accused by the victorious imperial powers, entirely without irony, of ill-treating its natives in Africa. But such judgments, still made today to distinguish a “benign” British and American imperialism from the German, French, Dutch and Belgian versions, try to suppress the vigorous synergies of racist imperialism. Marlow, the narrator of Joseph Conrad’s Heart of Darkness (1899), is clear-sighted about them: “All Europe contributed to the making of Kurtz,” he says. And to the new-fangled modes of exterminating the brutes, he might have added.
In 1920, a year after condemning Germany for its crimes against Africans, the British devised aerial bombing as routine policy in their new Iraqi possession – the forerunner to today’s decade-long bombing and drone campaigns in west and south Asia. “The Arab and Kurd now know what real bombing means,” a 1924 report by a Royal Air Force officer put it. “They now know that within 45 minutes a full-sized village … can be practically wiped out and a third of its inhabitants killed or injured.” This officer was Arthur “Bomber” Harris, who in the second world war unleashed the firestorms of Hamburg and Dresden, and whose pioneering efforts in Iraq helped German theorising in the 1930s about der totale krieg (the total war).
It is often proposed that Europeans were indifferent to or absent-minded about their remote imperial possessions, and that only a few dyed-in-the-wool imperialists like Rhodes, Kipling and Lord Curzon cared enough about them. This makes racism seem like a minor problem that was aggravated by the arrival of Asian and African immigrants in post-1945 Europe. But the frenzy of jingoism with which Europe plunged into a bloodbath in 1914 speaks of a belligerent culture of imperial domination, a macho language of racial superiority, that had come to bolster national and individual self-esteem.
Italy actually joined Britain and France on the Allied side in 1915 in a fit of popular empire-mania (and promptly plunged into fascism after its imperialist cravings went unslaked). Italian writers and journalists, as well as politicians and businessmen, had lusted after imperial power and glory since the late 19th century. Italy had fervently scrambled for Africa, only to be ignominiously routed by Ethiopia in 1896. (Mussolini would avenge that in 1935 by dousing Ethiopians with poison gas.) In 1911, it saw an opportunity to detach Libya from the Ottoman empire. Coming after previous setbacks, its assault on the country, greenlighted by both Britain and France, was vicious and loudly cheered at home. News of the Italians’ atrocities, which included the first bombing from air in history, radicalised many Muslims across Asia and Africa. But public opinion in Italy remained implacably behind the imperial gamble.
Germany’s own militarism, commonly blamed for causing Europe’s death spiral between 1914 and 1918, seems less extraordinary when we consider that from the 1880s, many Germans in politics, business and academia, and such powerful lobby groups as the Pan-German League (Max Weber was briefly a member), had exhorted their rulers to achieve the imperial status of Britain and France. Furthermore, all Germany’s military engagements from 1871 to 1914 occurred outside Europe. These included punitive expeditions in the African colonies and one ambitious foray in 1900 in China, where Germany joined seven other European powers in a retaliatory expedition against young Chinese who had rebelled against western domination of the Middle Kingdom.
 Troops under German command in Dar es Salaam, Tanzania (then part of German East Africa), circa 1914. Photograph: Hulton Archive/Getty Images
Troops under German command in Dar es Salaam, Tanzania (then part of German East Africa), circa 1914. Photograph: Hulton Archive/Getty ImagesDispatching German troops to Asia, the Kaiser presented their mission as racial vengeance: “Give no pardon and take no prisoners,” he said, urging the soldiers to make sure that “no Chinese will ever again even dare to look askance at a German”. The crushing of the “Yellow Peril” (a phrase coined in the 1890s) was more or less complete by the time the Germans arrived. Nevertheless, between October 1900 and spring 1901 the Germans launched dozens of raids in the Chinese countryside that became notorious for their intense brutality.
One of the volunteers for the disciplinary force was Lt Gen Lothar von Trotha, who had made his reputation in Africa by slaughtering natives and incinerating villages. He called his policy “terrorism”, adding that it “can only help” to subdue the natives. In China, he despoiled Ming graves and presided over a few killings, but his real work lay ahead, in German South-West Africa (contemporary Namibia) where an anti-colonial uprising broke out in January 1904. In October of that year, Von Trotha ordered that members of the Herero community, including women and children, who had already been defeated militarily, were to be shot on sight and those escaping death were to be driven into the Omaheke Desert, where they would be left to die from exposure. An estimated 60,000-70,000 Herero people, out of a total of approximately 80,000, were eventually killed, and many more died in the desert from starvation. A second revolt against German rule in south-west Africa by the Nama people led to the demise, by 1908, of roughly half of their population.
Such proto-genocides became routine during the last years of European peace. Running the Congo Free State as his personal fief from 1885 to 1908, King Leopold II of Belgium reduced the local population by half, sending as many as eight million Africans to an early death. The American conquest of the Philippines between 1898 and 1902, to which Kipling dedicated The White Man’s Burden, took the lives of more than 200,000 civilians. The death toll perhaps seems less startling when one considers that 26 of the 30 US generals in the Philippines had fought in wars of annihilation against Native Americans at home. One of them, Brigadier General Jacob H Smith, explicitly stated in his order to the troops that “I want no prisoners. I wish you to kill and burn. The more you kill and burn the better it will please me”. In a Senate hearing on the atrocities in the Philippines, General Arthur MacArthur (father of Douglas) referred to the “magnificent Aryan peoples” he belonged to and the “unity of the race” he felt compelled to uphold.
The modern history of violence shows that ostensibly staunch foes have never been reluctant to borrow murderous ideas from one another. To take only one instance, the American elite’s ruthlessness with blacks and Native Americans greatly impressed the earliest generation of German liberal imperialists, decades before Hitler also came to admire the US’s unequivocally racist policies of nationality and immigration. The Nazis sought inspiration from Jim Crow legislation in the US south, which makes Charlottesville, Virginia, a fitting recent venue for the unfurling of swastika banners and chants of “blood and soil”.
In light of this shared history of racial violence, it seems odd that we continue to portray the first world war as a battle between democracy and authoritarianism, as a seminal and unexpected calamity. The Indian writer Aurobindo Ghose was one among many anticolonial thinkers who predicted, even before the outbreak of war, that “vaunting, aggressive, dominant Europe” was already under “a sentence of death”, awaiting “annihilation” – much as Liang Qichao could see, in 1918, that the war would prove to be a bridge connecting Europe’s past of imperial violence to its future of merciless fratricide.
These shrewd assessments were not Oriental wisdom or African clairvoyance. Many subordinate peoples simply realised, well before Arendt published The Origins of Totalitarianism in 1951, that peace in the metropolitan west depended too much on outsourcing war to the colonies.
The experience of mass death and destruction, suffered by most Europeans only after 1914, was first widely known in Asia and Africa, where land and resources were forcefully usurped, economic and cultural infrastructure systematically destroyed, and entire populations eliminated with the help of up-to-date bureaucracies and technologies. Europe’s equilibrium was parasitic for too long on disequilibrium elsewhere.
In the end, Asia and Africa could not remain a safely remote venue for Europe’s wars of aggrandisement in the late 19th and 20th century. Populations in Europe eventually suffered the great violence that had long been inflicted on Asians and Africans. As Arendt warned, violence administered for the sake of power “turns into a destructive principle that will not stop until there is nothing left to violate”.
In our own time, nothing better demonstrates this ruinous logic of lawless violence, which corrupts both public and private morality, than the heavily racialised war on terror. It presumes a sub-human enemy who must be “smoked out” at home and abroad – and it has licensed the use of torture and extrajudicial execution, even against western citizens.
But, as Arendt predicted, its failures have only produced an even greater dependence on violence, a proliferation of undeclared wars and new battlefields, a relentless assault on civil rights at home – and an exacerbated psychology of domination, presently manifest in Donald Trump’s threats to trash the nuclear deal with Iran and unleash on North Korea “fire and fury like the world has never seen”.
It was always an illusion to suppose that “civilised” peoples could remain immune, at home, to the destruction of morality and law in their wars against barbarians abroad. But that illusion, long cherished by the self-styled defenders of western civilisation, has now been shattered, with racist movements ascendant in Europe and the US, often applauded by the white supremacist in the White House, who is making sure there is nothing left to violate.
The white nationalists have junked the old rhetoric of liberal internationalism, the preferred language of the western political and media establishment for decades. Instead of claiming to make the world safe for democracy, they nakedly assert the cultural unity of the white race against an existential threat posed by swarthy foreigners, whether these are citizens, immigrants, refugees, asylum-seekers or terrorists.
But the global racial order that for centuries bestowed power, identity, security and status on its beneficiaries has finally begun to break down. Not even war with China, or ethnic cleansing in the west, will restore to whiteness its ownership of the Earth for ever and ever. Regaining imperial power and glory has already proven to be a treacherous escapist fantasy – devastating the Middle East and parts of Asia and Africa while bringing terrorism back to the streets of Europe and America – not to mention ushering Britain towards Brexit.
No rousing quasi-imperialist ventures abroad can mask the chasms of class and education, or divert the masses, at home. Consequently, the social problem appears insoluble; acrimoniously polarised societies seem to verge on the civil war that Rhodes feared; and, as Brexit and Trump show, the capacity for self-harm has grown ominously.
This is also why whiteness, first turned into a religion during the economic and social uncertainty that preceded the violence of 1914, is the world’s most dangerous cult today. Racial supremacy has been historically exercised through colonialism, slavery, segregation, ghettoisation, militarised border controls and mass incarceration. It has now entered its last and most desperate phase with Trump in power.
We can no longer discount the “terrible probability” James Baldwin once described: that the winners of history, “struggling to hold on to what they have stolen from their captives, and unable to look into their mirror, will precipitate a chaos throughout the world which, if it does not bring life on this planet to an end, will bring about a racial war such as the world has never seen”. Sane thinking would require, at the very least, an examination of the history – and stubborn persistence – of racist imperialism: a reckoning that Germany alone among western powers has attempted.
Certainly the risk of not confronting our true history has never been as clear as on this Remembrance Day. If we continue to evade it, historians a century from now may once again wonder why the west sleepwalked, after a long peace, into its biggest calamity yet.
