Don't be fooled by Bush's defection: his cures are another form of denial
The president's avowed conversion on climate change is illusory. He is just drumming up new business for his chums George Monbiot
Tuesday January 30, 2007
The Guardian
George Bush proposes to deal with climate change by means of smoke and mirrors. So what's new? Only that it is no longer just a metaphor. After six years of obfuscation and denial, the US now insists that we find ways to block some of the sunlight reaching the earth. This means launching either mirrors or clouds of small particles into the atmosphere.
The demand appears in a recent US memo to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. It describes "modifying solar radiance" as "important insurance" against the threat of climate change. A more accurate description might be important insurance against the need to cut emissions.
Every scheme that could give us a chance of preventing runaway climate change should be considered on its merits. But the proposals for building a global parasol don't have very many. A group of nuclear weapons scientists at the Lawrence Livermore laboratory in California, apparently bored of experimenting with only one kind of mass death, have proposed launching into the atmosphere a million tonnes of tiny aluminium balloons, filled with hydrogen, every year. One unfortunate side-effect would be to eliminate the ozone layer.
Another proposal, from a scientist at the National Centre for Atmospheric Research, in Boulder, Colorado, suggests spraying billions of tonnes of sea-water into the air. Regrettably, the production of small salt particles, while generating obscuring mists, could cause droughts in the countries downwind. Another scheme would inject sulphate particles into the stratosphere. It is perhaps less dangerous than the others, but still carries a risk of causing changes in rainfall patterns. As for flipping a giant mirror into orbit, the necessary technologies are probably a century away. All these fixes appear more expensive than cutting the amount of energy we consume. None reduces the concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, which threatens to acidify the oceans, with grave consequences for the food chain.
The demand that money and research be diverted into these quixotic solutions is another indication that Bush's avowed conversion to the cause of cutting emissions is illusory. He is simply drumming up new business for his chums. In his state of the union address last week, he spoke of "the serious challenge of global climate change" and announced that he was raising the government's mandatory target for alternative transport fuels fivefold. This is wonderful news for the grain barons of the red states, who will grow the maize and rapeseed that will be turned into biofuel. It's a catastrophe for everyone else.
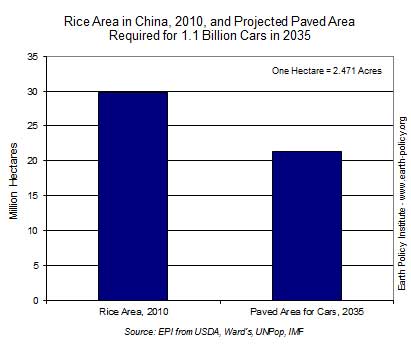
An analysis published last year by the Sarasin Bank found that until a new generation of vegetable fuels, made from straw or wood, is developed, "the present limit for the environmentally and socially responsible use of biofuels [is] roughly 5% of current petrol and diesel consumption in the EU and US". Bush now proposes to raise the proportion to 24% by 2017. Already, though the rich world has replaced just a fraction of 1% of its transport fuels, the UN Food and Agriculture Organisation reports that using crops to feed cars has raised world food prices, with serious consequences for the poor. Biofuels fall into the same category as atmospheric smoke and mirrors - a means of avoiding difficult decisions.
But at least, or so we are told, the argument over whether or not manmade climate change is happening is now over. On Friday the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change publishes the first installment of its vast report, which collates the findings of the world's climate scientists. Though conservative in its assumptions, it shows that if you persist in believing that there is no cause for concern, you must have buried your head till only your toes are showing. If even Bush now grudgingly acknowledges that there's a problem, surely we've seen the last of the cranks and charlatans who had managed to grab so much attention with their claims that global warming wasn't happening?
Some chance. A company called Wag TV is currently completing a 90-minute documentary for Channel 4 called The Great Global Warming Swindle. Manmade climate change, the channel tells us, is "a lie ... the biggest scam of modern times. The truth is that global warming is a multibillion-dollar worldwide industry: created by fanatically anti-industrial environmentalists; supported by scientists peddling scare stories to chase funding; and propped up by complicit politicians and the media ... The fact is that CO2 has no proven link to global temperatures ... solar activity is far more likely to be the culprit."
So it's the same old conspiracy theory we've been hearing from the denial industry for 10 years, and it carries as much scientific weight as the contention that the twin towers were brought down by missiles. The programme's thesis revolves around the deniers' favourite canard: that the "hockey-stick graph" showing rising global temperatures is based on a statistical mistake made in a paper by the scientists Michael Mann, Raymond Bradley and Malcolm Hughes. What it will not be showing is that their results have been repeated several times by other scientists using different statistical methods; that the paper claiming to have exposed the mistake has been comprehensively debunked; and that the lines of evidence used by Mann, Bradley and Hughes are just a few among hundreds demonstrating that 20th-century temperatures were anomalous.
The decision to commission this programme seems even odder when you discover who is making it. In 1997 the director, Martin Durkin, produced a similar series for Channel 4 called Against Nature, which also maintained that global warming was a scam dreamed up by environmentalists. It was riddled with hilarious scientific howlers. More damagingly, the only way in which Durkin could sustain his thesis was to deceive the people he interviewed and edit their answers to change their meaning. After complaints by his interviewees, the Independent Television Commission found that "the views of the four complainants, as made clear to the interviewer, had been distorted by selective editing" and that they had been "misled as to the content and purpose of the programmes when they agreed to take part". Channel 4 was obliged to broadcast one of the most humiliating primetime apologies it has made. Are institutional memories really so short?
So the whole weary business of pointing out that the evidence against man-made climate change is sparse and unable to withstand critical scrutiny, while the evidence in favour is overwhelming and repeatedly confirmed, must begin all over again. How often must scientists remind the media that a handful of cherry-picked studies does not amount to the refutation of an entire discipline?
But with Bush's defection, the band of quacks making these claims is diminishing fast. Now the oil and coal companies that support such people have changed their target. Instead of trying to persuade us that man-made global warming is a myth, they are seeking to divert us into doing everything except the one thing that has to happen: reducing our consumption of fuel. It is another species of denial.
George Bush's purpose - to insulate these companies from the need to cut production - is unchanged. He has simply found a new way of framing the argument.