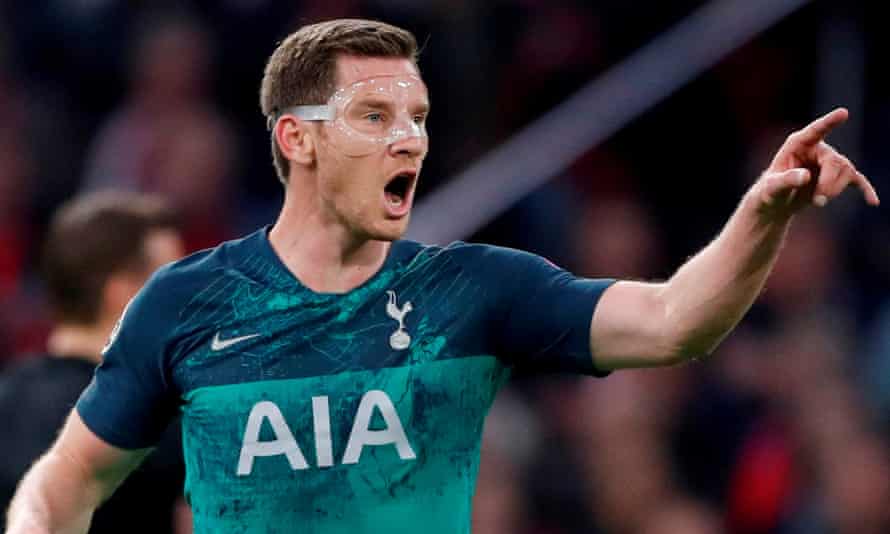
It was around the end of last year that people began to notice Jan Vertonghen was looking decidedly off the pace at Tottenham. He was slow off the mark, slow to the ball, slow to react. Occasionally entire passages of play seemed to pass him by. And so, naturally, as an underperforming player in a popular ball game, it felt only right that he should be subjected to the same pitch of ridicule and abuse as anyone else in his position.
I went back through social media during some of his poorer games last season and pulled out a few of the more representative comments from Spurs fans and others. “Legs gone.” “Sad, but hasn’t got a clue what day it is.” “Get this clown out of my club.” “Finished.” “Past it.” “Utter disgrace.” “Sell.” “Dead wood.” “Stealing a living.” “Happy if I never see him in the shirt again.”

Jan Vertonghen reveals head blow led to nine months of dizziness and headaches
Well, now we know what was really going on. Last week Vertonghen revealed that for most of last season he was enduring the after-effects of a concussion sustained against Ajax the previous April. “I suffered a lot from dizziness and headaches,” said Vertonghen, now at Benfica. “It affected me for eight or nine months. I still had a year left on my contract, and thought I had to play because I had to showcase myself to other clubs.”
On Monday a working group led by the Premier League and featuring the Football Association, the EFL, Professional Footballers’ Association and Women’s Super League sat down to discuss whether there should be restrictions on heading the ball in adult football. It follows a 2019 study by the University of Glasgow that found professional footballers were three times more likely to die of neurodegenerative diseases than the rest of the population.
Meanwhile, the former England hooker Steve Thompson is one of a number of former players launching legal action against World Rugby, the Rugby Football Union and Welsh Rugby Union for an alleged failure to protect them from repeated head traumas.
Thompson is 42 and has been diagnosed with dementia. He no longer remembers winning the World Cup in 2003. “Was it a massive love of my life?” he said of rugby union in an interview with this newspaper two weeks ago. “No, not really. But it was a job.”
A question to consider as you scroll through all this: what does it make you feel? Sadness? Or sadness with a “but”? But: Vertonghen and Thompson knew what they were doing. But: they were handsomely paid for their trouble. But: you can’t ban heading in football, that’s just ridiculous.
But: any of us could get a traumatic brain injury simply by walking down the street and into the path of a falling piano. Life is risky. Sport is dangerous.
Perhaps this is a moment to consider what we owe the people risking their safety for our entertainment
There is a broad school of thought here that at its core, the debate over head injuries in elite sport – one that can easily be extended to other areas of player welfare – is simply a matter of personal choice. If athletes are prepared to embark on a career in professional sport, then as long as they do so fully apprised of the risks and in possession of the latest medical science, who are we to impede them?
Occasionally you will even see this idea expressed in terms of liberation, self-actualisation, even gratification: the notion that danger is not only part of the basic thrill of sport, but also the very point. That the essence of sport is bound up in sacrifice. That on some level we are all animalistically addicted to testing ourselves, pushing ourselves, breaking ourselves. Or at the very least, watching with a beer while others do.

Steve Thompson: 'I can't remember winning the World Cup'
If we can no longer pay teenagers ridiculous money to give themselves brain damage for our gratification, then frankly are we even still free as a species? And ultimately, this is a question that cuts to the very core of what sport means, and who it serves. After all, choices are not made in a vacuum: they are influenced, impelled, incentivised.
Vertonghen played on because he felt his livelihood was on the line. Thompson played on because it was his job to do so. No scientific paper or well‑intentioned press release will ever override the profit motive. And so to focus on personal autonomy is to ignore the extent to which athletes, like all labour, are co-opted into an economy that they did not choose and over which they have little to no influence.
This is, of course, how sporting capitalism works: I get entertained, you get paid, and everything else is window dressing. Sporting capitalism simply buys off your fatigue, your mental health issues, your insecurities, your quality of life, your memory loss, your pain. If you tear a ligament, then it’s financially counterproductive for your club to make you play.
But a concussion? Well, we didn’t see anything, and obviously you can’t, so … how about we keep this one to ourselves? Partly this is a critique of a system that essentially regards the athlete as industrial plant: a part, a tool, a resource from which to extract performance value. But partly, too, this is a process in which we all participate. And for those of us who take pleasure from sport, perhaps this is a moment to consider what we owe the people risking their safety for our entertainment. To remember that welfare does not begin and end with a wage.
To bear in mind, above all, that within every superhuman athlete there is a human who bends and breaks like everyone else.