'People will forgive you for being wrong, but they will never forgive you for being right - especially if events prove you right while proving them wrong.' Thomas Sowell
Search This Blog
Showing posts with label pasmanda. Show all posts
Showing posts with label pasmanda. Show all posts
Wednesday, 3 July 2024
Friday, 23 June 2023
Attacking Modi in US shows IAMC using Indian Muslims as pawns
Narratives propagated by the likes of IAMC often rely on select stories, and it is concerning that the Western media accepts them without delving into the ground realities writes AMANA BEGAM in The Print
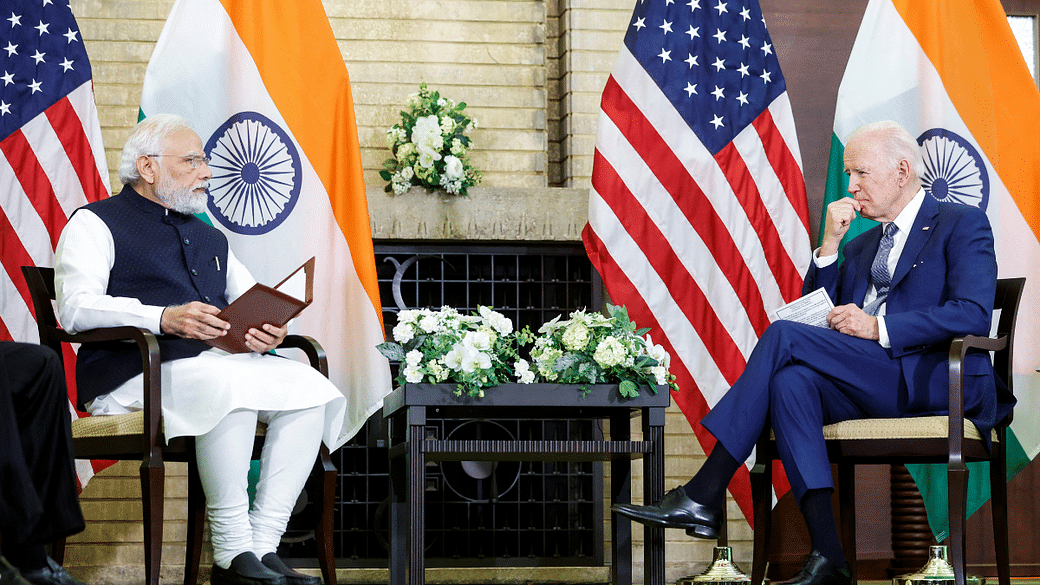
While PM Modi’s state visit to the US is being noticed across world capitals, his opponents in the US are busy doing what they love most — criticising him for his human rights record and accusing his government of suppressing dissent and implementing discriminatory policies against Muslims and other minority groups.
It is not uncommon to witness certain groups initiating campaigns on foreign soil, portraying a narrative of persecution of Indian Muslims. Raising one’s voice for human rights is indeed a crucial and meaningful endeavour. However, challenges arise when human rights issues are exploited as a tool for propaganda, distorting and manipulating the truth about a nation.
Being an Indian Pasmanda Muslim, I frequently witness the propagation of these false narratives against my homeland. Hence it is my sincere duty to raise my voice against them. India, as a nation, not only embraces the homeland of over one billion Hindus but also stands as a diverse abode for 200 million Muslims, 28 million Christians, 21 million Sikhs, 12 million Buddhists, 4.45 million Jains, and countless others.
It is truly disheartening to witness the portrayal of a nation with such a rich and inclusive history as a place where Muslims are purportedly on the verge of facing genocide. Such narratives often rely on select stories, and it is concerning that the Western media often accepts them without delving into the ground realities and comprehending the policies implemented by the Indian State. It is important for such storytellers to seek a more nuanced understanding by examining the comprehensive picture and taking into account the complexities and intricacies.
To begin with, organisations like the Indian American Muslim Council (IAMC) claim to represent the voice of Indian Muslims. However, they frequently disseminate false and misleading information through their tweets. Moreover, there have been instances where their tweets have been provocative and inflammatory. For instance, they tweeted an unsubstantiated claim stating that all victims in the Delhi riots were Muslims. This organisation has scheduled a protest outside the White House, which raises legitimate questions about their true intentions– do they genuinely prioritise the welfare of Indian Muslims or have ulterior motives and agendas at play?
Indian Muslims, stop being a pawn of anti-India forces
It is high time the Western media and geopolitical interest groups refrain from exploiting the term “Indian Muslims” for their own agendas. As for Indian Muslims, it is important that they themselves comprehend how they are being manipulated as pawns on the global stage, working against their own nation’s interests. It is imperative for them to speak out against these false narratives. We lead peaceful lives, enjoy equal rights and opportunities, have the freedom to practise our religion and make choices, and receive our fair share of benefits from welfare schemes run by the government. Our future is intertwined with our nation’s interests, and anything that generates an anti-India narrative ultimately goes against our own well-being.
Organisations like IAMC, which have no genuine connection with Indian Muslims, falsely claim to represent us while using us as pawns to further their own agendas. It is essential for Muslim intellectuals to see through these manipulations. First, the Muslim community was exploited as a mere vote bank. Now there is a risk of them being used as tools to perpetuate an anti-India narrative.
Examine Western media bias
The Western media has consistently portrayed a negative image of India since its Independence. Interestingly, failed states and countries in the middle of civil wars receive minimal attention.
PM Modi, during a national executive meeting of the BJP, clearly expressed a desire for outreach to the Muslim community, acknowledging that many within the community wish to connect with the party. He emphasised the importance of engaging with not only the economically disadvantaged Pasmanda and Bora Muslims but also educated Muslims. Previously, Modi has highlighted the integration of Pasmanda Muslims with the BJP, urging positive programmes to attract their support.
When BJP leaders have made objectionable statements about Muslims, leading to a tense atmosphere in the country, the party has taken disciplinary action against them too. Under the Modi government, a significant number of minority students have received education scholarships, surpassing previous administrations. Muslim women beneficiaries have expressed their gratitude for various government schemes, such as free ration, the abolition of instant divorce practices, free Covid vaccinations, Ujjawala cooking gas connections, and free housing, which have improved their lives. These initiatives demonstrate efforts to ensure the inclusion and well-being of Muslim communities in India.
It is important to address how Western media and human rights organisations often depict Indian Muslims as ostracised and living in a genocidal environment. For instance, the IAMC played a significant role in lobbying against India in 2019, leading to US Commission on International Religious Freedom recommending India to be blacklisted. For four consecutive years, the USCIRF has advised the US administration to designate India as a “Country of Particular Concern.” Ironically, in their assessments, they did not take into account the reality experienced by Indian Muslims. According to Pew Research, 98 per cent of Indian Muslims are free to practise their religion without hindrance. This stark contrast highlights the disconnect between the exaggerated narratives and the ground realities of religious freedom for Indian Muslims.
Don’t weaponise discourse
In their commentary, Western media and human rights organisations fail to carry voices of ordinary Indian Muslims. Providing a comprehensive and accurate understanding, based on data, helps avoid weaponisation of narratives that serve geopolitical interests.
Data often highlights the disparities in perceptions of discrimination among different communities. According to the Pew study, 80 per cent of African-Americans, 46 per cent of Hispanic Americans, and 42 per cent of Asian Americans stated they experience “a lot of discrimination” in the US. In comparison, 24 per cent of Indian Muslims say that there is widespread discrimination against them in India. Furthermore, the majority of Indian Muslims expressed pride in their Indian identity.
These statistics challenge the narrative of widespread persecution of Indian Muslims within their own nation. It raises the question of whether the same level of scrutiny should be applied to the United States, considering the reported discrimination experienced by minority communities there. It prompts us to reflect on whether the labelling of human rights violations should be applied selectively. And what explains the timing of such mongering — just before a State head is about to visit the country.

While PM Modi’s state visit to the US is being noticed across world capitals, his opponents in the US are busy doing what they love most — criticising him for his human rights record and accusing his government of suppressing dissent and implementing discriminatory policies against Muslims and other minority groups.
It is not uncommon to witness certain groups initiating campaigns on foreign soil, portraying a narrative of persecution of Indian Muslims. Raising one’s voice for human rights is indeed a crucial and meaningful endeavour. However, challenges arise when human rights issues are exploited as a tool for propaganda, distorting and manipulating the truth about a nation.
Being an Indian Pasmanda Muslim, I frequently witness the propagation of these false narratives against my homeland. Hence it is my sincere duty to raise my voice against them. India, as a nation, not only embraces the homeland of over one billion Hindus but also stands as a diverse abode for 200 million Muslims, 28 million Christians, 21 million Sikhs, 12 million Buddhists, 4.45 million Jains, and countless others.
It is truly disheartening to witness the portrayal of a nation with such a rich and inclusive history as a place where Muslims are purportedly on the verge of facing genocide. Such narratives often rely on select stories, and it is concerning that the Western media often accepts them without delving into the ground realities and comprehending the policies implemented by the Indian State. It is important for such storytellers to seek a more nuanced understanding by examining the comprehensive picture and taking into account the complexities and intricacies.
To begin with, organisations like the Indian American Muslim Council (IAMC) claim to represent the voice of Indian Muslims. However, they frequently disseminate false and misleading information through their tweets. Moreover, there have been instances where their tweets have been provocative and inflammatory. For instance, they tweeted an unsubstantiated claim stating that all victims in the Delhi riots were Muslims. This organisation has scheduled a protest outside the White House, which raises legitimate questions about their true intentions– do they genuinely prioritise the welfare of Indian Muslims or have ulterior motives and agendas at play?
Indian Muslims, stop being a pawn of anti-India forces
It is high time the Western media and geopolitical interest groups refrain from exploiting the term “Indian Muslims” for their own agendas. As for Indian Muslims, it is important that they themselves comprehend how they are being manipulated as pawns on the global stage, working against their own nation’s interests. It is imperative for them to speak out against these false narratives. We lead peaceful lives, enjoy equal rights and opportunities, have the freedom to practise our religion and make choices, and receive our fair share of benefits from welfare schemes run by the government. Our future is intertwined with our nation’s interests, and anything that generates an anti-India narrative ultimately goes against our own well-being.
Organisations like IAMC, which have no genuine connection with Indian Muslims, falsely claim to represent us while using us as pawns to further their own agendas. It is essential for Muslim intellectuals to see through these manipulations. First, the Muslim community was exploited as a mere vote bank. Now there is a risk of them being used as tools to perpetuate an anti-India narrative.
Examine Western media bias
The Western media has consistently portrayed a negative image of India since its Independence. Interestingly, failed states and countries in the middle of civil wars receive minimal attention.
PM Modi, during a national executive meeting of the BJP, clearly expressed a desire for outreach to the Muslim community, acknowledging that many within the community wish to connect with the party. He emphasised the importance of engaging with not only the economically disadvantaged Pasmanda and Bora Muslims but also educated Muslims. Previously, Modi has highlighted the integration of Pasmanda Muslims with the BJP, urging positive programmes to attract their support.
When BJP leaders have made objectionable statements about Muslims, leading to a tense atmosphere in the country, the party has taken disciplinary action against them too. Under the Modi government, a significant number of minority students have received education scholarships, surpassing previous administrations. Muslim women beneficiaries have expressed their gratitude for various government schemes, such as free ration, the abolition of instant divorce practices, free Covid vaccinations, Ujjawala cooking gas connections, and free housing, which have improved their lives. These initiatives demonstrate efforts to ensure the inclusion and well-being of Muslim communities in India.
It is important to address how Western media and human rights organisations often depict Indian Muslims as ostracised and living in a genocidal environment. For instance, the IAMC played a significant role in lobbying against India in 2019, leading to US Commission on International Religious Freedom recommending India to be blacklisted. For four consecutive years, the USCIRF has advised the US administration to designate India as a “Country of Particular Concern.” Ironically, in their assessments, they did not take into account the reality experienced by Indian Muslims. According to Pew Research, 98 per cent of Indian Muslims are free to practise their religion without hindrance. This stark contrast highlights the disconnect between the exaggerated narratives and the ground realities of religious freedom for Indian Muslims.
Don’t weaponise discourse
In their commentary, Western media and human rights organisations fail to carry voices of ordinary Indian Muslims. Providing a comprehensive and accurate understanding, based on data, helps avoid weaponisation of narratives that serve geopolitical interests.
Data often highlights the disparities in perceptions of discrimination among different communities. According to the Pew study, 80 per cent of African-Americans, 46 per cent of Hispanic Americans, and 42 per cent of Asian Americans stated they experience “a lot of discrimination” in the US. In comparison, 24 per cent of Indian Muslims say that there is widespread discrimination against them in India. Furthermore, the majority of Indian Muslims expressed pride in their Indian identity.
These statistics challenge the narrative of widespread persecution of Indian Muslims within their own nation. It raises the question of whether the same level of scrutiny should be applied to the United States, considering the reported discrimination experienced by minority communities there. It prompts us to reflect on whether the labelling of human rights violations should be applied selectively. And what explains the timing of such mongering — just before a State head is about to visit the country.
Monday, 31 May 2021
Tuesday, 12 November 2013
Pasmanda - Muslims that 'minority politics' left behind
The pasmanda’s quest for empowerment will help democratise Indian Islam and deepen democracy in the country
‘Pasmanda’, a Persian term meaning “those who have fallen behind,” refers to Muslims belonging to the shudra (backward) and ati-shudra (Dalit) castes. It was adopted as an oppositional identity to that of the dominant ashraf Muslims (forward castes) in 1998 by the Pasmanda Muslim Mahaz, a group which mainly worked in Bihar. Since then, however, the pasmanda discourse has found resonance elsewhere too.
The dominant perception is that Islam is an egalitarian religion and that Indian Muslims on the whole, especially in the post-Sachar scenario, are a marginalised community. The pasmanda counter-discourse takes issue with both these formulations. In terms of religious interpretation, Masood Falahi’s work Hindustan mein Zaat Paat aur Musalman (2006) has convincingly demonstrated how the notion of kufu (rules about possible marriage relations between groups) was read through the lens of caste by the ‘manuwadi’ ulema and how a parallel system of “graded inequality” was put into place in Indian Islam.
Caste-based disenfranchisement
As far as the social sphere is concerned, Ali Anwar’s Masawat ki Jung(2000) has documented caste-based disenfranchisement of Dalit and backward caste Muslims at the hands of self-styled ashraf leaders in community organisations like madrasas and personal law boards, representative institutions (Parliament and State Assemblies) and departments, ministries and institutions that claim to work for Muslims (minority affairs, Waqf boards, Urdu academies, AMU, Jamia Millia Islamia, etc). The book also underlines stories of humiliation, disrespect and violence on caste grounds that various pasmanda communities have to undergo on a daily basis, at least in northern parts of India.
Thus, pasmanda commentators contest the two key elements of mainstream ‘Muslim’ or ‘minority’ discourse —Islam as an egalitarian religion and Indian Muslims on the whole as an oppressed community. Islam may be normatively egalitarian but actual-existing Islam in Indian conditions is deeply hierarchical. Similarly, all Muslims are not oppressed, or not to the same degree, at any rate: Muslims are a differentiated community in terms of power, with dominant (ashraf) and subordinated (pasmanda) sections. Consequently, the so-called ‘minority politics’, which has been quite content in raising symbolic and emotional issues so far, is really the politics of dominant caste Muslims that secures their interests at the expense of pasmanda Muslims. Not surprisingly, a recurrent theme in pasmanda narratives is that minority politics has singularly failed to address the bread-and-butter concerns of the pasmanda Muslims, who constitute about 85 per cent of the Indian Muslim population and come primarily from occupational and service biradaris.
The notion of ‘minority’ and ‘majority’ communities in India — read primarily in terms of religious identity — is of modern origin and linked with the emergence and consolidation of a hegemonic secular nation-state project. In this sense, while ‘secular’ nationalism becomes the locus of legitimate power and violence, Hindu and Islamic nationalisms become the sites of illegitimate power. The seemingly epic battles that are constantly fought within this conceptual framework — around communal riots or ‘Hindu’/‘Islamic’ terror more recently in the post-9/11 world — have been instrumental in denying a voice to subordinated caste communities across religions and in securing the interests of ‘secular,’ Hindu or Muslim elites respectively. In this sense, the pasmanda articulation has highlighted the symbiotic nature of majoritarian and minoritarian fundamentalism and has sought to contest the latter from within in order to wage a decisive battle against the former. As Waqar Hawari, a pasmanda activist, says: “While Muslim politicians like Imam Bukhari and Syed Shahabuddin add thejodan [starter yoghurt], it is left to the Hindu fundamentalists to prepare the yoghurt of communalism. Both of them are responsible. We oppose the politics of both Hindu and Muslim fanaticism.”
Faith and ethnicity
The structures of social solidarity that pasmanda activists work with are deeply influenced by the entangled relation between faith and ethnicity. The domains of Hinduism and Islam are quite complex, with multiple resources and potentialities possible: in various ways they exceed the ‘Brahminism’ and ‘Ashrafism’ that have come to over-determine them over time. On the one hand, the pasmanda Muslims share a widespread feeling of ‘Muslimness’ with the upper-caste Muslims, a solidarity which is often parochialised by internal caste and maslak-based (sectarian) contradictions. On the other hand, pasmanda Muslims share an experience of caste-based humiliation and disrespect with subordinated caste Hindus, a solidarity which is equally interrupted by the discourse around religious difference incessantly reproduced by upper caste institutions. Since the express object of the pasmanda movement has been to raise the issue of caste-based exclusion of subordinate caste Muslims, it has stressed on caste-based solidarity across religions. As Ali Anwar, the founder of Pasmanda Muslim Mahaz, says: “There is a bond of pain between pasmanda Muslims and the pasmanda sections of other religions. This bond of pain is the supreme bond … That is why we have to shake hands with the pasmanda sections of other religions.”
This counter-hegemonic solidarity on caste lines is effectively encapsulated in the pasmanda slogan ‘Dalit-Pichda ek saman, Hindu ho ya Musalman’ (All Dalit-backward castes are alike, whether they be Hindu or Muslim). At the same time, birth-based caste distinctions are sought to be transcended from the vantage point of an egalitarian faith: “We are not setting the Dalit/Backward Caste Muslims against the so-called ashraf Muslims. Our movement is not directed against them. Rather, we seek to strengthen and empower our own people, to enable them to speak for themselves and to secure their rights and justice … We welcome well-meaning people of the so-called ashraf background … who are concerned about the plight of our people to join us in our struggle.” It is in the midst of such complex negotiations, the punctuated nature of faith and caste-based solidarities, that the pasmanda emerges as a political factor.
Overall, pasmanda politics has relied on transformative constitutionalism and democratic symbolism to attain its social justice goals — the deepening of existing affirmative action policies, adequate representation of pasmanda Muslims in political parties, state support for cottage and small-scale industries, democratisation of religious institutions and interpretative traditions, etc. Obviously, it confronts all the challenges that any counter-hegemonic identity movement faces in its formative phases: lack of resources and appropriate institutions, cooption of its leaders by state and other dominant ideological apparatuses, lack of relevant movement literature, internal power conflicts, and so on. Also, as Rammanohar Lohia said: “The policy of uplift of downgraded castes and groups is capable of yielding much poison. A first poison may come out of its immediate effects on men’s minds; it may speedily antagonise the Dvija without as speedily influencing the Sudras. With his undoubted alertness to developments and his capacity to mislead, the Dvija may succeed in heaping direct and indirect discredit on the practitioners of this policy long before the Sudra wakes up to it.” These are the challenges that the pasmanda activists face while confronting the ashrafiya-dominated minority politics. However, their struggle for a post-minority politics is on and one hopes it will democratise Indian Islam in the long run by triggering a process of internal reform. The pasmanda critique of the majority-minority or the secular-communal dyad will also contribute to a democratic deepening that will benefit all of India’s subaltern communities in the long run.
Monday, 17 June 2013
Muslims that 'minority politics' left behind
The pasmanda’s quest for empowerment will help democratise Indian Islam and deepen democracy in the country
‘Pasmanda’, a Persian term meaning “those who have fallen behind,” refers to Muslims belonging to the shudra (backward) and ati-shudra (Dalit) castes. It was adopted as an oppositional identity to that of the dominant ashraf Muslims (forward castes) in 1998 by the Pasmanda Muslim Mahaz, a group which mainly worked in Bihar. Since then, however, the pasmanda discourse has found resonance elsewhere too.
The dominant perception is that Islam is an egalitarian religion and that Indian Muslims on the whole, especially in the post-Sachar scenario, are a marginalised community. The pasmanda counter-discourse takes issue with both these formulations. In terms of religious interpretation, Masood Falahi’s work Hindustan mein Zaat Paat aur Musalman (2006) has convincingly demonstrated how the notion of kufu (rules about possible marriage relations between groups) was read through the lens of caste by the ‘manuwadi’ ulema and how a parallel system of “graded inequality” was put into place in Indian Islam.
---------
----------
Caste-based disenfranchisement
As far as the social sphere is concerned, Ali Anwar’s Masawat ki Jung (2000) has documented caste-based disenfranchisement of Dalit and backward caste Muslims at the hands of self-styled ashraf leaders in community organisations like madrasas and personal law boards, representative institutions (Parliament and State Assemblies) and departments, ministries and institutions that claim to work for Muslims (minority affairs, Waqf boards, Urdu academies, AMU, Jamia Millia Islamia, etc). The book also underlines stories of humiliation, disrespect and violence on caste grounds that various pasmanda communities have to undergo on a daily basis, at least in northern parts of India.
Thus, pasmanda commentators contest the two key elements of mainstream ‘Muslim’ or ‘minority’ discourse —Islam as an egalitarian religion and Indian Muslims on the whole as an oppressed community. Islam may be normatively egalitarian but actual-existing Islam in Indian conditions is deeply hierarchical. Similarly, all Muslims are not oppressed, or not to the same degree, at any rate: Muslims are a differentiated community in terms of power, with dominant (ashraf) and subordinated (pasmanda) sections. Consequently, the so-called ‘minority politics’, which has been quite content in raising symbolic and emotional issues so far, is really the politics of dominant caste Muslims that secures their interests at the expense of pasmanda Muslims. Not surprisingly, a recurrent theme in pasmanda narratives is that minority politics has singularly failed to address the bread-and-butter concerns of the pasmanda Muslims, who constitute about 85 per cent of the Indian Muslim population and come primarily from occupational and service biradaris.
The notion of ‘minority’ and ‘majority’ communities in India — read primarily in terms of religious identity — is of modern origin and linked with the emergence and consolidation of a hegemonic secular nation-state project. In this sense, while ‘secular’ nationalism becomes the locus of legitimate power and violence, Hindu and Islamic nationalisms become the sites of illegitimate power. The seemingly epic battles that are constantly fought within this conceptual framework — around communal riots or ‘Hindu’/‘Islamic’ terror more recently in the post-9/11 world — have been instrumental in denying a voice to subordinated caste communities across religions and in securing the interests of ‘secular,’ Hindu or Muslim elites respectively. In this sense, the pasmanda articulation has highlighted the symbiotic nature of majoritarian and minoritarian fundamentalism and has sought to contest the latter from within in order to wage a decisive battle against the former. As Waqar Hawari, a pasmanda activist, says: “While Muslim politicians like Imam Bukhari and Syed Shahabuddin add the jodan [starter yoghurt], it is left to the Hindu fundamentalists to prepare the yoghurt of communalism. Both of them are responsible. We oppose the politics of both Hindu and Muslim fanaticism.”
Faith and ethnicity
The structures of social solidarity that pasmanda activists work with are deeply influenced by the entangled relation between faith and ethnicity. The domains of Hinduism and Islam are quite complex, with multiple resources and potentialities possible: in various ways they exceed the ‘Brahminism’ and ‘Ashrafism’ that have come to over-determine them over time. On the one hand, the pasmanda Muslims share a widespread feeling of ‘Muslimness’ with the upper-caste Muslims, a solidarity which is often parochialised by internal caste and maslak-based (sectarian) contradictions. On the other hand, pasmanda Muslims share an experience of caste-based humiliation and disrespect with subordinated caste Hindus, a solidarity which is equally interrupted by the discourse around religious difference incessantly reproduced by upper caste institutions. Since the express object of the pasmanda movement has been to raise the issue of caste-based exclusion of subordinate caste Muslims, it has stressed on caste-based solidarity across religions. As Ali Anwar, the founder of Pasmanda Muslim Mahaz, says: “There is a bond of pain between pasmanda Muslims and the pasmanda sections of other religions. This bond of pain is the supreme bond … That is why we have to shake hands with the pasmanda sections of other religions.”
This counter-hegemonic solidarity on caste lines is effectively encapsulated in the pasmanda slogan ‘Dalit-Pichda ek saman, Hindu ho ya Musalman’ (All Dalit-backward castes are alike, whether they be Hindu or Muslim). At the same time, birth-based caste distinctions are sought to be transcended from the vantage point of an egalitarian faith: “We are not setting the Dalit/Backward Caste Muslims against the so-called ashraf Muslims. Our movement is not directed against them. Rather, we seek to strengthen and empower our own people, to enable them to speak for themselves and to secure their rights and justice … We welcome well-meaning people of the so-called ashraf background … who are concerned about the plight of our people to join us in our struggle.” It is in the midst of such complex negotiations, the punctuated nature of faith and caste-based solidarities, that the pasmanda emerges as a political factor.
Overall, pasmanda politics has relied on transformative constitutionalism and democratic symbolism to attain its social justice goals — the deepening of existing affirmative action policies, adequate representation of pasmanda Muslims in political parties, state support for cottage and small-scale industries, democratisation of religious institutions and interpretative traditions, etc. Obviously, it confronts all the challenges that any counter-hegemonic identity movement faces in its formative phases: lack of resources and appropriate institutions, cooption of its leaders by state and other dominant ideological apparatuses, lack of relevant movement literature, internal power conflicts, and so on. Also, as Rammanohar Lohia said: “The policy of uplift of downgraded castes and groups is capable of yielding much poison. A first poison may come out of its immediate effects on men’s minds; it may speedily antagonise the Dvija without as speedily influencing the Sudras. With his undoubted alertness to developments and his capacity to mislead, the Dvija may succeed in heaping direct and indirect discredit on the practitioners of this policy long before the Sudra wakes up to it.” These are the challenges that the pasmanda activists face while confronting the ashrafiya-dominated minority politics. However, their struggle for a post-minority politics is on and one hopes it will democratise Indian Islam in the long run by triggering a process of internal reform. The pasmanda critique of the majority-minority or the secular-communal dyad will also contribute to a democratic deepening that will benefit all of India’s subaltern communities in the long run.
(Khalid Anis Ansari is a PhD candidate at the University of Humanistic Studies, Utrecht, The Netherlands. He also works with The Patna Collective, New Delhi, and engages with the pasmanda movement as an interlocutor and knowledge-activist. Email: khalidanisansari@gmail.com)
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)