by Carole Cadwalladr in The Guardian
“The connectivity that is the heart of globalisation can be exploited by states with hostile intent to further their aims.[…] The risks at stake are profound and represent a fundamental threat to our sovereignty.”
Alex Younger, head of MI6, December, 2016
Alex Younger, head of MI6, December, 2016
“It’s not MI6’s job to warn of internal threats. It was a very strange speech. Was it one branch of the intelligence services sending a shot across the bows of another? Or was it pointed at Theresa May’s government? Does she know something she’s not telling us?”
Senior intelligence analyst, April 2017
Senior intelligence analyst, April 2017
In June 2013, a young American postgraduate called Sophie was passing through London when she called up the boss of a firm where she’d previously interned. The company, SCL Elections, went on to be bought by Robert Mercer, a secretive hedge fund billionaire, renamed Cambridge Analytica, and achieved a certain notoriety as the data analytics firm that played a role in both Trump and Brexit campaigns. But all of this was still to come. London in 2013 was still basking in the afterglow of the Olympics. Britain had not yet Brexited. The world had not yet turned.
“That was before we became this dark, dystopian data company that gave the world Trump,” a former Cambridge Analytica employee who I’ll call Paul tells me. “It was back when we were still just a psychological warfare firm.”
Was that really what you called it, I ask him. Psychological warfare? “Totally. That’s what it is. Psyops. Psychological operations – the same methods the military use to effect mass sentiment change. It’s what they mean by winning ‘hearts and minds’. We were just doing it to win elections in the kind of developing countries that don’t have many rules.”
Why would anyone want to intern with a psychological warfare firm, I ask him. And he looks at me like I am mad. “It was like working for MI6. Only it’s MI6 for hire. It was very posh, very English, run by an old Etonian and you got to do some really cool things. Fly all over the world. You were working with the president of Kenya or Ghana or wherever. It’s not like election campaigns in the west. You got to do all sorts of crazy shit.”
On that day in June 2013, Sophie met up with SCL’s chief executive, Alexander Nix, and gave him the germ of an idea. “She said, ‘You really need to get into data.’ She really drummed it home to Alexander. And she suggested he meet this firm that belonged to someone she knew about through her father.”
Who’s her father?
“Eric Schmidt.”
Eric Schmidt – the chairman of Google?
“Yes. And she suggested Alexander should meet this company called Palantir.”
I had been speaking to former employees of Cambridge Analytica for months and heard dozens of hair-raising stories, but it was still a gobsmacking moment. To anyone concerned about surveillance, Palantir is practically now a trigger word. The data-mining firm has contracts with governments all over the world – including GCHQ and the NSA. It’s owned by Peter Thiel, the billionaire co-founder of eBay and PayPal, who became Silicon Valley’s first vocal supporter of Trump.
In some ways, Eric Schmidt’s daughter showing up to make an introduction to Palantir is just another weird detail in the weirdest story I have ever researched.
A weird but telling detail. Because it goes to the heart of why the story of Cambridge Analytica is one of the most profoundly unsettling of our time. Sophie Schmidt now works for another Silicon Valley megafirm: Uber. And what’s clear is that the power and dominance of the Silicon Valley – Google and Facebook and a small handful of others – are at the centre of the global tectonic shift we are currently witnessing.

The money man: Robert Mercer, Trump supporter and owner of Cambridge Analytica. Photograph: Rex
It also reveals a critical and gaping hole in the political debate in Britain. Because what is happening in America and what is happening in Britain are entwined. Brexit and Trump are entwined. The Trump administration’s links to Russia and Britain are entwined. And Cambridge Analytica is one point of focus through which we can see all these relationships in play; it also reveals the elephant in the room as we hurtle into a general election: Britain tying its future to an America that is being remade - in a radical and alarming way - by Trump.
There are three strands to this story. How the foundations of an authoritarian surveillance state are being laid in the US. How British democracy was subverted through a covert, far-reaching plan of coordination enabled by a US billionaire. And how we are in the midst of a massive land grab for power by billionaires via our data. Data which is being silently amassed, harvested and stored. Whoever owns this data owns the future.
My entry point into this story began, as so many things do, with a late-night Google. Last December, I took an unsettling tumble into a wormhole of Google autocompletesuggestions that ended with “did the holocaust happen”. And an entire page of results that claimed it didn’t.
Google’s algorithm had been gamed by extremist sites and it was Jonathan Albright, a professor of communications at Elon University, North Carolina, who helped me get to grips with what I was seeing. He was the first person to map and uncover an entire “alt-right” news and information ecosystem and he was the one who first introduced me to Cambridge Analytica.
He called the company a central point in the right’s “propaganda machine”, a line I quoted in reference to its work for the Trump election campaign and the referendum Leave campaign. That led to the second article featuring Cambridge Analytica – as a central node in the alternative news and information network that I believed Robert Mercer and Steve Bannon, the key Trump aide who is now his chief strategist, were creating. I found evidence suggesting they were on a strategic mission to smash the mainstream media and replace it with one comprising alternative facts, fake history and rightwing propaganda.
Mercer is a brilliant computer scientist, a pioneer in early artificial intelligence, and the co-owner of one of the most successful hedge funds on the planet (with a gravity-defying 71.8% annual return). And, he is also, I discovered, good friends with Nigel Farage. Andy Wigmore, Leave.EU’s communications director, told me that it was Mercer who had directed his company, Cambridge Analytica, to “help” the Leave campaign.
The second article triggered two investigations, which are both continuing: one by the Information Commissioner’s Office into the possible illegal use of data. And a second by the Electoral Commission which is “focused on whether one or more donations – including services – accepted by Leave.EU was ‘impermissable’”.
What I then discovered is that Mercer’s role in the referendum went far beyond this. Far beyond the jurisdiction of any UK law. The key to understanding how a motivated and determined billionaire could bypass ourelectoral laws rests on AggregateIQ, an obscure web analytics company based in an office above a shop in Victoria, British Columbia.
It was with AggregateIQ that Vote Leave (the official Leave campaign) chose to spend £3.9m, more than half its official £7m campaign budget. As did three other affiliated Leave campaigns: BeLeave, Veterans for Britain and the Democratic Unionist party, spending a further £757,750. “Coordination” between campaigns is prohibited under UK electoral law, unless campaign expenditure is declared, jointly. It wasn’t. Vote Leave says the Electoral Commission “looked into this” and gave it “a clean bill of health”.
How did an obscure Canadian company come to play such a pivotal role in Brexit? It’s a question that Martin Moore, director of the centre for the study of communication, media and power at King’s College London has been asking too. “I went through all the Leave campaign invoices when the Electoral Commission uploaded them to its site in February. And I kept on discovering all these huge amounts going to a company that not only had I never heard of, but that there was practically nothing at all about on the internet. More money was spent with AggregateIQ than with any other company in any other campaign in the entire referendum. All I found, at that time, was a one-page website and that was it. It was an absolute mystery.”
Moore contributed to an LSE report published in April that concluded UK’s electoral laws were “weak and helpless” in the face of new forms of digital campaigning. Offshore companies, money poured into databases, unfettered third parties… the caps on spending had come off. The laws that had always underpinned Britain’s electoral laws were no longer fit for purpose. Laws, the report said, that needed “urgently reviewing by parliament”.
AggregateIQ holds the key to unravelling another complicated network of influence that Mercer has created. A source emailed me to say he had found that AggregateIQ’s address and telephone number corresponded to a company listed on Cambridge Analytica’s website as its overseas office: “SCL Canada”. A day later, that online reference vanished.
There had to be a connection between the two companies. Between the various Leave campaigns. Between the referendum and Mercer. It was too big a coincidence. But everyone – AggregateIQ, Cambridge Analytica, Leave.EU, Vote Leave – denied it. AggregateIQ had just been a short-term “contractor” to Cambridge Analytica. There was nothing to disprove this. We published the known facts. On 29 March, article 50 was triggered.
Then I meet Paul, the first of two sources formerly employed by Cambridge Analytica. He is in his late 20s and bears mental scars from his time there. “It’s almost like post-traumatic shock. It was so… messed up. It happened so fast. I just woke up one morning and found we’d turned into the Republican fascist party. I still can’t get my head around it.”
He laughed when I told him the frustrating mystery that was AggregateIQ. “Find Chris Wylie,” he said.
Who’s Chris Wylie?
“He’s the one who brought data and micro-targeting [individualised political messages] to Cambridge Analytica. And he’s from west Canada. It’s only because of him that AggregateIQ exist. They’re his friends. He’s the one who brought them in.”
There wasn’t just a relationship between Cambridge Analytica and AggregateIQ, Paul told me. They were intimately entwined, key nodes in Robert Mercer’s distributed empire. “The Canadians were our back office. They built our software for us. They held our database. If AggregateIQ is involved then Cambridge Analytica is involved. And if Cambridge Analytica is involved, then Robert Mercer and Steve Bannon are involved. You need to find Chris Wylie.”
I did find Chris Wylie. He refused to comment.
Key to understanding how data would transform the company is knowing where it came from. And it’s a letter from “Director of Defence Operations, SCL Group”, that helped me realise this. It’s from “Commander Steve Tatham, PhD, MPhil, Royal Navy (rtd)” complaining about my use in my Mercer article of the word “disinformation”.
I wrote back to him pointing out references in papers he’d written to “deception” and “propaganda”, which I said I understood to be “roughly synonymous with ‘disinformation’.” It’s only later that it strikes me how strange it is that I’m corresponding with a retired navy commander about military strategies that may have been used in British and US elections.
What’s been lost in the US coverage of this “data analytics” firm is the understanding of where the firm came from: deep within the military-industrial complex. A weird British corner of it populated, as the military establishment in Britain is, by old-school Tories. Geoffrey Pattie, a former parliamentary under-secretary of state for defence procurement and director of Marconi Defence Systems, used to be on the board, and Lord Marland, David Cameron’s pro-Brexit former trade envoy, a shareholder.
Steve Tatham was the head of psychological operations for British forces in Afghanistan. The Observer has seen letters endorsing him from the UK Ministry of Defence, the Foreign Office and Nato.
SCL/Cambridge Analytica was not some startup created by a couple of guys with a Mac PowerBook. It’s effectively part of the British defence establishment. And, now, too, the American defence establishment. An ex-commanding officer of the US Marine Corps operations centre, Chris Naler, has recently joined Iota Global, a partner of the SCL group.
This is not just a story about social psychology and data analytics. It has to be understood in terms of a military contractor using military strategies on a civilian population. Us. David Miller, a professor of sociology at Bath University and an authority in psyops and propaganda, says it is “an extraordinary scandal that this should be anywhere near a democracy. It should be clear to voters where information is coming from, and if it’s not transparent or open where it’s coming from, it raises the question of whether we are actually living in a democracy or not.”
Paul and David, another ex-Cambridge Analytica employee, were working at the firm when it introduced mass data-harvesting to its psychological warfare techniques. “It brought psychology, propaganda and technology together in this powerful new way,” David tells me.
Steve Bannon, former vice-president of Cambridge Analytica, now a key adviser to Donald Trump. Photograph: Jonathan Ernst/Reuters
And it was Facebook that made it possible. It was from Facebook that Cambridge Analytica obtained its vast dataset in the first place. Earlier, psychologists at Cambridge University harvested Facebook data (legally) for research purposes and published pioneering peer-reviewed work about determining personality traits, political partisanship, sexuality and much more from people’s Facebook “likes”. And SCL/Cambridge Analytica contracted a scientist at the university, Dr Aleksandr Kogan, to harvest new Facebook data. And he did so by paying people to take a personality quiz which also allowed not just their own Facebook profiles to be harvested, but also those of their friends – a process then allowed by the social network.
Facebook was the source of the psychological insights that enabled Cambridge Analytica to target individuals. It was also the mechanism that enabled them to be delivered on a large scale.
The company also (perfectly legally) bought consumer datasets – on everything from magazine subscriptions to airline travel – and uniquely it appended these with the psych data to voter files. It matched all this information to people’s addresses, their phone numbers and often their email addresses. “The goal is to capture every single aspect of every voter’s information environment,” said David. “And the personality data enabled Cambridge Analytica to craft individual messages.”
Finding “persuadable” voters is key for any campaign and with its treasure trove of data, Cambridge Analytica could target people high in neuroticism, for example, with images of immigrants “swamping” the country. The key is finding emotional triggers for each individual voter.
Cambridge Analytica worked on campaigns in several key states for a Republican political action committee. Its key objective, according to a memo the Observer has seen, was “voter disengagement” and “to persuade Democrat voters to stay at home”: a profoundly disquieting tactic. It has previously been claimed that suppression tactics were used in the campaign, but this document provides the first actual evidence.
But does it actually work? One of the criticisms that has been levelled at my and others’ articles is that Cambridge Analytica’s “special sauce” has been oversold. Is what it is doing any different from any other political consultancy?
“It’s not a political consultancy,” says David. “You have to understand this is not a normal company in any way. I don’t think Mercer even cares if it ever makes any money. It’s the product of a billionaire spending huge amounts of money to build his own experimental science lab, to test what works, to find tiny slivers of influence that can tip an election. Robert Mercer did not invest in this firm until it ran a bunch of pilots – controlled trials. This is one of the smartest computer scientists in the world. He is not going to splash $15m on bullshit.”
Tamsin Shaw, an associate professor of philosophy at New York University, helps me understand the context. She has researched the US military’s funding and use of psychological research for use in torture. “The capacity for this science to be used to manipulate emotions is very well established. This is military-funded technology that has been harnessed by a global plutocracy and is being used to sway elections in ways that people can’t even see, don’t even realise is happening to them,” she says. “It’s about exploiting existing phenomenon like nationalism and then using it to manipulate people at the margins. To have so much data in the hands of a bunch of international plutocrats to do with it what they will is absolutely chilling.
“We are in an information war and billionaires are buying up these companies, which are then employed to go to work in the heart of government. That’s a very worrying situation.”
A project that Cambridge Analytica carried out in Trinidad in 2013 brings all the elements in this story together. Just as Robert Mercer began his negotiations with SCL boss Alexander Nix about an acquisition, SCL was retained by several government ministers in Trinidad and Tobago. The brief involved developing a micro-targeting programme for the governing party of the time. And AggregateIQ – the same company involved in delivering Brexit for Vote Leave – was brought in to build the targeting platform.
David said: “The standard SCL/CA method is that you get a government contract from the ruling party. And this pays for the political work. So, it’s often some bullshit health project that’s just a cover for getting the minister re-elected. But in this case, our government contacts were with Trinidad’s national security council.”
The security work was to be the prize for the political work. Documents seen by the Observer show that this was a proposal to capture citizens’ browsing history en masse, recording phone conversations and applying natural language processing to the recorded voice data to construct a national police database, complete with scores for each citizen on their propensity to commit crime.
“The plan put to the minister was Minority Report. It was pre-crime. And the fact that Cambridge Analytica is now working inside the Pentagon is, I think, absolutely terrifying,” said David.
These documents throw light on a significant and under-reported aspect of the Trump administration. The company that helped Trump achieve power in the first place has now been awarded contracts in the Pentagon and the US state department. Its former vice-president Steve Bannon now sits in the White House. It is also reported to be in discussions for “military and homeland security work”.
In the US, the government is bound by strict laws about what data it can collect on individuals. But, for private companies anything goes. Is it unreasonable to see in this the possible beginnings of an authoritarian surveillance state?
A state that is bringing corporate interests into the heart of the administration. Documents detail Cambridge Analytica is involved with many other right-leaning billionaires, including Rupert Murdoch. One memo references Cambridge Analytica trying to place an article with a journalist in Murdoch’s Wall Street Journal: “RM re-channeled and connected with Jamie McCauley from Robert Thomson News Corp office,” it says.
It makes me think again about the story involving Sophie Schmidt, Cambridge Analytica and Palantir. Is it a telling detail, or is it a clue to something else going on? Cambridge Analytica and Palantir both declined to comment for this article on whether they had any relationship. But witnesses and emails confirm that meetings between Cambridge Analytica and Palantir took place in 2013. The possibility of a working relationship was at least discussed.
Further documents seen by the Observer confirm that at least one senior Palantir employee consulted with Cambridge Analytica in relation to the Trinidad project and later political work in the US. But at the time, I’m told, Palantir decided it was too much of a reputational risk for a more formal arrangement. There was no upside to it. Palantir is a company that is trusted to handle vast datasets on UK and US citizens for GCHQ and the NSA, as well as many other countries.
Now though, they are both owned by ideologically aligned billionaires: Robert Mercer and Peter Thiel. The Trump campaign has said that Thiel helped it with data. A campaign that was led by Steve Bannon, who was then at Cambridge Analytica.
A leading QC who spends a lot of time in the investigatory powers tribunal said that the problem with this technology was that it all depended on whose hands it was in.
“On the one hand, it’s being done by companies and governments who say ‘you can trust us, we are good and democratic and bake cakes at the weekend’. But then the same expertise can also be sold on to whichever repressive regime.”
In Britain, we still trust our government. We respect our authorities to uphold our laws. We trust the rule of law. We believe we live in a free and fair democracy. Which is what, I believe, makes the last part of this story so profoundly unsettling.
And it was Facebook that made it possible. It was from Facebook that Cambridge Analytica obtained its vast dataset in the first place. Earlier, psychologists at Cambridge University harvested Facebook data (legally) for research purposes and published pioneering peer-reviewed work about determining personality traits, political partisanship, sexuality and much more from people’s Facebook “likes”. And SCL/Cambridge Analytica contracted a scientist at the university, Dr Aleksandr Kogan, to harvest new Facebook data. And he did so by paying people to take a personality quiz which also allowed not just their own Facebook profiles to be harvested, but also those of their friends – a process then allowed by the social network.
Facebook was the source of the psychological insights that enabled Cambridge Analytica to target individuals. It was also the mechanism that enabled them to be delivered on a large scale.
The company also (perfectly legally) bought consumer datasets – on everything from magazine subscriptions to airline travel – and uniquely it appended these with the psych data to voter files. It matched all this information to people’s addresses, their phone numbers and often their email addresses. “The goal is to capture every single aspect of every voter’s information environment,” said David. “And the personality data enabled Cambridge Analytica to craft individual messages.”
Finding “persuadable” voters is key for any campaign and with its treasure trove of data, Cambridge Analytica could target people high in neuroticism, for example, with images of immigrants “swamping” the country. The key is finding emotional triggers for each individual voter.
Cambridge Analytica worked on campaigns in several key states for a Republican political action committee. Its key objective, according to a memo the Observer has seen, was “voter disengagement” and “to persuade Democrat voters to stay at home”: a profoundly disquieting tactic. It has previously been claimed that suppression tactics were used in the campaign, but this document provides the first actual evidence.
But does it actually work? One of the criticisms that has been levelled at my and others’ articles is that Cambridge Analytica’s “special sauce” has been oversold. Is what it is doing any different from any other political consultancy?
“It’s not a political consultancy,” says David. “You have to understand this is not a normal company in any way. I don’t think Mercer even cares if it ever makes any money. It’s the product of a billionaire spending huge amounts of money to build his own experimental science lab, to test what works, to find tiny slivers of influence that can tip an election. Robert Mercer did not invest in this firm until it ran a bunch of pilots – controlled trials. This is one of the smartest computer scientists in the world. He is not going to splash $15m on bullshit.”
Tamsin Shaw, an associate professor of philosophy at New York University, helps me understand the context. She has researched the US military’s funding and use of psychological research for use in torture. “The capacity for this science to be used to manipulate emotions is very well established. This is military-funded technology that has been harnessed by a global plutocracy and is being used to sway elections in ways that people can’t even see, don’t even realise is happening to them,” she says. “It’s about exploiting existing phenomenon like nationalism and then using it to manipulate people at the margins. To have so much data in the hands of a bunch of international plutocrats to do with it what they will is absolutely chilling.
“We are in an information war and billionaires are buying up these companies, which are then employed to go to work in the heart of government. That’s a very worrying situation.”
A project that Cambridge Analytica carried out in Trinidad in 2013 brings all the elements in this story together. Just as Robert Mercer began his negotiations with SCL boss Alexander Nix about an acquisition, SCL was retained by several government ministers in Trinidad and Tobago. The brief involved developing a micro-targeting programme for the governing party of the time. And AggregateIQ – the same company involved in delivering Brexit for Vote Leave – was brought in to build the targeting platform.
David said: “The standard SCL/CA method is that you get a government contract from the ruling party. And this pays for the political work. So, it’s often some bullshit health project that’s just a cover for getting the minister re-elected. But in this case, our government contacts were with Trinidad’s national security council.”
The security work was to be the prize for the political work. Documents seen by the Observer show that this was a proposal to capture citizens’ browsing history en masse, recording phone conversations and applying natural language processing to the recorded voice data to construct a national police database, complete with scores for each citizen on their propensity to commit crime.
“The plan put to the minister was Minority Report. It was pre-crime. And the fact that Cambridge Analytica is now working inside the Pentagon is, I think, absolutely terrifying,” said David.
These documents throw light on a significant and under-reported aspect of the Trump administration. The company that helped Trump achieve power in the first place has now been awarded contracts in the Pentagon and the US state department. Its former vice-president Steve Bannon now sits in the White House. It is also reported to be in discussions for “military and homeland security work”.
In the US, the government is bound by strict laws about what data it can collect on individuals. But, for private companies anything goes. Is it unreasonable to see in this the possible beginnings of an authoritarian surveillance state?
A state that is bringing corporate interests into the heart of the administration. Documents detail Cambridge Analytica is involved with many other right-leaning billionaires, including Rupert Murdoch. One memo references Cambridge Analytica trying to place an article with a journalist in Murdoch’s Wall Street Journal: “RM re-channeled and connected with Jamie McCauley from Robert Thomson News Corp office,” it says.
It makes me think again about the story involving Sophie Schmidt, Cambridge Analytica and Palantir. Is it a telling detail, or is it a clue to something else going on? Cambridge Analytica and Palantir both declined to comment for this article on whether they had any relationship. But witnesses and emails confirm that meetings between Cambridge Analytica and Palantir took place in 2013. The possibility of a working relationship was at least discussed.
Further documents seen by the Observer confirm that at least one senior Palantir employee consulted with Cambridge Analytica in relation to the Trinidad project and later political work in the US. But at the time, I’m told, Palantir decided it was too much of a reputational risk for a more formal arrangement. There was no upside to it. Palantir is a company that is trusted to handle vast datasets on UK and US citizens for GCHQ and the NSA, as well as many other countries.
Now though, they are both owned by ideologically aligned billionaires: Robert Mercer and Peter Thiel. The Trump campaign has said that Thiel helped it with data. A campaign that was led by Steve Bannon, who was then at Cambridge Analytica.
A leading QC who spends a lot of time in the investigatory powers tribunal said that the problem with this technology was that it all depended on whose hands it was in.
“On the one hand, it’s being done by companies and governments who say ‘you can trust us, we are good and democratic and bake cakes at the weekend’. But then the same expertise can also be sold on to whichever repressive regime.”
In Britain, we still trust our government. We respect our authorities to uphold our laws. We trust the rule of law. We believe we live in a free and fair democracy. Which is what, I believe, makes the last part of this story so profoundly unsettling.
Donald Trump with Peter Thiel, one of his key Silicon Valley supporters. Photograph: Drew Angerer/Getty Images
The details of the Trinidad project finally unlocked the mystery that was AggregateIQ. Trinidad was SCL’s first project using big data for micro-targeting before the firm was acquired by Mercer. It was the model that Mercer was buying into. And it brought together all the players: the Cambridge psychologist Aleksandr Kogan, AggregateIQ, Chris Wylie, and two other individuals who would play a role in this story: Mark Gettleson, a focus group expert who had previously worked for the Lib Dems. And Thomas Borwick, the son of Victoria Borwick, the Conservative MP for Kensington.
When my article linking Mercer and Leave.EU was published in February, no one was more upset about it than former Tory adviser Dominic Cummings, the campaign strategist for Vote Leave. He launched an irate Twitter tirade. The piece was “full of errors & itself spreads disinformation” “CA had ~0% role in Brexit referendum”.
A week later the Observer revealed AggregateIQ’s possible link to Cambridge Analytica. Cummings’s Twitter feed went quiet. He didn’t return my messages or my emails.
Questions had already been swirling about whether there had been any coordination between the Leave campaigns. In the week before the referendum, Vote Leave donated money to two other Leave groups – £625,000 to BeLeave, run by fashion student Darren Grimes, and £100,000 to Veterans for Britain, who both then spent this money with AggregateIQ.
The Electoral Commission has written to AggregateIQ. A source close to the investigation said that AggregateIQ responded by saying it had signed a non-disclosure agreement. And since it was outside British jurisdiction, that was the end of it. Vote Leave refers to this as the Electoral Commission giving it “a clean bill of health”.
On his blog, Dominic Cummings has written thousands of words about the referendum campaign. What is missing is any details about his data scientists. He “hired physicists” is all he’ll say. In the books on Brexit, other members of the team talk about “Dom’s astrophysicists”, who he kept “a tightly guarded secret”. They built models, using data “scraped” off Facebook.
Finally, after weeks of messages, he sent me an email. We were agreed on one thing, it turned out. He wrote: “The law/regulatory agencies are such a joke the reality is that anybody who wanted to cheat the law could do it easily without people realising.” But, he says, “by encouraging people to focus on non-stories like Mercer’s nonexistent role in the referendum you are obscuring these important issues”.
And to finally answer the question about how Vote Leave found this obscure Canadian company on the other side of the planet, he wrote: “Someone found AIQ [AggregateIQ] on the internet and interviewed them on the phone then told me – let’s go with these guys. They were clearly more competent than any others we’d spoken to in London.”
The most unfortunate aspect of this – for Dominic Cummings – is that this isn’t credible. It’s the work of moments to put a date filter on Google search and discover that in late 2015 or early 2016, there are no Google hits for “Aggregate IQ”. There is no press coverage. No random mentions. It doesn’t even throw up its website. I have caught Dominic Cummings in what appears to be an alternative fact.
But what is an actual fact is that Gettleson and Borwick, both previously consultants for SCL and Cambridge Analytica, were both core members of the Vote Leave team. They’re both in the official Vote Leave documents lodged with the Electoral Commission, though they coyly describe their previous work for SCL/Cambridge Analytica as “micro-targeting in Antigua and Trinidad” and “direct communications for several PACs, Senate and Governor campaigns”.
And Borwick wasn’t just any member of the team. He was Vote Leave’s chief technology officer.
This story may involve a complex web of connections, but it all comes back to Cambridge Analytica. It all comes back to Mercer. Because the connections must have been evident. “AggregateIQ may not have belonged to the Mercers but they exist within his world,” David told me. “Almost all of their contracts came from Cambridge Analytica or Mercer. They wouldn’t exist without them. During the whole time the referendum was going on, they were working every day on the [Ted] Cruz campaign with Mercer and Cambridge Analytica. AggregateIQ built and ran Cambridge Analytica’s database platforms.”
The details of the Trinidad project finally unlocked the mystery that was AggregateIQ. Trinidad was SCL’s first project using big data for micro-targeting before the firm was acquired by Mercer. It was the model that Mercer was buying into. And it brought together all the players: the Cambridge psychologist Aleksandr Kogan, AggregateIQ, Chris Wylie, and two other individuals who would play a role in this story: Mark Gettleson, a focus group expert who had previously worked for the Lib Dems. And Thomas Borwick, the son of Victoria Borwick, the Conservative MP for Kensington.
When my article linking Mercer and Leave.EU was published in February, no one was more upset about it than former Tory adviser Dominic Cummings, the campaign strategist for Vote Leave. He launched an irate Twitter tirade. The piece was “full of errors & itself spreads disinformation” “CA had ~0% role in Brexit referendum”.
A week later the Observer revealed AggregateIQ’s possible link to Cambridge Analytica. Cummings’s Twitter feed went quiet. He didn’t return my messages or my emails.
Questions had already been swirling about whether there had been any coordination between the Leave campaigns. In the week before the referendum, Vote Leave donated money to two other Leave groups – £625,000 to BeLeave, run by fashion student Darren Grimes, and £100,000 to Veterans for Britain, who both then spent this money with AggregateIQ.
The Electoral Commission has written to AggregateIQ. A source close to the investigation said that AggregateIQ responded by saying it had signed a non-disclosure agreement. And since it was outside British jurisdiction, that was the end of it. Vote Leave refers to this as the Electoral Commission giving it “a clean bill of health”.
On his blog, Dominic Cummings has written thousands of words about the referendum campaign. What is missing is any details about his data scientists. He “hired physicists” is all he’ll say. In the books on Brexit, other members of the team talk about “Dom’s astrophysicists”, who he kept “a tightly guarded secret”. They built models, using data “scraped” off Facebook.
Finally, after weeks of messages, he sent me an email. We were agreed on one thing, it turned out. He wrote: “The law/regulatory agencies are such a joke the reality is that anybody who wanted to cheat the law could do it easily without people realising.” But, he says, “by encouraging people to focus on non-stories like Mercer’s nonexistent role in the referendum you are obscuring these important issues”.
And to finally answer the question about how Vote Leave found this obscure Canadian company on the other side of the planet, he wrote: “Someone found AIQ [AggregateIQ] on the internet and interviewed them on the phone then told me – let’s go with these guys. They were clearly more competent than any others we’d spoken to in London.”
The most unfortunate aspect of this – for Dominic Cummings – is that this isn’t credible. It’s the work of moments to put a date filter on Google search and discover that in late 2015 or early 2016, there are no Google hits for “Aggregate IQ”. There is no press coverage. No random mentions. It doesn’t even throw up its website. I have caught Dominic Cummings in what appears to be an alternative fact.
But what is an actual fact is that Gettleson and Borwick, both previously consultants for SCL and Cambridge Analytica, were both core members of the Vote Leave team. They’re both in the official Vote Leave documents lodged with the Electoral Commission, though they coyly describe their previous work for SCL/Cambridge Analytica as “micro-targeting in Antigua and Trinidad” and “direct communications for several PACs, Senate and Governor campaigns”.
And Borwick wasn’t just any member of the team. He was Vote Leave’s chief technology officer.
This story may involve a complex web of connections, but it all comes back to Cambridge Analytica. It all comes back to Mercer. Because the connections must have been evident. “AggregateIQ may not have belonged to the Mercers but they exist within his world,” David told me. “Almost all of their contracts came from Cambridge Analytica or Mercer. They wouldn’t exist without them. During the whole time the referendum was going on, they were working every day on the [Ted] Cruz campaign with Mercer and Cambridge Analytica. AggregateIQ built and ran Cambridge Analytica’s database platforms.”
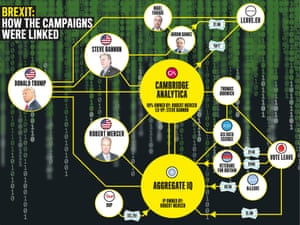 Illustration: James Melaugh
Illustration: James MelaughCummings won’t say who did his modelling. But invoices lodged with the Electoral Commission show payments to a company called Advanced Skills Institute. It takes me weeks to spot the significance of this because the company is usually referred to as ASI Data Science, a company that has a revolving cast of data scientists who have gone on to work with Cambridge Analytica and vice versa. There are videos of ASI data scientists presenting Cambridge Analytica personality models and pages for events the two companies have jointly hosted. ASI told the Observer it had no formal relationship with Cambridge Analytica.
Here’s the crucial fact: during the US primary elections, Aggregate IQ signed away its intellectual property (IP). It didn’t own its IP: Robert Mercer did. For AggregateIQ to work with another campaign in Britain, the firm would have to have had the express permission of Mercer. Asked if it would make any comment on financial or business links between “Cambridge Analytica, Robert Mercer, Steve Bannon, AggregateIQ, Leave.EU and Vote Leave”, a spokesperson for Cambridge Analytica said: “Cambridge Analytica did no paid or unpaid work for Leave.EU.”
This story isn’t about cunning Dominic Cummings finding a few loopholes in the Electoral Commission’s rules. Finding a way to spend an extra million quid here. Or (as the Observer has also discovered )underdeclaring the costs of his physicists on the spending returns by £43,000. This story is not even about what appears to be covert coordination between Vote Leave and Leave.EU in their use of AggregateIQ and Cambridge Analytica. It’s about how a motivated US billionaire – Mercer and his chief ideologue, Bannon – helped to bring about the biggest constitutional change to Britain in a century.
Because to understand where and how Brexit is connected to Trump, it’s right here. These relationships, which thread through the middle of Cambridge Analytica, are the result of a transatlantic partnership that stretches back years. Nigel Farage and Bannon have been close associates since at least 2012. Bannon opened the London arm of his news website Breitbart in 2014 to support Ukip – the latest front “in our current cultural and political war”, he told the New York Times.
Britain had always been key to Bannon’s plans, another ex-Cambridge Analytica employee told me on condition of anonymity. It was a crucial part of his strategy for changing the entire world order.
“He believes that to change politics, you have to first change the culture. And Britain was key to that. He thought that where Britain led, America would follow. The idea of Brexit was hugely symbolically important to him.”
On 29 March, the day article 50 was triggered, I called one of the smaller campaigns, Veterans for Britain. Cummings’s strategy was to target people in the last days of the campaign and Vote Leave gave the smaller group £100,000 in the last week. A small number of people they identified as “persuadable” were bombarded with more than a billion ads, the vast majority in the last few days.
I asked David Banks, Veterans for Britain’s head of communications, why they spent the money with AggregateIQ.
“I didn’t find AggegrateIQ. They found us. They rang us up and pitched us. There’s no conspiracy here. They were this Canadian company which was opening an office in London to work in British politics and they were doing stuff that none of the UK companies could offer. Their targeting was based on a set of technologies that hadn’t reached the UK yet. A lot of it was proprietary, they’d found a way of targeting people based on behavioural insights. They approached us.”
It seems clear to me that David Banks didn’t know there might have been anything untoward about this. He’s a patriotic man who believes in British sovereignty and British values and British laws. I don’t think knew about any overlap with these other campaigns. I can only think that he was played.
And that we, the British people, were played. In his blog, Dominic Cummings writes that Brexit came down to “about 600,000 people – just over 1% of registered voters”. It’s not a stretch to believe that a member of the global 1% found a way to influence this crucial 1% of British voters. The referendum was an open goal too tempting a target for US billionaires not to take a clear shot at. Or I should say US billionaires and other interested parties, because in acknowledging the transatlantic links that bind Britain and America, Brexit and Trump, so tightly, we also must acknowledge that Russia is wrapped somewhere in this tight embrace too.
For the last month, I’ve been writing about the links between the British right, the Trump administration and the European right. And these links lead to Russia from multiple directions. Between Nigel Farage and Donald Trump and Cambridge Analytica.
A map shown to the Observer showing the many places in the world where SCL and Cambridge Analytica have worked includes Russia, Lithuania, Latvia, Ukraine, Iran and Moldova. Multiple Cambridge Analytica sources have revealed other links to Russia, including trips to the country, meetings with executives from Russian state-owned companies, and references by SCL employees to working for Russian entities.
Article 50 has been triggered. AggregateIQ is outside British jurisdiction. The Electoral Commission is powerless. And another election, with these same rules, is just a month away. It is not that the authorities don’t know there is cause for concern. The Observer has learned that the Crown Prosecution Service did appoint a special prosecutor to assess whether there was a case for a criminal investigation into whether campaign finance laws were broken. The CPS referred it back to the electoral commission. Someone close to the intelligence select committee tells me that “work is being done” on potential Russian interference in the referendum.
Gavin Millar, a QC and expert in electoral law, described the situation as “highly disturbing”. He believes the only way to find the truth would be to hold a public inquiry. But a government would need to call it. A government that has just triggered an election specifically to shore up its power base. An election designed to set us into permanent alignment with Trump’s America.
Martin Moore of King’s College, London, pointed out that elections were a newly fashionable tool for would-be authoritarian states. “Look at Erdoğan in Turkey. What Theresa May is doing is quite anti-democratic in a way. It’s about enhancing her power very deliberately. It’s not about a battle of policy between two parties.”
This is Britain in 2017. A Britain that increasingly looks like a “managed” democracy. Paid for by a US billionaire. Using military-style technology. Delivered by Facebook. And enabled by us. If we let this referendum result stand, we are giving it our implicit consent. This isn’t about Remain or Leave. It goes far beyond party politics. It’s about the first step into a brave, new, increasingly undemocratic world.
Key names
SCL Group
British company with 25 years experience in military “psychological operations” and “election management”.
Cambridge Analytica
Data analytics company formed in 2014. Robert Mercer owns 90%. SCL owns 10%. Carried out major digital targeting campaigns for Donald Trump campaign, Ted Cruz’s nomination campaign and multiple other US Republican campaigns – mostly funded by Mercer. Gave Nigel Farage’s Leave.EU “help” during referendum.
Robert Mercer
US billionaire hedge fund owner who was Trump’s biggest donor. Owns Cambridge Analytica and the IP [intellectual property] ofAggregateIQ. Friend of Farage. Close associate of Steve Bannon.
Steve Bannon
Trump’s chief strategist. Vice-president of Cambridge Analytica during referendum period. Friend of Farage.
Alexander Nix
Director of Cambridge Analytica and SCL Group.
Christopher Wylie
Canadian who first brought data expertise and microtargeting to Cambridge Analytica; recruited AggregateIQ.
AggregateIQ
Data analytics company based in Victoria, British Columbia, Canada. Worked for Mercer-funded Pacs that supported the Trump campaign. Robert Mercer owns AggregateIQ’s IP. Paid £3.9m by Vote Leave to “micro-target” voters on social media during referendum campaign. Outside British jurisdiction.
Veterans for Britain
Given £100,000 by Vote Leave. Spent it with AggregateIQ.
BeLeave
Youth Leave campaign set up by 23-year-old student. Given £625,000 by Vote Leave & £50,000 by another donor. Spent it with AggregateIQ.
DUP
Democratic Unionist Party of Northern Ireland. Spent £32,750 with AggregrateIQ.
Thomas Borwick
Vote Leave’s chief technology officer. Previously worked with SCL/Cambridge Analytica and AggregateIQ.
ASI Data Science
Data science specialists. Links with Cambridge Analytica, including staff moving between the two and holding joint events. Paid £114,000 by Vote Leave. Vote Leave declared £71,000 to Electoral Commission.
Donald Trump
US president. Campaign funded by Mercer and run by Bannon. Data services supplied by Cambridge Analytica and AggregrateIQ.
Nigel Farage
Former Ukip leader. Leader of Leave.EU. Friend of Trump, Mercer and Bannon.
Arron Banks
Bristol businessman. Co-founder of Leave.EU. Owns data company and insurance firm. Single biggest donor to Leave – £7.5m.





