“Blessed is the nation that doesn’t need heroes" Goethe. “Hero-worship is strongest where there is least regard for human freedom.” Herbert Spencer
Search This Blog
Sunday 31 October 2021
On Stupidity: How do Smart People Outsmart Themselves
What is stupidity? Ever since the mid-20th century, the idea of stupidity, especially in the context of politics, has been studied by various sociologists and psychologists. One of the pioneers in this regard was the German scholar and theologian Dietrich Bonhoeffer.
During the rise of Nazi rule in Germany, Bonhoeffer was baffled by the silence of millions of Germans when the Nazis began to publicly humiliate and brutalise Jewish people. Bonhoeffer condemned this. He asked how could a nation that had produced so many philosophers, scientists and artists, suddenly become so apathetic and even sympathetic towards state violence and oppression.
Unsurprisingly, in 1943, Bonhoeffer was arrested. Two years later, he was executed. While awaiting execution, Bonhoeffer began to put his thoughts on paper. These were posthumously published in the shape of a book, Letters and Papers from Prison. One of the chapters in the book is called, ‘On Stupidity.’ Bonhoeffer wrote: “Every strong upsurge of power in the public sphere, be it political or religious, infects a large part of humankind with stupidity. The power of the one needs the stupidity of the other.”
According to Bonhoeffer, because of the overwhelming impact of a rising power, humans are deprived of their inner independence and they give up establishing an autonomous position towards the emerging circumstances. They become mere tools in the hands of the power, and begin to willingly surrender their capacity for independent thinking. Bonhoeffer wrote that holding a rational debate with such a person is futile, because it feels that one is not dealing with a person, but with slogans and catchwords.
So, to Bonhoeffer, stupidity was not about lack of intelligence, but about a mind that had almost voluntarily closed itself to reason, especially after being impacted and/or swayed by the rise of an assertive external power.
In a 2020 essay for The New Statesman, the British philosopher Sacha Golob writes that being stupid and dumb were not the same thing. For example, intelligence (or lack thereof) can somewhat be measured through IQ tests. But even those who score high in these tests can do ‘stupid’ things or carry certain ‘stupid ideas.’
Golob gave the example of the novelist Arthur Conan Doyle, who created the famous fictional character, Sherlock Holmes. Holmes, a private detective, was an ideal product of the ‘Age of Reason’, imagined by Doyle as a man who shunned emotions and dealt only in reason, logic and the scientific method. Yet, later on in life, Doyle became the antithesis of his character, Holmes. He got into a silly argument with the celebrated illusionist Harry Houdini when the latter rubbished Doyle’s belief that one could communicate with spirits (in a seance).
The question is, how could a man who had created a super-rationalist character such as Sherlock Holmes, begin to believe in seances? In fact, Doyle also began to believe in the existence of fairies. Every time someone would successfully debunk Doyle’s beliefs, Doyle would go to great lengths to provide a counter-argument, but one which was even more absurd.
Golob writes this is what stupidity is. And it can even be found in supposedly very intelligent people too. According to the American psychologist Ray Hyman, “Conan Doyle used his smartness to outsmart himself.” This can also answer why one sometimes comes across highly educated and informed men and women unabashedly spouting conspiracy theories that have either been convincingly debunked, or cannot be proven outside the domain of wishful thinking. By continuing to insist on the validity of such theories, one is simply using his/her smartness to outsmart oneself.
What about the leaders whose rise to power, according to Bonhoeffer, triggers stupidity across a large body of people? Take the example of today’s prominent populists, whose supporters are often referred to as being stupid. But as mentioned earlier, these leaders too are explained in a similar manner.
The truth is, dumbness, if it means a substantial lack of intelligence, is not what explains prominent political leaders. Had they been dumb, they would never be at the top of the heap. But as we have already established, stupidity and dumbness are two very different things; leaders can be stupid.
In this context, Golob explains stupidity as “the lack of conceptual resources.” By this he means that some leaders lack the right conceptual tools for the job. He writes that this can lead to a ‘conceptual failure’, where a leader is unable to fully grasp the concept of (political, economic or social) reality that he/she is operating in. They may excel in what they understand, but enter the domain of stupidity when they don’t. However, it is quite clear by now that today’s populist leaders may have had the intelligence to propel themselves to power, but they really do not have the conceptual tools to remain there.
Take PM Imran Khan. As an opposition leader, he understood well the concept of fiery, emotional rhetoric that can become a venting vessel for many. However, this tool becomes impotent in the conceptual context of actually being in power. Khan lacks the conceptual tools to understand the many economic and political quagmires the country has slid into. The more he fails in this, the more he falls back on concepts that he actually understands: i.e. fiery rhetoric (but one that does not sound very convincing anymore), and issues of morality.
He understands the latter well because, when he was a dashing ‘playboy’ in his pre-political days, he was often attacked for being immoral. He understood what the concept of morality is in Pakistani society. He now uses this as a tool to distract his thinning support from his obvious lack of understanding of what is actually happening around him in terms of the country’s drastic economic meltdown.
So, politically and economically, as things crumble around him, he stubbornly continues to “address issues of social immorality” because, by now, this is the only concept he can grasp. This is another case of political stupidity and conceptual failure, or of smartness outsmarting itself.
Saturday 30 October 2021
What oath do IAS, IPS, IRS officials take when you join the Indian Government?

By the time you are reading this, Aryan Khan would be walking out of jail, if 25 days too late. Everything we know about the case as yet tells us there was nothing to justify his arrest, incarceration and being charged under such a draconian law in any case. His ordeal, however, has given us another ‘star’ of sorts, Sameer Dawood/Dnyandev Wankhede.
What kind of star — good or bad, a wronged hero or a villain who finally got caught out — you can decide. He’s a polarising figure. For some, he’s a reservation fraud who allegedly claimed a place in the quota reserved for Scheduled Castes, hiding the fact that he’s a Muslim. No problem with that, except that caste-based reservation wouldn’t be available to him. For others, he’s a Muslim and a Dalit who’s being victimised by entitled elites only because he dared to go after them.
For some, he’s a bully and probable “blackmailer” who targeted the rich and famous, especially in Bollywood, for fame, and allegedly, ransom. For others, he’s finally the one brave narc who decided to do his job , no matter how powerful his quarry.
We cannot take any side on this, and we aren’t. Because we do not have the facts. Our instinct comes from subjectivity, because that’s how we’d see the facts arrayed before us. We shall get off the kerb on this, and focus on something else. Less tangible, and not polarising. It is called propriety in government service. Especially as applied to the All India and Class I Services.
Let me ask you a trick question. How many IAS officers can you name in the country right now? Not members of your family or pals, but from the headlines, especially the recent ones? Or IPS officers? And finally, that one service we see so little of in our normal lives directly, the Indian Revenue Service, the so-called ‘taxman’ or woman.
So, is there a prominent IRS officer you can name off the bat? I bet it would be Sameer Wankhede. He’s not only the most famous IRS officer in the country today, but in a very long time. It is serendipitous that the two most headlined names from the All India Services at this point, IAS and IPS, have also not necessarily been there for good reasons.
Former Comptroller and Auditor General Vinod Rai gave a grovelling apology to Congress leader Sanjay Nirupam for making false allegations over the 2G case, where he conjured up that notional loss figure of Rs 1.76 lakh crore in 2007.
It was an obvious exaggeration. But such was the mood at that point you couldn’t argue with him without risking being labelled ‘pro-corruption’. Now that story has unravelled. As indeed, unfortunately, India’s telecom sector. The same thing happened soon enough with coal.
The IPS now. The same Mumbai which produced Wankhede, the zonal narcotics chief who now, in his own defence, is citing the testimony of the young man he charged with a crime with a possible 10-year sentence (‘see, even Aryan says he’s made no charge of extortion against me’), has also given us a police commissioner who’s absconding. All of Maharashtra Police cannot find one of its most senior officers, and non-bailable warrants are being posted everywhere.
If IPS, IRS and IAS are the trinity of our vaunted civil services and Param Bir Singh, Sameer Wankhede and Vinod Rai are their representatives in today’s most prominent — and bad — headlines, what does it tell us?
We have chosen that order deliberately. The IPS guy on top because he’s an absconder, ducking multiple criminal charges; the IRS man next because he’s in court seeking protection from arrest and yet to answer a hundred questions on his conduct; and the IAS last, for once, because at least one thing we know about Vinod Rai from reputation and track record is that he is, financially, spotless. Just that it has not achieved the best results for India.
These three stars of today speak poorly for our civil services in their own different ways. It is to fight for these services that lakhs of our brightest young people slog for years at coaching academies, often making their parents sell their land and buffaloes, in that one hope: My kid will crack UPSC. Then, they walk into their respective academies with pride in their hearts, stars in their eyes and mostly — I speak from experience of having spoken at these academies and interacted with young recruits — a great deal of idealism.
No, I am not about to lapse into convenient mass condemnation. Mine has never been the ‘sab chor hain’ view. It is absolutely to the contrary, which I dared to say even during those bizarre Anna Hazare months. The point here is, for every Param Bir Singh, there are thousands of others in his service doing their jobs honestly, sincerely, and at very modest government salaries. As there must be in the IAS or the IRS. It is just that we do not know about them. It is just that people who are becoming famous have done so for all the wrong reasons.
Trick questions again: Name the last six incumbents in the office of the Cabinet Secretary, Director, Intelligence Bureau, and Chairperson of the Central Board of Direct Taxes? If you can name six of each, that is 18 who sat at the apex respectively of these three services, I’d say you are brilliant. But you know the three names in the headlines today, sadly. Or some of you might recall the name of the young IAS officer who was asking his police to ‘smash the farmers’ heads’ in Haryana, or one in Chhattisgarh bashing up a passerby on camera for ‘defying the lockdown’ and other such. Good guys go unnoticed, unsung. Tragic, because they are straight, professional, and play by the book.
Now, what is that book? Bollywood deserves our eternal gratitude because it can always make a telling point for us. People dug out this clip from that otherwise noisy nothing of a movie Tiranga (made in 1993 by Mehul Kumar), where Raj Kumar, in his characteristic, much-mimicked drawl, pulls out two papers from his pocket to confront the corrupt traitor of a police officer. These are for you, he says. One is the order of my release from jail, and the other for your arrest. The clip is being shared with the caption ‘Aryan Khan to Wankhede’.
Go to the movie on YouTube and listen to the context of that clip. What oath do you take when you join this service, don this uniform, he asks, and then reads out the oath every Indian joining all-India services mandatorily takes while joining their service: ‘I do swear/solemnly affirm that I will be faithful and bear true allegiance to…the Constitution of India…that I will carry out the duties of my office loyally, honestly and with impartiality’.
We shall leave it to the conscience of these latest ‘superstars’ of the civil services to ask themselves if they’ve been true to this oath. It’s also a question many others in these services need to ask themselves, as they lock up students for sedition and UAPA only because of the cricket team they support, civil, servant, fame, or for sharing the Greta Thunberg toolkit, or trumping up charges against anybody they think the political bosses want ‘fixed.’ In 2021, they aren’t better than the notorious Soviet hatchet man of seven decades ago, Lavrentiy Beria, who offered to arrest somebody Stalin was irritated with. But under which charge, Stalin apparently asked him. You give me the man, Beria said, and I will give you the charge.
Late S.S. Khera was one of those immortal doyens of the old ICS, and so self-effacing that Google also throws up so little on him. He was India’s first Sikh Cabinet Secretary (1962-64), made his fame using tanks to stop the Partition riots in Meerut in 1947, and totally frowned at civil servants seeking fame. One mention in the newspapers, he said, is one black mark. Two, a bad ACR. And a photo should invite the sack. Now we know the times have changed in six decades. But we also see what this madness for fame and stardom has done to some people from great services. Even as most others work sincerely, in relative anonymity.
Friday 29 October 2021
Thursday 28 October 2021
Information Asymmetry
From the Economist Schools Brief

IN 2007 the state of Washington introduced a new rule aimed at making the labour market fairer: firms were banned from checking job applicants’ credit scores. Campaigners celebrated the new law as a step towards equality—an applicant with a low credit score is much more likely to be poor, black or young. Since then, ten other states have followed suit. But when Robert Clifford and Daniel Shoag, two economists, recently studied the bans, they found that the laws left blacks and the young with fewer jobs, not more.
Before 1970, economists would not have found much in their discipline to help them mull this puzzle. Indeed, they did not think very hard about the role of information at all. In the labour market, for example, the textbooks mostly assumed that employers know the productivity of their workers—or potential workers—and, thanks to competition, pay them for exactly the value of what they produce.
You might think that research upending that conclusion would immediately be celebrated as an important breakthrough. Yet when, in the late 1960s, George Akerlof wrote “The Market for Lemons”, which did just that, and later won its author a Nobel prize, the paper was rejected by three leading journals. At the time, Mr Akerlof was an assistant professor at the University of California, Berkeley; he had only completed his PhD, at MIT, in 1966. Perhaps as a result, the American Economic Review thought his paper’s insights trivial. The Review of Economic Studies agreed. The Journal of Political Economy had almost the opposite concern: it could not stomach the paper’s implications. Mr Akerlof, now an emeritus professor at Berkeley and married to Janet Yellen, the chairman of the Federal Reserve, recalls the editor’s complaint: “If this is correct, economics would be different.”
In a way, the editors were all right. Mr Akerlof’s idea, eventually published in the Quarterly Journal of Economics in 1970, was at once simple and revolutionary. Suppose buyers in the used-car market value good cars—“peaches”—at $1,000, and sellers at slightly less. A malfunctioning used car—a “lemon”—is worth only $500 to buyers (and, again, slightly less to sellers). If buyers can tell lemons and peaches apart, trade in both will flourish. In reality, buyers might struggle to tell the difference: scratches can be touched up, engine problems left undisclosed, even odometers tampered with.
To account for the risk that a car is a lemon, buyers cut their offers. They might be willing to pay, say, $750 for a car they perceive as having an even chance of being a lemon or a peach. But dealers who know for sure they have a peach will reject such an offer. As a result, the buyers face “adverse selection”: the only sellers who will be prepared to accept $750 will be those who know they are offloading a lemon.
Smart buyers can foresee this problem. Knowing they will only ever be sold a lemon, they offer only $500. Sellers of lemons end up with the same price as they would have done were there no ambiguity. But peaches stay in the garage. This is a tragedy: there are buyers who would happily pay the asking-price for a peach, if only they could be sure of the car’s quality. This “information asymmetry” between buyers and sellers kills the market.
Is it really true that you can win a Nobel prize just for observing that some people in markets know more than others? That was the question one journalist asked of Michael Spence, who, along with Mr Akerlof and Joseph Stiglitz, was a joint recipient of the 2001 Nobel award for their work on information asymmetry. His incredulity was understandable. The lemons paper was not even an accurate description of the used-car market: clearly not every used car sold is a dud. And insurers had long recognised that their customers might be the best judges of what risks they faced, and that those keenest to buy insurance were probably the riskiest bets.
Yet the idea was new to mainstream economists, who quickly realised that it made many of their models redundant. Further breakthroughs soon followed, as researchers examined how the asymmetry problem could be solved. Mr Spence’s flagship contribution was a 1973 paper called “Job Market Signalling” that looked at the labour market. Employers may struggle to tell which job candidates are best. Mr Spence showed that top workers might signal their talents to firms by collecting gongs, like college degrees. Crucially, this only works if the signal is credible: if low-productivity workers found it easy to get a degree, then they could masquerade as clever types.
This idea turns conventional wisdom on its head. Education is usually thought to benefit society by making workers more productive. If it is merely a signal of talent, the returns to investment in education flow to the students, who earn a higher wage at the expense of the less able, and perhaps to universities, but not to society at large. One disciple of the idea, Bryan Caplan of George Mason University, is currently penning a book entitled “The Case Against Education”. (Mr Spence himself regrets that others took his theory as a literal description of the world.)
Signalling helps explain what happened when Washington and those other states stopped firms from obtaining job-applicants’ credit scores. Credit history is a credible signal: it is hard to fake, and, presumably, those with good credit scores are more likely to make good employees than those who default on their debts. Messrs Clifford and Shoag found that when firms could no longer access credit scores, they put more weight on other signals, like education and experience. Because these are rarer among disadvantaged groups, it became harder, not easier, for them to convince employers of their worth.
Signalling explains all kinds of behaviour. Firms pay dividends to their shareholders, who must pay income tax on the payouts. Surely it would be better if they retained their earnings, boosting their share prices, and thus delivering their shareholders lightly taxed capital gains? Signalling solves the mystery: paying a dividend is a sign of strength, showing that a firm feels no need to hoard cash. By the same token, why might a restaurant deliberately locate in an area with high rents? It signals to potential customers that it believes its good food will bring it success.
Signalling is not the only way to overcome the lemons problem. In a 1976 paper Mr Stiglitz and Michael Rothschild, another economist, showed how insurers might “screen” their customers. The essence of screening is to offer deals which would only ever attract one type of punter.
Suppose a car insurer faces two different types of customer, high-risk and low-risk. They cannot tell these groups apart; only the customer knows whether he is a safe driver. Messrs Rothschild and Stiglitz showed that, in a competitive market, insurers cannot profitably offer the same deal to both groups. If they did, the premiums of safe drivers would subsidise payouts to reckless ones. A rival could offer a deal with slightly lower premiums, and slightly less coverage, which would peel away only safe drivers because risky ones prefer to stay fully insured. The firm, left only with bad risks, would make a loss. (Some worried a related problem would afflict Obamacare, which forbids American health insurers from discriminating against customers who are already unwell: if the resulting high premiums were to deter healthy, young customers from signing up, firms might have to raise premiums further, driving more healthy customers away in a so-called “death spiral”.)
The car insurer must offer two deals, making sure that each attracts only the customers it is designed for. The trick is to offer one pricey full-insurance deal, and an alternative cheap option with a sizeable deductible. Risky drivers will balk at the deductible, knowing that there is a good chance they will end up paying it when they claim. They will fork out for expensive coverage instead. Safe drivers will tolerate the high deductible and pay a lower price for what coverage they do get.
This is not a particularly happy resolution of the problem. Good drivers are stuck with high deductibles—just as in Spence’s model of education, highly productive workers must fork out for an education in order to prove their worth. Yet screening is in play almost every time a firm offers its customers a menu of options.
Airlines, for instance, want to milk rich customers with higher prices, without driving away poorer ones. If they knew the depth of each customer’s pockets in advance, they could offer only first-class tickets to the wealthy, and better-value tickets to everyone else. But because they must offer everyone the same options, they must nudge those who can afford it towards the pricier ticket. That means deliberately making the standard cabin uncomfortable, to ensure that the only people who slum it are those with slimmer wallets.
Hazard undercuts Eden
Adverse selection has a cousin. Insurers have long known that people who buy insurance are more likely to take risks. Someone with home insurance will check their smoke alarms less often; health insurance encourages unhealthy eating and drinking. Economists first cottoned on to this phenomenon of “moral hazard” when Kenneth Arrow wrote about it in 1963.
Moral hazard occurs when incentives go haywire. The old economics, noted Mr Stiglitz in his Nobel-prize lecture, paid considerable lip-service to incentives, but had remarkably little to say about them. In a completely transparent world, you need not worry about incentivising someone, because you can use a contract to specify their behaviour precisely. It is when information is asymmetric and you cannot observe what they are doing (is your tradesman using cheap parts? Is your employee slacking?) that you must worry about ensuring that interests are aligned.
Such scenarios pose what are known as “principal-agent” problems. How can a principal (like a manager) get an agent (like an employee) to behave how he wants, when he cannot monitor them all the time? The simplest way to make sure that an employee works hard is to give him some or all of the profit. Hairdressers, for instance, will often rent a spot in a salon and keep their takings for themselves.
But hard work does not always guarantee success: a star analyst at a consulting firm, for example, might do stellar work pitching for a project that nonetheless goes to a rival. So, another option is to pay “efficiency wages”. Mr Stiglitz and Carl Shapiro, another economist, showed that firms might pay premium wages to make employees value their jobs more highly. This, in turn, would make them less likely to shirk their responsibilities, because they would lose more if they were caught and got fired. That insight helps to explain a fundamental puzzle in economics: when workers are unemployed but want jobs, why don’t wages fall until someone is willing to hire them? An answer is that above-market wages act as a carrot, the resulting unemployment, a stick.
And this reveals an even deeper point. Before Mr Akerlof and the other pioneers of information economics came along, the discipline assumed that in competitive markets, prices reflect marginal costs: charge above cost, and a competitor will undercut you. But in a world of information asymmetry, “good behaviour is driven by earning a surplus over what one could get elsewhere,” according to Mr Stiglitz. The wage must be higher than what a worker can get in another job, for them to want to avoid the sack; and firms must find it painful to lose customers when their product is shoddy, if they are to invest in quality. In markets with imperfect information, price cannot equal marginal cost.
The concept of information asymmetry, then, truly changed the discipline. Nearly 50 years after the lemons paper was rejected three times, its insights remain of crucial relevance to economists, and to economic policy. Just ask any young, black Washingtonian with a good credit score who wants to find a job.
If markets are so good at directing resources, why do companies exist?
The Economist Schools Brief
ONE morning, an economist went to buy a shirt. The one he chose was a marvel of global production. It was made in Malaysia using German machines. The cloth was woven from Indian cotton grown from seeds developed in America. The collar lining came from Brazil; the artificial fibre from Portugal. Millions of shirts of every size and colour are sold every day, writes Paul Seabright, the shirt-buying economist, in his 2004 book, “The Company of Strangers”. No authority is in charge. The firms that make up the many links in the chain that supplied his shirt had merely obeyed market prices.
Throwing light on the magic of market co-ordination was a mainstay of the “classical” economics of the late-18th and 19th centuries. Then, in 1937, a paper published by Ronald Coase, a British economist, pointed out a glaring omission. The standard model of economics did not fit with what goes on within companies. When an employee switches from one division to another, for instance, he does not do so in response to higher wages, but because he is ordered to. The question posed by Coase was profound, if awkward for economics: why are some activities directed by market forces and others by firms?
His answer was that firms are a response to the high cost of using markets. It is often cheaper to direct tasks by fiat than to negotiate and enforce separate contracts for every transaction. Such “exchange costs” are low in markets for standardised goods, wrote Coase. A well-defined task can easily be put out to the market, where a contractor is paid a fixed sum for doing it. The firm comes into its own when simple contracts of this kind will not suffice. Instead, an employee agrees to follow varied and changing instructions, up to agreed limits, for a fixed salary.
Coase had first set out his theory while working as a lecturer in Dundee, in 1932, having spent the prior academic year in America, visiting factories and businesses. “The nature of the firm”, his paper, did not appear for another five years, in part because he was reluctant to rush into print. Though widely cited today, it went largely unread at first. But a second paper, “The problem of social cost”, published in 1960, by which time he had moved to America, brought him to prominence. It argued that private bargaining could resolve social problems, such as pollution, as long as property rights are well defined and transaction costs are low (they rarely are). He had been asked to expound his new theory earlier that year to a sceptical audience of University of Chicago economists. By the end of the evening, he had won everyone around. Coase was invited to join the university’s faculty in 1964; and there he remained until his death in 2013 at the age of 102.
In 1991 Coase was awarded the Nobel prize for economics, largely on the strength of these two papers. But as late as 1972, he lamented that “The nature of the firm” had been “much cited and little used”. In a strange way, Coase himself was partly to blame. The idea of transaction costs was such a good catch-all explanation for tricky subjects that it was used to close down further inquiry. In fact, Coase’s paper raised as many difficult questions as it answered. If firms exist to reduce transaction costs, why have market transactions at all? Why not further extend the firm’s boundaries? In short, what decides how the economy as a whole is organised?
Almost as soon as Coase had wished for it, a body of more rigorous research on such questions began to flourish. Central to it was the idea that it is difficult to specify all that is required of a business relationship, so some contracts are necessarily “incomplete”. Important figures in this field include Oliver Williamson, winner of the Nobel prize in economics in 2009, and Oliver Hart and Bengt Holmstrom, who shared the prize in 2016. These and other Coase apostles drew on the work of legal theorists in distinguishing between spot transactions and business relations that require longer-term or flexible contracts.
Spot markets cover most transactions. Once money is exchanged for goods, the deal is completed. The transaction is simple: one party wants, another supplies. There is little scope for dispute, so a written contract can be dispensed with. If one party is unhappy, he will take his business elsewhere next time. Spot markets are thus largely self-policing. They are well suited to simple, low-value transactions, such as buying a newspaper or taking a taxi.
Things become trickier when the parties are locked into a deal that is costly to get out of. Take a property lease, for instance. A business that is evicted from its premises might not quickly find a building with similar features. Equally, if a tenant suddenly quit, the landlord might not find a replacement straight away. Each could threaten the other in a bid for a better rent. The answer is a long-term contract that specifies the rent, the tenure and use of the property. Both parties benefit.
But for many business arrangements, it is difficult to set down all that is required of each party in all circumstances. In such cases, formal contracts are by necessity “incomplete” and sustained largely by trust. An employment contract is of this type. It has a few formal terms: job title, work hours, initial pay and so on, but many of the most important duties and obligations are not written down. It is thus like a “mini-society with a vast array of norms beyond those centred on the exchange and its immediate processes”, wrote Mr Williamson. Such a contract stays in force mostly because its breakdown would hurt both parties. And because market forces are softened in such a contract, it calls for an alternative form of governance: the firm.
One of the first papers to elucidate these ideas was published in 1972 by Armen Alchian and Harold Demsetz. They defined the firm as the central contractor in a team-production process. When output is the result of a team effort, it is hard to put the necessary tasks out to the market. That is because it is tricky to measure the contribution of each member to the finished work and to then allocate their rewards accordingly. So the firm is needed to act as both co-ordinator and monitor of a team.
Chain tale
If a team of workers requires a firm as monitor, might that also be true for teams of suppliers? In some cases, firms are indeed vertically integrated, meaning that suppliers of inputs and producers of final goods are under the same ownership. But in other cases, suppliers and their customers are separate entities. When is one set-up right and not the other?
A paper published in 1986 by Sanford Grossman and Mr Hart sharpened the thinking on this. They distinguished between two types of rights over a firm’s assets (its plant, machinery, brands, client lists and so on): specific rights, which can be contracted out, and residual rights, which come with ownership. Where it becomes costly for a company to specify all that it wants from a supplier, it might make sense to acquire it in order to claim the residual rights (and the profits) from ownership. But, as Messrs Grossman and Hart noted, something is also lost through the merger. The supplier’s incentive to innovate and to control costs vanishes, because he no longer owns the residual rights.
To illustrate this kind of relationship, they used the example of an insurance firm that pays a commission to an agent for selling policies. To encourage the agent to find high-quality clients, which are more likely to renew a policy, the firm defers some portion of the agent’s pay and ties it to the rate of policy renewals. The agent is thus induced to work hard to find good clients. But there is a drawback. The insurance firm now has an incentive of its own to shirk. While the agent is busting a gut to find the right sort of customers, the firm can take advantage by, say, cutting its spending on advertising its policies, raising their price or lowering their quality.
There is no set-up in which the incentives of firm and agent can be perfectly aligned. But Messrs Grossman and Hart identified a next-best solution: the party that brings the most to any venture in terms of “non-contractible” effort should own the key assets, which in this case is the client list. So the agent ought to own the list wherever policy renewals are sensitive to sales effort, as in the case of car insurance, for which people tend to shop around more. The agent would keep the residual rights and be rewarded for the effort to find the right sort of client. If the insurance firm shirks, the agent can simply sell the policies of a rival firm to his clients. But in cases where the firm brings more to the party than the sales agent—for example, when clients are “stickier” and the first sale is crucial, as with life insurance—a merger would make more sense.
This framework helps to address one of the questions raised by Coase’s original paper: when should a firm “make” and when should it “buy”? It can be applied to vertical business ties of all kinds. For instance, franchises have to abide by a few rules that can be set down in a contract, but get to keep the residual profits in exchange for a royalty fee paid to the parent firm. That is because the important efforts that the parent requires of a franchisee are not easy to put in a contract or to enforce.
The management of ties between a firm and its “stakeholders” (its customers, suppliers, employees and investors) is another variation on this theme. A firm often wants to put restraints on the parties it does business with. Luxury-goods firms or makers of fancy sound equipment may ban retailers from discounting their goods as a way to spur them to compete with rivals on the quality of their shops, service and advice.
Inside the cubicle
If one of the challenges set by Coase was to explain where the boundary between firms and markets lies, another was for economic analysis not to cease once it reached the factory gate or office lobby. A key issue is how agreements are structured. Why, for instance, do employment contracts have so few formal obligations? One insight from the literature is that a tightly specified contract can have perverse outcomes. If teachers are paid according to test results, they will “teach to the test” and pay less regard to other tasks, such as inspiring pupils to think independently. If chief executives are paid to boost the firm’s short-term share price, they will cut investment projects that may benefit shareholders in the long run.
Mr Holmstrom and Paul Milgrom established that where important tasks are hard to monitor, and where a balance of activities is needed, then a contract should shun strong incentives tied to any one task. The best approach is to pay a fixed salary and to leave the balance of tasks unspecified. A related idea developed by Mr Hart and John Moore is of a job contract as a “reference point” rather than as a detailed map. Another insight is that deferred forms of pay, such as company pension schemes and promotions based on seniority, help cement long-term ties with employees and reward them for investing in skills specific to the relationship.
Coase noted in 1937 that the degree to which the mechanism of price is superseded by the firm varies with the circumstances. Eighty years on, the boundary between the two might appear to be dissolving altogether. The share of self-employed contractors in the labour force has risen. The “gig economy” exemplified by Uber drivers is mushrooming.
Yet firms are unlikely to wither away. Prior to Uber, most taxi drivers were already self-employed. Spot-like job contracts are becoming more common, but flexibility comes at a cost. Workers have little incentive to invest in firm-specific skills, so productivity suffers. And even if Mr Seabright’s shirt was delivered by a set of market-based transactions, the supply chains for complex goods, such as an iPhone or an Airbus A380 superjumbo, rely on long-term contracts that are often “incomplete”. Coase was the first to spot an enduring truth. Successful economies need both the benign dictatorship of the firm and the invisible hand of the market.
Coase’s theory of the firm: a reading list
1 “The Nature of the Firm” by R H Coase, Economica, 1937
2 “The Problem of Social Cost” by R H Coase, Journal of Law and Economics, 1960
3 “Industrial Organisation: A Proposal for Research” by R H Coase, NBER, 1972
4 “Production, Information Costs and Economic Organisation” by Armen A Alchian and Harold Demsetz, American Economic Review, 1972
5 “Transaction-Cost Economics: The Governance of Contractural Relations” by Oliver E Williamson, Journal of Law and Economics, 1979
6 “The Costs and Benefits of Ownership: A Theory of Vertical and Lateral Integration” by Sanford Grossman and Oliver Hart, Journal of Political Economy, 1986
7 “Multitask Principal-Agent Analysis: Incentive Contracts, Asset Ownership and Job Design” by Bengt Holmstrom and Paul Milgrom, Journal of Law, Economics and Organisation, 1991
8 “The Firm as Sub-economy” by Bengt Holmstrom, Journal of Law Economics & Organisation, 1999
9 “The Theory of the the Firm as Governance Structure: From Choice to Contract” by Oliver E Williamson, 2002
10 “Contracts as Reference Points” by Oliver Hart and John Moore, Quarterly Journal of Economics, 2008
Wednesday 27 October 2021
Don’t blame Nehru’s Socialism for Air India fate. Read the 1944 Bombay Plan first
Air India’s privatisation is finally underway, albeit, belatedly. Consequently, this has led to conversations around the planned economy, and in turn blamed the Socialist economy for India’s woes. These debates presume that India was forced into planning; this assumption undermines the country’s economic history, and disregards the role that Indian businesses played in shaping economic policy leading up to Independence.
In 1944, during the height of the Bengal famine, and with the seeming inevitability of Independence, J.R.D. Tata and seven other industrialists and executives — G.D. Birla, Purushottam Das Thakurdas, Ardeshir Shroff, Kasturbhai Lalbhai, Ardeshir Dalal, John Matthai, and Lal Shri Ram — came together to write a manifesto on the future of the Indian economy post-Independence. This was known as the Bombay Plan, or more formally called A Plan of Economic Development for India. The authors of the plan helped set up the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), Federation of Indian Chambers of Commerce and Industry (FICCI), supported the Indian National Congress (INC) during the Freedom struggle and even sat on the viceroy’s executive council during WWII.
View on economy
The Bombay Plan aimed to express the authors’ views on the post-Independence economy. It had the following components: a transition from agricultural domination to industrialisation; the allocation of resources through centralised planning, and the division of industries into ‘basic industries’, dominated by the State, and ‘consumer industries’, left to the private sector. From its outset, the plan acknowledged the primacy of the State in organising the economy and providing basic necessities to citizens. Historians such as Medha Kudaisya call the plan “a revolutionary idea” in State planning since it adopted a middle way for the private sector to coexist in a planned economy. On the other hand, Vivek Chibber in Locked in Place, argues that the plan was a way for businesses to entrench their own vested interests. (Vivek Chibber, Locked in Place: State-Building and Late Industrialization in India (Princeton, N.J. ; Princeton University Press, 2006), 86.)
The principle objective of the plan was “to bring about a doubling of the present per capita income within a period of fifteen years from the time the plan comes into operation,” and increase production of power and capital goods. It then went on to define a reasonable living standard, cost of housing, clothing and food to individuals, housing requirements, and the provision of essential infrastructure like sewage treatment, water and electricity. It planned to achieve these aims in three ‘leaps’ spread over five years, analogous to the Five-Year Plans. The table below reflects these priorities.
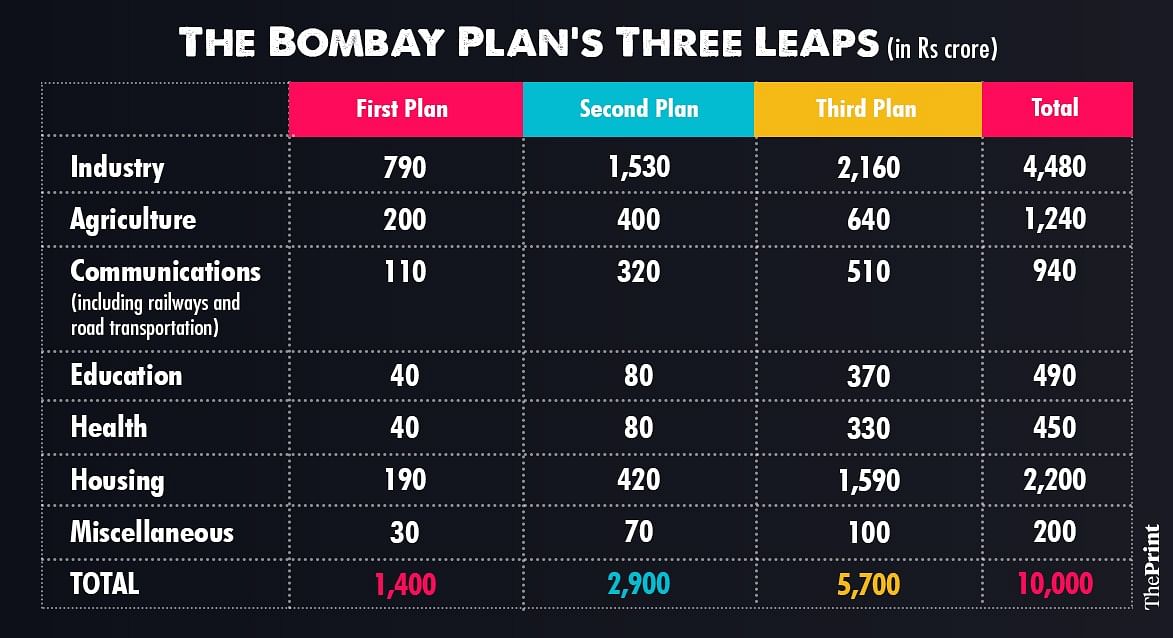 Graphic by Ramandeep Kaur | ThePrint
Graphic by Ramandeep Kaur | ThePrintThe planners argued for a ‘mixed-economy’ model, where the government would take control of ‘basic industries,’ and the private sector would take charge of ‘consumer industries’. Basic industries included transportation, chemicals, power generation, and steel production. More significantly, they argued that nationalisation of basic industries could reduce income disparities and that the government had to prioritise basic industries over consumption to reduce poverty. The planners conclude this section by saying, “for the success of our economic plan that the basic industries, on which ultimately the whole economic development of the country depends, should be developed as rapidly as possible,” emphasising that the government needed to take a leading role in the economy to ensure their provision. This shows that the the business community conceded the centrality of the State in building India’s economy.
The plan was well received, with endorsements from FICCI, RBI Governor C.D. Deshmukh, and the viceroy, who in response to the plan document had established a Department of Planning and Development in 1944 (Tryst with Prosperity). Newspaper editorials in India and abroad supported the plan. The Glasgow Herald commended the planners for thinking about issues such as “public health, population control and education” that “Indian political leaders [could not] be induced to think about, however urgent.” The New York Times reported that “the main political factions in India do not seem to be coming forward with any such practical approaches,” reiterating the view that India’s political elite had not considered policy solutions to India’s problems. However, the plan document was criticised as well for being inaccurate and a vehicle for the elite to entrench their interests over the interests of the poor by K.T. Shah, general secretary of the 1937-38 NPC and Gulzarilal Nanda, future Planning Minister (1951-63)and other economists. Its calculations relied on statistics from 1932, making its assumptions highly outdated and it underestimated the costs of implementing its aims.
Influence on economic planning
The document was significant since it reframed debates on State planning — from arguing if the State should dominate the economy, to analysing the extent to which the State should be involved in the economy. Its influence on Indian economic planning is clearly seen in the immediate aftermath of WWII, and in the First and Second Five-Year Plans that prioritised agricultural development and industrial growth, respectively. It also paved the way for India to adopt a third way in structuring its political economy by providing an opportunity to the country to combine aspects of Western capitalism, Soviet planning, and Western Socialism, allowing India to chart its own independent course. To many, the plan was a way for businesses to signal to the INC leadership that it was willing to accept the supremacy of the State in the economy, while acknowledging the role of the private sector in supporting consumption activity.
Insisting that Nehruvian Socialism was the cause for India’s economic ills without acknowledging the political and economic contexts of post-Independence India reflects an incomplete understanding of India’s formative years after independence. The Bombay Plan is an essential document to understanding the events that led to the creation of India’s planned economy, and reiterates the view that planning was not imposed on the country, but was widely debated across the private and public sphere in the years leading up to Independence.
Monday 25 October 2021
Thursday 21 October 2021
End to China’s estate market boom could spell trouble for the economy
 The Kangbashi district of Ordos in Inner Mongolia, famed for being a ‘ghost city’, has since filled up a bit. Photograph: Qilai Shen/Corbis/Getty
The Kangbashi district of Ordos in Inner Mongolia, famed for being a ‘ghost city’, has since filled up a bit. Photograph: Qilai Shen/Corbis/Getty In China today, the buzz is all about how the government there too has stumbled into an energy crisis with widespread power cuts. Yet this and other supply shocks will eventually pass, while the $300bn (£218bn) of debt enveloping China’s second biggest property developer, Evergrande, is of greater significance. It suggests China’s long housing boom is over, and bodes badly for the increasingly troubled economy, with implications for the rest of the world too.
China’s real estate market has been called the most important sector in the world economy. Valued at about $55tn, it is now twice the size of its US equivalent, and four times larger than China’s GDP. Taking into account construction and other property-related goods and services, annual housing activity accounts for about 29% of China’s GDP, far above the 10%-20% typical of most developed nations.
Real estate busts can be as painful as the preceding booms were exuberant. China, however, has only known growth as its previous housing welfare system was transformed from the 1990s onwards. A protracted housing downturn is now poised to add to the Chinese economy’s other mounting headwinds, with significant and unpredictable implications.
The signs were there 10 years ago, when the spotlight fell on China’s “ghost cities”. One of the most publicised was the Kangbashi district of the city of Ordos in Inner Mongolia, famed for its gleaming but empty office blocks and apartment towers, barren boulevards, deserted highways, and vacant shops and plazas. However, ghost cities turned out to be more bad investment than overinvestment. Ordos and similar cities remained eyesores for a while but have since filled up a bit.
Aside from ghost cities, the property sector prospered in the 2000s and 2010s because Beijing not only appeared to want a maturing real-estate market, but promoted it hard to underpin growth and the formation of a propertied, urban middle class. Developers had no qualms about borrowing heavily, because credit was freely available and they felt the government would always support the market if needed.
By the time the pandemic struck in 2020, it had certainly become a case of overinvestment. About a fifth of China’s housing units now lie vacant, often because they are too expensive for the population, 40% of whom earn barely 1,000 yuan (£115) a month. For second and third homes, the vacancy rates are higher still.
Meanwhile, since 2017, Beijing’s attitude towards rampant credit creation and the financialisation of housing – treating it as a commodity rather than as somewhere to live – has undergone a sea change. Xi Jinping told that year’s Communist party congress that “houses are built to be inhabited, not for speculation”, and that action would be taken to curb demand, overbuilding and rising home prices. Tighter mortgage terms and restrictions on multiple-home ownership followed.
Last year, regulators tightened regulations on developers designed to curb debt, preserve cash, and limit overbuilding. The government is sensitive to high housing costs, which are deemed to be excessive and a disincentive to larger family size. The crackdown chimes with its recent “common prosperity” drive, ostensibly designed to address rampant inequality, which has also seen a regulatory clampdown on big tech firms such as Alibaba, Didi and Tencent.
Those changes have exposed the financial fragility of developers and moved the precarious housing bubble centre stage. Even if, as seems likely, the Chinese authorities can keep the fallout from Evergrande from becoming a Lehman-type shock, a downturn in the property and construction sector could well aggravate China’s looming economic slowdown. Some expect China’s growth rate to slide to 1%-2%, for a while at least.
Banks and property companies are likely to restrict building activity and financing as they restructure broken balance sheets and Chinese households will be wary about taking on new mortgages. Household debt has risen from about $2tn in 2010 to more than $10tn last year, with the ratio of debt to disposable income surging to about 130%, significantly higher than in the US. With incomes rising only slowly, especially in the gig or informal economy, which now accounts for about three-fifths of employment, households are likely to remain on the back foot.
Demographics, especially the low 1.3 fertility rate, are also working against the economy. China’s working age and main home buying age groups are declining. The number of prime-age, first-time homebuyers – those in the 25-39 bracket – is set to fall by 25% in the next 20 years from 327 million to 247 million. The urbanisation rate, moreover, which doubled to 64% between 1996 and 2020, is bound to slow. There will be fewer marriages, fewer children and lower household formation.
In the last 10 to 15 years, local and provincial governments could always be relied upon to boost real estate and infrastructure spending to get the economy out of a hole if needed. They are already heavily in debt, however, and under pressure to find resources to support Xi’s “common prosperity” programme.
It is harder to predict what will happen to home prices in China. If they do, for the first time, decline far or over any length of time, expect to see much bigger problems emerge for banks and for consumers as negative wealth effects spread among the urban population.
We do not know how well China will manage to wean itself off real estate construction and services, but it will not be easy or painless. There will be important consequences for China’s economy, possibly its leadership, and the way China projects its influence abroad. Stay tuned.
Wednesday 20 October 2021
Sunday 17 October 2021
Thursday 14 October 2021
Monday 11 October 2021
Wednesday 6 October 2021
Too big to jail: why the crackdowns on dodgy finance have been so ineffective
 'HSBC admitted “criminal conduct” and was fined a record $1.9bn and signed a deferred prosecution agreement.’ Photograph: Lim Huey Teng/Reuters
'HSBC admitted “criminal conduct” and was fined a record $1.9bn and signed a deferred prosecution agreement.’ Photograph: Lim Huey Teng/ReutersWed 6 Oct 2021 11.00 BST
The Pandora papers data leak has once again highlighted the predatory practices of the world’s political and financial elites – enriching themselves by looting the public purse, or exploiting laws which they themselves helped to establish.
Aabout $3.6tn (£2.6tn) of the proceeds from bribery, embezzlement, money laundering, tax evasion and cronyism are laundered each year, undermining the social fabric of nations across the globe.
It is not the first time that tax avoidance, bribery, corruption, money-laundering and a lack of transparency have been exposed. The Panama papers, the Paradise papers, the HSBC leaks, the Jersey leaks, the FinCEN files, the Bahamas leaks and others have provided abundant evidence of dodgy financial dealings. The UK finance industry – aided by armies of accountants, lawyers and finance experts – is central to this trade, yet little has changed since those first revelations emerged.
The inertia is institutionalised because the political system is available for hire to people with fat wallets. Financial contributions to political parties create an atmosphere where scrutiny, and unwelcome laws, are discouraged. As Mohamed Amersi, who funded Boris Johnson’s campaign to become prime minister and whose financial dealings were revealed this week, puts it: “You get access, you get invitations, you get privileged relationships, if you are part of the setup.”
Further, parliament’s register of members’ financial interests shows that too many MPs and lords are on the payroll of corporations, including some engaged in illicit financial flows. The inevitable outcome is poor laws and a lack of regulation.
In 2018, the government launched the national economic crime centre to tackle high-level fraud and money laundering. The centre has yet to prosecute a single case – even though there is plenty of evidence of wrongdoing. In some cases, banks may even have forged customer signatures on court documents used to repossess homes and recover debts.
The 2017 Criminal Finances Act introduced the offence of failure to prevent the facilitation of tax evasion. No corporate body has been prosecuted. Little has been done to shackle the tax abuses industry dominated by big accounting firms even though, on some occasions, judges have declared their avoidance schemes to be unlawful. Despite the potential loss of huge amounts of tax revenues, no major firm has been investigated, fined or prosecuted. On the contrary, they continue to advise government departments, and sometimes receive lucrative government contracts.
The 2010 Bribery Act introduced the offence of “failure to prevent bribery”, to enable regulators to sue corporations for corrupt practices. The Crown Prosecution Service has secured just one conviction. The under-resourced Serious Fraud Office has secured just one conviction after the company itself pleaded guilty. Separately, Standard Chartered Bank, Rolls-Royce and four other companies were effectively let off with a deferred prosecution agreement.
The UK political system excels at cover-ups and protects wrongdoers. In 2012, a US Senate committee documented HSBC’s involvement in money laundering. The bank admitted “criminal conduct” and was fined a record $1.9bn and signed a deferred prosecution agreement. Yet though HSBC was supervised by the Bank of England and the Financial Services Authority, there was no UK investigation.
Later, a letter emerged from the then chancellor George Osborne, along with correspondence from the governor of the Bank of England and the Financial Services Authority, urging the US authorities to go easy on HSBC as it was too big to jail. There was no ministerial statement in the UK parliament to explain the cover-up.
The Bank of Commerce and Credit International (BCCI) was closed by the Bank of England in 1991. It was the biggest banking fraud of the 20th century, yet the then Conservative government did not order an independent investigation. Through US investigations I became aware of a secret document codenamed the Sandstorm Report. Using freedom of information laws I requested a copy: the government refused. After five and half years of litigation, judges ordered the UK government to release a copy to me. It shows that the government has been protecting individuals, including dead ones, connected with al-Qaida, Saudi intelligence, royal families in the Middle East, smuggling, murder, financial crimes and other nefarious practices.
I recently raised the HSBC and BCCI cover-ups in the House of Lords. The minister did not respond.
The UK remains a favourite destination for dirty money because the political and regulatory system is ineffective. An independent public inquiry into the finance industry is long overdue, but even if one were granted it would be hard to be optimistic: it seems our law enforcement agencies have been captured by corporations. The revelation that the City of London police fraud investigation unit is now funded by Lloyds Bank – an organisation severely criticised by the all-party parliamentary group on fair business banking for its role in the unresolved frauds at HBOS – does not inspire any confidence. Will it take another financial crash to generate enough political pressure to change the system?